【Spring 系列】精通 Spring Cache
文章目录
-
- 思考题
- 使用方式
- Cache 注解详解
-
- @CacheConfig
- @Cacheable
- @CachePut
- @CacheEvict
- @Caching
- 最佳实践
- 扩展性分析
-
- 自定义 KeyGenerator
- 自定义 CacheManager
- 自定义 Cache
- 自定义 CacheResolver
- 自定义 CacheManagerCustomizers
- 自定义 CacheErrorHandler
- Spring Cache 实现原理
-
- CacheManager
- Cache
- CachingConfigurer
- Redis 实现
-
- RedisCacheManager
- RedisCache
- 拦截器实现原理
-
- 注解开启缓存
- 代理创建
- AOP 处理
-
- 初始化 Spring Cache 的 Advisor
- PointCut 处理逻辑
-
- 缓存注解过滤
- Cache 注解解析
- Advice 的处理逻辑
- Spring Boot Cache 自动配置
- 总结
Spring 3.1 版本引入基于 annotation 的 cache 技术,提供了一套抽象的缓存实现方案,通过注解方式使用缓存,基于配置的方式灵活使用不同缓存组件。代码具有相当的灵活性和扩展性,本文基于 Spring 5.x 源码一起分析 Spring Cache 的代码艺术。
思考题
1、sync 有啥限制? 参考 CacheAspectSupport 的 determineSyncFlag
2、spring cache 实现 redis 如何操作不同redis库?
使用方式
1、 开启缓存能力
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
2、在应用启动类添加@EnableCaching注解
@EnableCaching
public class RedisCacheConfig {
}
3、在业务方法添加@Cacheable等注解
@Cacheable(value = "user", key = "#id")
@Override
public User get(long id) {
// 我们假设从数据库读取
log.info("查询用户【id】= {}", id);
return DATABASES.get(id);
}
4、模拟请求
@GetMapping("get")
public User get(long id) {
return userService.get(id);
}
详细例子参考 spring cache 示例
Cache 注解详解
Spring Cache 相关的注解有 5 个:
- @CacheConfig 可以在类级别上标注一些公用的缓存属性,所有方法共享。
- @Cacheable 在调用方法的同时能够根据方法的请求参数对结果进行缓存。
- @CachePut 调用发放的同时进行 Cache 存储,作用于方法上。
- @CacheEvict 删除,作用于方法上。
- @Caching 用于处理复杂的缓存情况,一次性设置多个缓存,作用于方法上。
@CacheConfig
CacheConfig 注解包含以下配置:
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface CacheConfig {
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
}
如果你在一个类中使用多个 Cache 注解,并且这些 Cache 注解有公共的基础操作,比如:使用相同的 Cache key 生成规则,使用相同的 Cache Name 前缀等等,那么你就可以定义一个 CacheConfig 来统一单独管理这些 Cache 操作。
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user", cacheManager = "userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@CachePut(key = "#user.id")
@Override
public User saveOrUpdate(User user) {
DATABASES.put(user.getId(), user);
log.info("保存用户【user】= {}", user);
return user;
}
@Cacheable(key = "#id")
@Override
public User get(long id) {
// 我们假设从数据库读取
log.info("查询用户【id】= {}", id);
return DATABASES.get(id);
}
}
上面示例中的 两个 Cache Key 都会有一个公共前缀 ”user“。需要注意的是:CacheConfig 注解的优先级高于同类当中别的注解,如果你在 CacheConfig 中配置了 cacheNames,方法中也配置了,那么 CacheConfig 中的 cacheNames 会覆盖掉方法上的配置。
@Cacheable
@Cacheable 是我们最常使用的注解:
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
String unless() default "";
boolean sync() default false;
}
@Cacheable:主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存。同时在查询时,会先从缓存中获取,若不存在才再发起对数据库的访问。该注解主要有下面几个参数:
- value、cacheNames:两个等同的参数(cacheNames 为Spring 4 新增,作为 value 的别名),用于指定缓存存储的集合名。由于 Spring 4 中新增了 @CacheConfig,因此在 Spring 3 中原本必须有的 value 属性,也成为非必需项了。
- key:缓存对象存储在 Map 集合中的 key 值,非必需,缺省按照函数的所有参数组合作为 key 值,若自己配置需使用 SpEL表 达式,比如:@Cacheable(key = “#p0”):使用函数第一个参数作为缓存的 key 值,更多关于 SpEL 表达式的详细内容可参考官方文档。
- condition:缓存对象的条件,非必需,也需使用SpEL表达式,只有满足表达式条件的内容才会被缓存,比如:@Cacheable(key = “#p0”, condition = “#p0.length() < 3”),表示只有当第一个参数的长度小于3的时候才会被缓存,若做此配置上面的AAA用户就不会被缓存,读者可自行实验尝试。
- unless:另外一个缓存条件参数,非必需,需使用 SpEL 表达式。它不同于 condition 参数的地方在于它的判断时机,该条件是在函数被调用之后才做判断的,所以它可以通过对 result 进行判断。
- keyGenerator:用于指定 key 生成器,非必需。若需要指定一个自定义的 key 生成器,我们需要去实现org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator 接口,并使用该参数来指定。需要注意的是,该参数与 key 是互斥。
- cacheManager:用于指定使用哪个缓存管理器,非必需。只有当有多个时才需要使用。
- cacheResolver:用于指定使用那个缓存解析器,非必需。需通过
org.springframework.cache.interceptor.CacheResolver 接口来实现自己的缓存解析器,并用该参数指定。 - sync:多线程环境下存在多个操作使用相同的参数同步调用相同的 key,默认情况下缓存不锁定任何资源所以可能导致多次计算。对于这种情况,sync 属性可以将底层锁住,使得只有一个线程进行操作,其他线程堵塞直到更新完缓存返回结果。
@CachePut
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface CachePut {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
String unless() default "";
}
@CachePut:配置于方法上,能够根据参数定义条件来进行缓存,它与 @Cacheable 不同的是,它不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入缓存中,所以主要用于数据新增和修改操作上。它的参数与 @Cacheable 类似,具体功能可参考上面对 @Cacheable 参数的解析。
- 如果函数返回值null,下次进行该key值查询时,还会查一次数据库,此时相当于@CacheEvict注解;
- 如果函数返回值不为null,此时会进行该key值缓存的更新,更新缓存值为返回的数据;
@CacheEvict
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface CacheEvict {
@AliasFor("cacheNames")
String[] value() default {};
@AliasFor("value")
String[] cacheNames() default {};
String key() default "";
String keyGenerator() default "";
String cacheManager() default "";
String cacheResolver() default "";
String condition() default "";
boolean allEntries() default false;
boolean beforeInvocation() default false;
}
@CacheEvict:配置于函数上,通常用在删除方法上,用来从缓存中移除相应数据。除了同 @Cacheable 一样的参数之外,它还有下面两个参数:
- allEntries:非必需,默认为 false。当为 true 时,会移除所有数据。
- beforeInvocation:非必需,默认为 false,会在调用方法之后移除数据;当为 true 时,会在调用方法之前移除数据。
@Caching
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Caching {
Cacheable[] cacheable() default {};
CachePut[] put() default {};
CacheEvict[] evict() default {};
}
@Caching 注解适用于复杂缓存操作的场景,当你有多个缓存操作的需求,比如下例:你需要先删除缓存,再插入新数据到缓存:
@Caching(evict = @CacheEvict(key = "#user.id"),
put = @CachePut(key = "#user.id"))
@Override
public User update(User user) {
DATABASES.put(user.getId(), user);
log.info("保存用户【user】= {}", user);
return user;
}
那么你可以使用 @Caching 注解来操作多个缓存。
Spring EL 对 Cache 的支持
| Name | Location | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| methodName | Root object | 被调用的方法的名称 | #root.methodName |
| method | Root object | 被调用的方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | Root object | 当前调用方法的对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | Root object | 当前调用方法的类 | #root.targetClass |
| args | Root object | 当前方法的参数 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | Root object | 当前方法的缓存集合 | #root.caches[0].name |
| Argument name | Evaluation context | 当前方法的参数名称 | #iban or #a0 (you can also use #p0 or #p<#arg> notation as an alias). |
| result | Evaluation context | 方法返回的结果(要缓存的值)。 只有在 unless 、@CachePut(用于计算键)或@CacheEvict(beforeInvocation=false)中才可用.对于支持的包装器(例如 Optional),#result引用的是实际对象,而不是包装器 | #result |
最佳实践
1、定义多个 CacheName,不同的 CacheName 使用不同的 CacheManager
2、定义不同的 CacheName,不同的 CacheName 使用不同的 CacheConfiguration
扩展性分析
自定义 KeyGenerator
自定义 CacheManager
自定义 Cache
自定义 CacheResolver
参考默认实现 SimpleCacheResolver
自定义 CacheManagerCustomizers
自定义 CacheErrorHandler
参考默认实现 SimpleCacheErrorHandler
Spring Cache 实现原理
CacheManager
定义缓存管理接口 CacheManager,根据名称区分不同的 Cache
CacheManager 支持多种实现包括 JCache、EhCache、Caffeine、Redis。
AbstractCacheManager 实现比较简单,核心是提供了三个扩展点
1、loadCaches: 初始化时加载缓存
2、decorateCache:当增加缓存时,对缓存进行装饰
3、getMissingCache:当获取缓存时,如果查不到缓存时,对缓存进行处理。
这三个扩展点非常值得借鉴。
比如,通过 TransactionAwareCacheDecorator 使得缓存支持事务
Cache
定义缓存统一接口 Cache

Cache 支持多种实现,EhCache,ConcurrentHashMap、JCache、CaffeineCache、RedisCache
CachingConfigurer
public interface CachingConfigurer {
CacheManager cacheManager();
CacheResolver cacheResolver();
KeyGenerator keyGenerator();
CacheErrorHandler errorHandler();
}
Redis 实现
RedisCacheManager
RedisCacheManager 的功能实现有几个亮点
1、支持事务
2、不同的 Cache 根据 cacheName 进行区分
3、不同的 cache 支持使用不同的配置(比如不同的 Cache 连接不同的 Redis 库)
4、CacheWriter 可配置
RedisCache
RedisCache 实现有一个比较有意思的地方
1、RedisCacheWriter 通过 RedisConnectionFactory 执行 的 Redis 操作(value为 byte 数组)
2、利用 ConversionService 使得 key 支持多种类型。
拦截器实现原理
注解开启缓存
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import({CachingConfigurationSelector.class})
public @interface EnableCaching {
// 决定使用 jdk 动态代理还是 cglib 代理
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
// 决定使用 Spring AOP 还是 AspjectJ
AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY;
int order() default Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
public class CachingConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableCaching> {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) {
switch (adviceMode) {
case PROXY:
return getProxyImports();
case ASPECTJ:
return getAspectJImports();
default:
return null;
}
}
/**
* Return the imports to use if the {@link AdviceMode} is set to {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}.
* Take care of adding the necessary JSR-107 import if it is available.
*/
private String[] getProxyImports() {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(3);
result.add(AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName());
result.add(ProxyCachingConfiguration.class.getName());
if (jsr107Present && jcacheImplPresent) {
result.add(PROXY_JCACHE_CONFIGURATION_CLASS);
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(result);
}
}
1、导入 CachingConfigurationSelector
2、由于是 Spring Aop,会导入 AutoProxyRegistrar 和 ProxyCachingConfiguration。其中 AutoProxyRegistrar 用于创建代理对象。ProxyCachingConfiguration 配置 Aop 相关配置
代理创建
创建代理工厂,然后选择是否需要直接代理目标类,然后装配增强器,然后调用JdkDynamicAopProxy或者CglibAopProxy创建代理。
参考 Spring AOP 章节。
AOP 处理
初始化 Spring Cache 的 Advisor
ProxyCachingConfiguration 复用了父类的能力并且定了AOP的三个核心组件(Pointcut,Advice和Advisor)
@Configuration
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public class ProxyCachingConfiguration extends AbstractCachingConfiguration {
@Bean(name = CacheManagementConfigUtils.CACHE_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME)
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor cacheAdvisor() {
BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor();
advisor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
advisor.setAdvice(cacheInterceptor());
if (this.enableCaching != null) {
advisor.setOrder(this.enableCaching.<Integer>getNumber("order"));
}
return advisor;
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource() {
return new AnnotationCacheOperationSource();
}
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
public CacheInterceptor cacheInterceptor() {
CacheInterceptor interceptor = new CacheInterceptor();
interceptor.configure(this.errorHandler, this.keyGenerator, this.cacheResolver, this.cacheManager);
interceptor.setCacheOperationSource(cacheOperationSource());
return interceptor;
}
}
ProxyCachingConfiguration 核心是初始化 Cache 的 Advisor:
1、 BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor :初始化 Cache 的 Advisor
2、CacheOperationSource:初始化 Cache 的 Pointcut
3、CacheInterceptor:初始化 Cache 的 Advice
备注:
Spring AOP 的创建过程本质是实现一个 BeanPostProcessor,在创建 bean 的过程中创建 Proxy,并且为 Proxy 绑定所有适用于该 bean 的 advisor,最终暴露给容器。
Spring 中 AOP 几个关键的概念 advisor, advice, pointcut
advice = 切面拦截中插入的行为
pointcut = 切面的切入点
advisor = advice + pointcut
PointCut 处理逻辑
缓存注解过滤
abstract class CacheOperationSourcePointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {
protected CacheOperationSourcePointcut() {
setClassFilter(new CacheOperationSourceClassFilter());
}
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
CacheOperationSource cas = getCacheOperationSource();
return (cas != null && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(cas.getCacheOperations(method, targetClass)));
}
}
public class BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor extends AbstractBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor {
private CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource;
private final CacheOperationSourcePointcut pointcut = new CacheOperationSourcePointcut() {
@Override
protected CacheOperationSource getCacheOperationSource() {
return cacheOperationSource;
}
};
}
判断逻辑很简单:targetClass 的 method 由 Cache 相关注解,即返回 true。具体的实现是 CacheOperationSource 的 getCacheOperations 方法返回值。
下面看下 CacheOperationSource 的 getCacheOperations 实现。
public interface CacheOperationSource {
// targetClass 是否是候选类
default boolean isCandidateClass(Class<?> targetClass) {
return true;
}
// 找到类或方法的 Cache 注解
Collection<CacheOperation> getCacheOperations(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass);
}
public abstract class AbstractFallbackCacheOperationSource implements CacheOperationSource {
public Collection<CacheOperation> getCacheOperations(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return null;
}
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(method, targetClass);
// 优先从缓存查询
Collection<CacheOperation> cached = this.attributeCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached != null) {
return (cached != NULL_CACHING_ATTRIBUTE ? cached : null);
}
else {
// 找到类或方法的 CacheOperation
Collection<CacheOperation> cacheOps = computeCacheOperations(method, targetClass);
if (cacheOps != null) {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, cacheOps);
}
else {
this.attributeCache.put(cacheKey, NULL_CACHING_ATTRIBUTE);
}
return cacheOps;
}
}
private Collection<CacheOperation> computeCacheOperations(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass) {
// 是否必须是 public 方法
if (allowPublicMethodsOnly() && !Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
return null;
}
Method specificMethod = AopUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// 通过 CacheAnnotationParser 从方法查找 Cache 注解(与具体的注解解耦,由 parser 决定)
Collection<CacheOperation> opDef = findCacheOperations(specificMethod);
if (opDef != null) {
return opDef;
}
// 通过 CacheAnnotationParser 从类查找 Cache 注解(与具体的注解解耦,由 parser 决定)
opDef = findCacheOperations(specificMethod.getDeclaringClass());
if (opDef != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return opDef;
}
//
if (specificMethod != method) {
// Fallback is to look at the original method.
opDef = findCacheOperations(method);
if (opDef != null) {
return opDef;
}
opDef = findCacheOperations(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (opDef != null && ClassUtils.isUserLevelMethod(method)) {
return opDef;
}
}
return null;
}
1、遍历目标类的方法,找到有缓存注解的方法
1.1、 先从类找,之后从方法找
1.2、 找到类中第一个有 Cache 注解的方法
2、不管是否找到,都加入缓存
Cache 注解解析
Cache 相关注解解析在 CacheAnnotationParser 中,默认只有一个实现 SpringCacheAnnotationParser,解析Cache 注解、类上的缓存注解转换成CacheOperation
public AnnotationCacheOperationSource(boolean publicMethodsOnly) {
this.publicMethodsOnly = publicMethodsOnly;
this.annotationParsers = Collections.singleton(new SpringCacheAnnotationParser());
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected Collection<CacheOperation> findCacheOperations(Class<?> clazz) {
return determineCacheOperations(parser -> parser.parseCacheAnnotations(clazz));
}
@Override
@Nullable
protected Collection<CacheOperation> findCacheOperations(Method method) {
return determineCacheOperations(parser -> parser.parseCacheAnnotations(method));
}
protected Collection<CacheOperation> determineCacheOperations(CacheOperationProvider provider) {
Collection<CacheOperation> ops = null;
for (CacheAnnotationParser annotationParser : this.annotationParsers) {
Collection<CacheOperation> annOps = provider.getCacheOperations(annotationParser);
if (annOps != null) {
if (ops == null) {
ops = annOps;
}
else {
Collection<CacheOperation> combined = new ArrayList<>(ops.size() + annOps.size());
combined.addAll(ops);
combined.addAll(annOps);
ops = combined;
}
}
}
return ops;
}
private Collection<CacheOperation> parseCacheAnnotations(
DefaultCacheConfig cachingConfig, AnnotatedElement ae, boolean localOnly) {
Collection<? extends Annotation> anns = (localOnly ?
AnnotatedElementUtils.getAllMergedAnnotations(ae, CACHE_OPERATION_ANNOTATIONS) :
AnnotatedElementUtils.findAllMergedAnnotations(ae, CACHE_OPERATION_ANNOTATIONS));
if (anns.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
final Collection<CacheOperation> ops = new ArrayList<>(1);
anns.stream().filter(ann -> ann instanceof Cacheable).forEach(
ann -> ops.add(parseCacheableAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, (Cacheable) ann)));
anns.stream().filter(ann -> ann instanceof CacheEvict).forEach(
ann -> ops.add(parseEvictAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, (CacheEvict) ann)));
anns.stream().filter(ann -> ann instanceof CachePut).forEach(
ann -> ops.add(parsePutAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, (CachePut) ann)));
anns.stream().filter(ann -> ann instanceof Caching).forEach(
ann -> parseCachingAnnotation(ae, cachingConfig, (Caching) ann, ops));
return ops;
}
AnnotationCacheOperationSource 默认构造器使用的是 SpringCacheAnnotationParser 解析器,解析操作最终委托给 SpringCacheAnnotationParser.parseCacheAnnotations,将注解分别解析成对应的操作
Advice 的处理逻辑
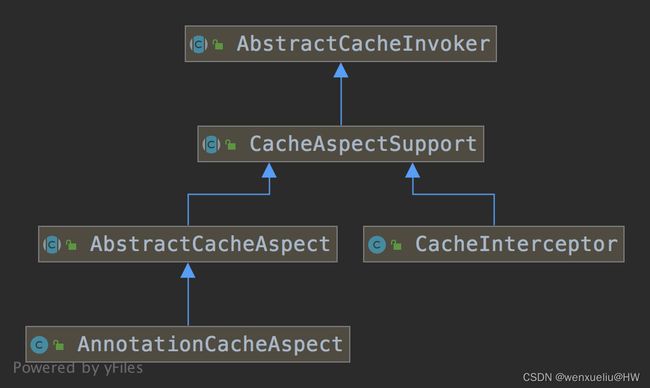
Advice 的核心处理都在 CacheAspectSupport,当拦截到调用时,将调用封装成CacheOperationInvoker并交给父类执行,父类CacheAspectSupport 实现了SmartInitializingSingleton 接口,在单例初始化后容器会调用 afterSingletonsInstantiated 方法:
1、首先检查是否是同步操作(@Cacheable特性),
1.1、如果是且满足条件缓存,获取逻辑并返回
1.2、否则返回业务逻辑免缓存调用invokeOperation
2、执行@CacheEvict的前置清除(beforeInvocation=true)
3、检查@Cacheable是否命中缓存
3.1、如果没有命中,则放入需要执行CachePutRequest列表暂存
3.2、如果检查缓存命中且没有@CachePut,则返回结果
3.3、否则使用业务查询结果作为返回结果,并且填充需要缓存的结果。
4、收集@CachePut操作,把@CachePut和@Cacheable未命中的请求同步到缓存
5、清理@CacheEvict的缓存(beforeInvocation=false)。
public class CacheInterceptor extends CacheAspectSupport implements MethodInterceptor, Serializable {
@Override
@Nullable
public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
CacheOperationInvoker aopAllianceInvoker = () -> {
try {
return invocation.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper(ex);
}
};
try {
return execute(aopAllianceInvoker, invocation.getThis(), method, invocation.getArguments());
}
catch (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper th) {
throw th.getOriginal();
}
}
}
protected Object execute(CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
// Check whether aspect is enabled (to cope with cases where the AJ is pulled in automatically)
if (this.initialized) {
Class<?> targetClass = getTargetClass(target);
CacheOperationSource cacheOperationSource = getCacheOperationSource();
if (cacheOperationSource != null) {
Collection<CacheOperation> operations = cacheOperationSource.getCacheOperations(method, targetClass);
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(operations)) {
return execute(invoker, method,
new CacheOperationContexts(operations, method, args, target, targetClass));
}
}
}
return invoker.invoke();
}
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
// Special handling of synchronized invocation
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, () -> unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker))));
}
catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
}
}
else {
return invokeOperation(invoker);
}
}
// 处理 @CacheEvicts
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// 是否命中缓存
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<>();
// 缓存没有命中,
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
// 缓存命中,且不是 @CachePut
if (cacheHit != null && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
// If there are no put requests, just use the cache hit
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// 缓存没有命中或 @CachePut
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// 处理 @CachePut
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
// 处理 @CacheEvicts
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}
Spring Boot Cache 自动配置
spring-boot-autoconfigure有个包叫cache,毫无以为这里就是springboot定义并自动开启缓存配置的地方,该包下基本都是*Configuration类型的类,也就是Springboot自带的缓存相关配置,我们简单分析一下CacheAutoConfiguration/CacheConfigurations/GenericCacheConfiguration/NoOpCacheConfiguration/SimpleCacheConfiguration/CaffeineCacheConfiguration和RedisCacheConfiguration这几个配置类。
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(CacheManager.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(CacheAspectSupport.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = CacheManager.class, name = "cacheResolver")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ CouchbaseAutoConfiguration.class, HazelcastAutoConfiguration.class,
HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration.class, RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@Import(CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers(
ObjectProvider<CacheManagerCustomizer<?>> customizers) {
return new CacheManagerCustomizers(
customizers.orderedStream().collect(Collectors.toList()));
}
@Bean
public CacheManagerValidator cacheAutoConfigurationValidator(
CacheProperties cacheProperties, ObjectProvider<CacheManager> cacheManager) {
return new CacheManagerValidator(cacheProperties, cacheManager);
}
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(AbstractEntityManagerFactoryBean.class)
protected static class CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration
extends EntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor {
public CacheManagerJpaDependencyConfiguration() {
super("cacheManager");
}
}
}
/**
* {@link ImportSelector} to add {@link CacheType} configuration classes.
*/
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;
}
}
final class CacheConfigurations {
private static final Map<CacheType, Class<?>> MAPPINGS;
static {
Map<CacheType, Class<?>> mappings = new EnumMap<>(CacheType.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.GENERIC, GenericCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.EHCACHE, EhCacheCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.HAZELCAST, HazelcastCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.INFINISPAN, InfinispanCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.JCACHE, JCacheCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.COUCHBASE, CouchbaseCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.REDIS, RedisCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.CAFFEINE, CaffeineCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.SIMPLE, SimpleCacheConfiguration.class);
mappings.put(CacheType.NONE, NoOpCacheConfiguration.class);
MAPPINGS = Collections.unmodifiableMap(mappings);
}
public static String getConfigurationClass(CacheType cacheType) {
Class<?> configurationClass = MAPPINGS.get(cacheType);
Assert.state(configurationClass != null, () -> "Unknown cache type " + cacheType);
return configurationClass.getName();
}
public static CacheType getType(String configurationClassName) {
for (Map.Entry<CacheType, Class<?>> entry : MAPPINGS.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().getName().equals(configurationClassName)) {
return entry.getKey();
}
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unknown configuration class " + configurationClassName);
}
}
总结
至此我们把上面说过的内容总结一下:
- BeanFactoryCacheOperationSourceAdvisor:配置 Cache 的切面和拦截实现。拦截的对象即解析出来的 CacheOperation 对象。每一个 CacheOperation 在执行的时候被封装为 CacheOperationContext 对象(一个方法可能被多个注解修饰),最终通过 CacheResolver 解析出缓存对象 Cache。
- CacheOperation:封装了@CachePut、@Cacheable、@CacheEvict的属性信息,以便于拦截的时候能直接操作此对象来执行逻辑。解析注解对应的代码为 CacheOperation 的工作是 CacheAnnotationParser 来完成的。
- CacheInterceptor:CacheInterceptor 执行真正的方法执行和 Cache 操作。最终调用其父类提供的四个 do 方法处理 Cache。
以上整体过程为 Spring 启动对相关注解所在类或者方法的拦截和注入,从而实现 Cache 逻辑。