【学习笔记】【C++】【Leetcode 分门别类讲解】
目录
- 概述
- 一、时间复杂度分析
- 二、数组问题
-
- 1、参考练习题- 双指针-对撞指针
- 2、双索引技术-滑动窗口
- 三、查找问题-查找表
-
- 1、参考练习题 - 集合与映射
- 2、set 和 map
- 2、滑动窗口 + 查找表
- 四、链表问题
-
- 1、链表问题
- 2、链表排序问题
- 3、不仅是穿针引线的链表问题
- 4、双指针
- 五、栈、队列、优先队列
-
- 1、基础使用
- 2、栈和递归的紧密关系
- 3、队列问题
-
- 3.1、队列与树
- 3.2、队列与图
- 3.2、优先队列 :堆
- 六、二叉树与递归 - 链接
- 七、递归和回溯 - 链接
- 八、动态规划问题 - 链接
- 九、贪心算法
-
- 1、贪心算法基础
- 2、贪心算法与动态规划
- 3、贪心选择性质
- 十、改错题
- 参考
概述
一、时间复杂度分析

图的遍历:邻接表实现 :O(e+V) ;邻接矩阵实现O(e2) ;e为节点数,V为边数。
字符串数组,先对字符串排顺序,再将数组按照字典序排序:时间复杂度:O( nslogs+snlogn),因为排序n个字符串+n个字符串的排序(字符串也得遍历一遍)
对动态数组的扩容和缩容来说,均摊下去时间复杂度只是O(1);所以造成动态数组的操作,整体的均摊时间复杂度为O(1);
但是要注意用lazy resize,避免复杂度震荡(及不停的扩容缩容)
二、数组问题
二分查找问题:
- 明确变量的含义、维护好循环不变量,根据循环不变量定义边界问题。
- 不同的循环不变量会使得代码边界问题发生改变。
- 小数据集的调试,很重要。
【二分查找】
1、参考练习题- 双指针-对撞指针
1147. 段式回文
暴力匹配;哈希思想+重新匹配解决哈希冲突;
283. 移动零
不断swap;单指针一直往左挪;
88. 合并两个有序数组
从后往前做;
167. 两数之和 II - 输入有序数组
对撞指针;
125. 验证回文串
对撞指针;+tolower()
344. 反转字符串
辅助栈;对撞指针;
345. 反转字符串中的元音字母
对撞指针;
11. 盛最多水的容器
对撞指针;考虑好指针移动条件。
2、双索引技术-滑动窗口
涉及连续子数组的问题,我们通常有两种思路:一是滑动窗口、二是前缀和。
209. 长度最小的子数组
我的:从len=1开始一直到len ==length暴力做,边加边减。能过。O(n2)
题意:滑动窗口;窗口大小一直改变即可。O(n)
前缀和+二分查找:正整数数组保证前缀和单调性。前缀和之间的差,就是每个连续子数组。O(nlogn)
3. 无重复字符的最长子串
滑动窗口,窗口往右挪。
76. 最小覆盖子串
滑动窗口+检查匹配;检查匹配可以优化;
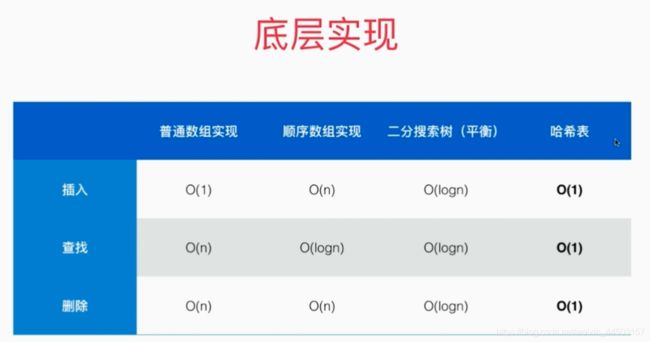
三、查找问题-查找表
查找元素有无:集合 set
查找对应关系:字典 map
stl 中容器类屏蔽了是实现细节,应该了解标准库中常见容器的使用。
常见操作: insert find erase change
1、参考练习题 - 集合与映射
349. 两个数组的交集
使用set 记录一个数组元素,遍历另一个元素的时候查到了就存进一个set中。
最后用构造函数返回即可。
set<int> record(num1.begin(), num1.end());
//遍历另一个数组。
return vector<int>(resultset.begin(), resultset.end());
350. 两个数组的交集 II
用一个map存较小的vec各个元素的频次。
访问另一个vec,只要存在相同元素,就压入结果中,并将map中对应频次–(确保压入的次数是两个数组中较少的频次);
两个有序数组中的交集
有序问题:首先想二分
- 方法一:双指针遍历。0(n)
- 方法二:在长的数组中二分搜索小的数组。O(nlongm)m为短数组长度。
注意:C++ stl中实现的map,只要用 [ ]访 问过的元素,如果之前不存在,也会插入这个元素,相应的val会是默认值。
所以对应操作之前,为了排除二义性,先find 一下存不存在这个元素,再去用[ ]操作。
2、set 和 map
不同的底层实现方式,时间复杂度不同。哈希表的优秀的代价是失去了顺序性。
而平衡树实现可以:
- 求数据集中最值;
- 某个元素前驱后继
- 某个元素的floor、ceil
- 某个元素的rank
- 某个排位的元素 select
242. 有效的字母异位词
用哈希map存字频,然后对比。
202. 快乐数
结果只会跌为1或者成环,不会越来越大。
所以问题转变为成环。
用set记录成环。或者快慢指针来求环。
290. 单词规律
两个哈希,【双射】。两个互相映射即可。
注意:字符集、空串;
205. 同构字符串
和上面的题类似。
注意:字符集、空串、映射自己;
451. 根据字符出现频率排序
记录字频
1. 两数之和
排序+双索引;索引要记录。O(nlogn)
查找表;有重复数字,hash -value 存vector O(n)
查找表;存hash 的时候,就判断前面有没有。重复数字组成的不会干扰结果(因为重复的能实现,也能在插入冲突的时候实现)。
15. 三数之和
排序+双指针;注意去重问题。
注意:不同的三元组处理方式、多个解的顺序、无解;
18. 四数之和
我套用三数之和,在外面再包装了一层四数。
16. 最接近的三数之和
类似于三数之和;加上一些剪枝操作即可;
源码链接: 两数之和、三数之和、四数之和
454. 四数相加 II
哈希存一个数,暴力枚举其他三种O(n3)
哈希存两个数和,暴力枚举其他两中O(n2)
49. 字母异位词分组
存哈希;
如果规定字符无重复,直接不用排序存,直接存int做哈希。
447. 回旋镖的数量 //***
暴力 ;O(n3)
对于每个点,算一下对其他点的距离,存进哈希,然后这个点能产生的贡献就是一样哈希key 的数量,做排列Am2 = m*(m-1);O(n2)
注意:计算平方和以后不用开根,减少运算同时减少产生小数的误差使得哈希计算误差的问题。
注意:平方和可能越界,对于题目中-10000~10000的数据最大是20000*20000 不会越界。
INT_MAX 开根约为:46,340
//预处理所有的距离存进二维数组。减少重复计算。
149. 直线上最多的点数 //***
一个点 m 与其他点的斜率计算下来存在map中,于是map中斜率出现的次数最多的数量,就是经过这个点最多的点数。
因为map存的是点 m 与其他点的斜率,也就是说计算的这些直线都是经过点 m 的。所以斜率相同的就是同一个直线上的。
只需要这样遍历所有的点即可。
/难点在于斜率计算:
- 因为存在y1-y2=0使得斜率无限大,x1-x2=0使得斜率无限小。
- 斜率为浮点数,有精度影响,哈希会出问题。
解决方案:
- 为了解决浮点数,因为只要确定了分子分母即可,我们直接存成string = “分子” + “分母”;并且都是化简为最小的。这样就能同一个斜率检索的到了。并保证分子为非负数。
- 为了解决斜率问题,无限小的时候让存的x=1,无限大的时候让存的y =1;
其中求公约数:
int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
2、滑动窗口 + 查找表
219. 存在重复元素 II
滑动窗口+暴力;(超时)
查找表;更新键值即可;
查找表+滑动窗口
220. 存在重复元素 III //***
查找表,计算lower_bound,只要lowerbound 存在,且小于num+t,就存在。
lower_bound(v) : 大于等于V的最小的那个
/注意:这个题的测试用例在int 的边界,如果加上值或者减值,会溢出。 要存long or long long
四、链表问题
1、链表问题
206. 反转链表 同 剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表 //简单题
- 最简单的是:迭代+栈保存;然后弹出的时候指向栈顶即可;
- 然后是递归:往next 递归,然后将其返回的节点的next指向自己,再返回自己;
- 然后是三指针迭代:翻转当前节点,需要保存的是:下一个节点和上一个节点;
92. 反转链表 II
- 有了反转链表的基础,只需要相对其多保存两个节点,最好再加一个dummyhead即可;
83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素
很简单了,只需要往后遍历即可; 不知道需不需要delete掉节点;
ListNode* deleteDuplicates(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
while(cur->next && cur->val == cur->next->val)
{
// ListNode* delete_node = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
// delete delete_node;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return head;
}
86. 分隔链表
- 辅助栈;按大于等于和小于压入栈;再弹出链接;也是稳定的partition
- 和辅助栈思想一致,直接不用栈,就链成两个链表,最后再接起来即可;
ListNode* partition(ListNode* head, int x) {
ListNode* _less = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* _more = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur_less = _less;
ListNode* cur_more = _more;
while(head)
{
if(head->val<x)
{
cur_less->next = head;
cur_less = cur_less->next;
}
else
{
cur_more->next = head;
cur_more = cur_more->next;
}
head = head->next;
}
cur_more->next = nullptr;
if(cur_more == _more)
{
delete _more;
cur_less = _less->next;
delete _less;
return cur_less;
}
else
{
cur_less->next = _more->next;
delete _more;
cur_less = _less->next;
delete _less;
return cur_less;
}
}
328. 奇偶链表
和上一个题一个思路,更简单些;
2. 两数相加
因为是简单题;所以可以多想一点;
这个题完全可以只new 最后一个进位!其他的空间都用之前的,然后不用的也可以delete 掉;但是判题系统万一不让删,暂时不删不是自己new 的了;
全程只new 了一个dummy head 和最后一个进位;其他的都可以用以前的空间;
ListNode* addTwoNumbers(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *cur = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *dummy_head = cur;
bool carry= false; //named carry?
while(l1|| l2|| carry)
{
if(!l1&&!l2)
{
cur->next = new ListNode(1);
carry =false;
}
else if(!l1)
{
int temp = (l2->val+carry);
cur->next = l2;
carry = (temp>=10) ? true:false;
l2->val = temp%10;
cur = cur->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else if(!l2)
{
int temp = (l1->val+carry);
cur->next = l1;
carry = (temp>=10) ? true:false;
l1->val = temp%10;
cur = cur->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
int temp = (l1->val+l2->val+carry);
cur->next = l1;
carry = (temp>=10) ? true:false;
l1->val = temp%10;
cur = cur->next;
l1 = l1->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
cur=dummy_head->next;
delete dummy_head;
return cur;
}
445. 两数相加 II
压栈来做;弹出相加+进位carry
203. 移除链表元素
其实就是教会你用一下dummy_head。这样就不需要多考虑一个头节点问题;
82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
这个题不做个dummyhead 就很麻烦了;
三指针去做就行;
dummyhead 不一定需要new;可以直接栈里申请,然后取指针就行;到时候还不需要delete;
21. 合并两个有序链表
- 迭代思想;栈上新建头节点,不用delete;
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode dummyhead = ListNode(-1);
ListNode* cur = &dummyhead;
while(l1||l2)
{
if(!l1)
{
cur->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else if(!l2)
{
cur->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
if(l1->val <= l2->val)
{
cur ->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummyhead.next;
}
- 递归思想 ;理解递归更清晰;
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(!l1 && !l2)
{
return nullptr;
}
else if(!l1)
return l2;
else if(!l2)
return l1;
else
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
return l1;
}
else
{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
- 迭代思想;简单易做; 保存cur 之后的三个节点
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummy_head(-1,head);
ListNode* cur = &dummy_head;
while(cur->next && cur->next->next)
{
ListNode* temp1 = cur->next;
ListNode* temp2 = temp1->next;
temp1->next = temp2->next;
temp2->next = temp1;
cur->next = temp2;
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return dummy_head.next;
}
- 递归思想,稍微动脑:保存head 之后的三个节点;
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(!head ||!head->next)
return head;
ListNode* temp1 = head->next;
ListNode* temp2 = head->next->next;
head->next = swapPairs(temp2);
temp1->next = head;
return temp1;
}
25. K 个一组翻转链表
- 迭代+存之间K个节点;十分清晰;只需要存起来中间的节点进行翻转即可;但是不是常数项空间;O(K)空间
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(k<=1||head ==nullptr) return head;
ListNode dummyhead(-1,head);
ListNode* cur = &dummyhead;
ListNode* pre =cur;
vector<ListNode*> vec(k,nullptr);
cur = cur->next;
while(cur)
{
int i=0;
for(;i<vec.size()&& cur;i++)
{
vec[i] = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
if(i!=vec.size()) break ;
pre ->next = vec.back();
pre = vec[0];
vec[0]->next = cur;
for(int j=vec.size()-1;j>0;j--)
vec[j]->next =vec[j-1];
}
return dummyhead.next;
}
- 迭代+不存节点;需要常数项个存储空间,选择和之前翻转链表一样的想法;要做的就是局部翻转+链接到原链表中。
class Solution {
public:
pair<ListNode*,ListNode*> reverse(ListNode* head,ListNode* tail)
{
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
ListNode* cur = head;
while(cur!=tail)
{
ListNode* _next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = _next;
}
cur->next = pre;
return {tail,head};
}
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(k<=1) return head;
ListNode dummy_head(-1,head);
ListNode* cur = &dummy_head;
ListNode* pre = cur;
while(cur)
{
ListNode* _next = nullptr;
ListNode* head_t = cur->next,*tail_t = cur;
int i=0;
for(;i<k&& tail_t->next;i++)
tail_t = tail_t->next;
if(i!=k) break;
_next = tail_t->next;
tie(head_t,tail_t)= reverse(head_t,tail_t);
cur->next = head_t;
tail_t->next = _next;
cur = tail_t;
}
return dummy_head.next;
}
};
2、链表排序问题
147. 对链表进行插入排序
- 排序过程从前到后找合适的位置;
- 排序的时候从当前点往后找;然后再从头开始遍历;性能优!
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummy_head(-1, head);
ListNode* cur = dummy_head.next;
ListNode* pre = &dummy_head;
while (cur->next)
{
if (cur->val > cur->next->val)
{
pre->next = cur->next;
ListNode* cur_t = cur;
while (cur_t->next && !(cur->val >= cur_t->val &&cur->val <= cur_t->next->val))
cur_t = cur_t->next;
ListNode* _next = cur_t->next;
cur_t->next = cur;
cur->next = _next;
pre = &dummy_head;
cur = dummy_head.next;
}
else
{
pre = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return dummy_head.next;
}
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummy_head(-1, head);
ListNode* cur = dummy_head.next;
ListNode* pre = &dummy_head;
while (cur&&cur->next)
{
if (cur->val > cur->next->val)
{
ListNode* temp = cur->next;
pre =cur;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
cur = temp;
ListNode* cur_t = &dummy_head;
while (cur_t->next && cur->val > cur_t->next->val)
cur_t = cur_t->next;
ListNode* _next = cur_t->next;
cur_t->next = cur;
cur->next = _next;
cur = pre;
}
else
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy_head.next;
}
148. 排序链表
- 对链表排序,只能是归并;且可以不用O(n)空间来排序。需要自下而上排序;
- merge返回这段排好序后的头尾,其中尾巴和后面连上了,需要返回头部供之前的链接;
- 返回尾部是为了给下次头部留指针;
- 归并最长需要
pair<ListNode*,ListNode*> merge(ListNode* left,ListNode* head2,ListNode* _end)
{
ListNode dummy_head(-1);
ListNode* cur = &dummy_head;
ListNode* right = head2;
while(left !=head2 || right!=_end)
{
if(left ==head2)
{
cur->next = right;
while(cur->next !=_end)
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = _end;
break;
}
else if(right ==_end)
{
cur->next = left;
while(cur->next !=head2)
cur = cur->next;
cur->next = _end;
break;
}
else
{
if(left->val <= right->val)
{
cur->next = left;
left = left->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
else
{
cur->next = right;
right = right->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
}
return {dummy_head.next,cur};
}
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummy_head(-1,head);
ListNode* _pre = &dummy_head;
ListNode* head1;ListNode* head2;ListNode* _end;
int length = 0;
while(_pre->next)
{
length++;
_pre = _pre->next;
}
for(int i =1;i<length;i *=2)
{
_pre = &dummy_head;
while(_pre&&_pre->next)
{
head1= _pre->next;
head2= _pre;
_end = _pre;
for(int j=0;j<i+1&&head2;j++)
head2 = head2->next;
for(int j=0;j<2*i+1&&_end;j++)
_end = _end->next;
if(head2 ==nullptr) break;
auto [l,r] = merge(head1,head2,_end);
_pre->next = l;
_pre = r;
}
}
return dummy_head.next;
}
3、不仅是穿针引线的链表问题
237. 删除链表中的节点
- 讨巧的题;注意见过了这种题就行了 ;记得改变值是个解决方案;
4、双指针
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 快慢指针问题
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode dummyhead(-1,head);
ListNode* fast = &dummyhead;
ListNode* slow = fast;
int i=0;
for(;i<n&&fast->next;i++)
fast = fast->next;
if(i<n) return dummyhead.next;
while(fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* del_node = slow->next;
slow->next = del_node->next;
delete del_node;
return dummyhead.next;
}
61. 旋转链表
- 注意边界问题;多考虑几个测试用例,就好了;
- 或者考虑成环,再合适点切开
ListNode* rotateRight(ListNode* head, int k) {
if(!head) return head;
if(k ==0) return head;
ListNode* last = head;
int length =1;
while(last->next)
{
last = last->next;
length++;
}
k = k%length;
if(k ==0) return head;
ListNode* new_head = head;
ListNode* new_head_pre = new_head;
for(int i=0;i<length-k-1;i++)
{
new_head_pre = new_head_pre->next;
}
last->next = head;
new_head = new_head_pre->next;
new_head_pre->next = nullptr;
return new_head;
}
143. 重排链表
- 分开前后,后面反转开始交叉
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, ListNode* temp)
{
while (temp)
{
out << temp->val << "-> ";
temp = temp->next;
}
out << endl;
return out;
}
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head)
{
if(!head) return head;
ListNode* cur = head;
ListNode* pre = nullptr;
while (cur&& cur->next)
{
ListNode* _next = cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = _next;
}
cur->next = pre;
return cur;
}
void reorderList(ListNode* head) {
if (!head) return ;
ListNode dummyhead(-1, head);
ListNode* cur = &dummyhead;
ListNode* fast = cur;
while (fast&&fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
ListNode* newhead = cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
ListNode dummyhead2(-1, reverse(newhead));
ListNode* cur1 = dummyhead.next;;
ListNode* cur2 = dummyhead2.next;
ListNode dummyhead3(-1);
cur = &dummyhead3;
while (cur1 || cur2)
{
if (!cur1)
{
cur->next = cur2;
break;
}
else if (!cur2)
{
cur->next = cur1;
break;
}
else
{
cur->next = cur1;
cur = cur->next;
cur1 = cur1->next;
cur->next = cur2;
cur = cur->next;
cur2 = cur2->next;
}
}
head = dummyhead3.next;
return;
}
234. 回文链表
- O(n) 时间O(1) 空间,需要中间切断,翻转再回文;
ListNode* reverse(ListNode* head)
{
if(!head) return head;
ListNode* cur =head;
ListNode* pre =nullptr;
while(cur&& cur->next)
{
ListNode* _next =cur->next;
cur->next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur= _next;
}
cur->next =pre;
return cur;
}
bool isPalindrome(ListNode* head) {
ListNode dummyhead(-1,head);
ListNode* cur =&dummyhead;
ListNode* fast =&dummyhead;
while(fast&& fast->next)
{
cur = cur->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
fast =cur->next;
cur->next = nullptr;
ListNode dummyhead2(-1,reverse(fast));
cur =dummyhead.next;
fast = dummyhead2.next;
while(cur&&fast)
{
if(cur->val!=fast->val) return false;
cur = cur->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return true;
}
五、栈、队列、优先队列
1、基础使用
20. 有效的括号
- 栈的应用
bool isValid(string s) {
stack<char> my_stack;
for(auto & it:s)
{
if(it =='{'||it =='['||it =='(')
my_stack.push(it);
else
switch(it)
{
case('}'):
if(my_stack.empty()||my_stack.top()!='{') return false;
my_stack.pop();
break;
case(']'):
if(my_stack.empty()||my_stack.top()!='[') return false;
my_stack.pop();
break;
case(')'):
if(my_stack.empty()||my_stack.top()!='(') return false;
my_stack.pop();
break;
default :return false;
}
}
if(!my_stack.empty()) return false;
return true;
}
150. 逆波兰表达式求值
- 逆波兰表达式是更利于计算机运算的表达式形式, 需要用到栈(先进后出的数据结构).
- 纯数学表达式,也可用栈实现;
- 数组,入数字栈;
- 符号,如果符号栈顶符号优先级大于该符号,就将其取出来,并取两个数来运算;将结果压入数字栈,该符号也压入符号栈;
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> my_stack;
int res = 0;
for(auto &it:tokens)
{
if(it == "*")
{
int a=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
int b=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
res = a*b;
my_stack.push(res);
}
else if(it == "/")
{
int a=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
int b=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
res = b/a;
my_stack.push(res);
}
else if(it == "+")
{
int a=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
int b=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
res = a+b;
my_stack.push(res);
}
else if(it == "-")
{
int a=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
int b=my_stack.top();
my_stack.pop();
res = b-a;
my_stack.push(res);
}
else
my_stack.push(stoi(it));
}
return my_stack.top();
}
71. 简化路径
- 需要注意的是各种边界
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,queue<string> temp)
{
while(!temp.empty())
{
os<<temp.front()<<" -> ";
temp.pop();
}
os<<endl;
return os;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os,deque<string> temp)
{
while(!temp.empty())
{
os<<temp.front()<<" -> ";
temp.pop_front();
}
os<<endl;
return os;
}
class Solution {
public:
string simplifyPath(string path) {
queue<string> myque;
int j=1;int i=1;
for(;i<path.size();i++)
{
if(path[i] =='/')
{
if(i>j)
myque.push(path.substr(j,i-j));
j=i+1;
}
}
if(i>j)
myque.push(path.substr(j,i-j));
// cout<
deque<string> res_que;
while(!myque.empty())
{
if(myque.front() == ".")
myque.pop();
else if(myque.front() == "..")
{
if(!res_que.empty())
res_que.pop_back();
myque.pop();
}
else
{
res_que.push_back(myque.front());
myque.pop();
}
}
// cout<
if(res_que.empty()) return "/";
string res = "";
while(!res_que.empty())
{
res+="/";
res+=res_que.front();
res_que.pop_front();
}
return res;
}
};
2、栈和递归的紧密关系
- 二叉树的遍历,迭代的方法中,可以使用颜色标记法; 否则后序遍历很难写
【C++】【二叉树】二叉树的前、中、后序遍历;迭代、染色法、颜色标记法;
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<TreeNode* > aux;
aux.push(root);
vector<int> res;
while(!aux.empty())
{
TreeNode* temp = aux.top();
aux.pop();
if(temp)
{
res.push_back(temp->val);
aux.push(temp->right);
aux.push(temp->left);
}
}
return res;
}
94. 二叉树的中序遍历 染色法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<pair<TreeNode*,bool>> aux;
vector<int> res;
aux.push({root,false});
while(!aux.empty())
{
auto [temp,passed] = aux.top();
aux.pop();
if(temp)
if(passed)
res.push_back(temp->val);
else
{
aux.push({temp->right,false});
aux.push({temp,true});
aux.push({temp->left,false});
}
}
return res;
}
};
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 染色法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
stack<pair<TreeNode*,bool>> aux;
vector<int> res;
aux.push({root,false});
while(!aux.empty())
{
auto [temp,passed] = aux.top();
aux.pop();
if(temp)
if(passed)
res.push_back(temp->val);
else
{
aux.push({temp,true});
aux.push({temp->right,false});
aux.push({temp->left,false});
}
}
return res;
}
};
341. 扁平化嵌套列表迭代器 //***
- 递归取出来
class NestedIterator {
public:
vector<int> res;
int index;
void dfs(const vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nestedList.size(); i++)
if (nestedList[i].isInteger())
res.push_back(nestedList[i].getInteger());
else
{
dfs(nestedList[i].getList());
}
}
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
dfs(nestedList);
index = 0;
}
int next() {
return res[index++];
}
bool hasNext() {
return index<res.size();
}
};
- 正常应该做到的迭代器;遇到list 就递归进去
class NestedIterator {
public:
int index;
int _min_index;
int size;
int _min_size;
vector<NestedInteger> *_List;
NestedIterator *_min_ite;
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
_List = &nestedList;
size = nestedList.size();
index = 0;
_min_ite =nullptr;
}
int next() {
if((*_List)[index].isInteger())
return (*_List)[index++].getInteger();
else
return _min_ite->next();
}
bool hasNext() {
while(index<size)
{
if((*_List)[index].isInteger())
return true;
else
{
if(!_min_ite)
_min_ite = new NestedIterator((*_List)[index].getList());
if(_min_ite->hasNext())
return true;
else
{
delete _min_ite;
_min_ite = nullptr;
index++;
}
}
}
return false;
}
};
- 题解版本,栈模拟递归;
class NestedIterator {
private:
// pair 中存储的是列表的当前遍历位置,以及一个尾后迭代器用于判断是否遍历到了列表末尾
stack<pair<vector<NestedInteger>::iterator, vector<NestedInteger>::iterator>> stk;
public:
NestedIterator(vector<NestedInteger> &nestedList) {
stk.emplace(nestedList.begin(), nestedList.end());
}
int next() {
// 由于保证调用 next 之前会调用 hasNext,直接返回栈顶列表的当前元素,然后迭代器指向下一个元素
return stk.top().first++->getInteger();
}
bool hasNext() {
while (!stk.empty()) {
auto &p = stk.top();
if (p.first == p.second) { // 遍历到当前列表末尾,出栈
stk.pop();
continue;
}
if (p.first->isInteger()) {
return true;
}
// 若当前元素为列表,则将其入栈,且迭代器指向下一个元素
auto &lst = p.first++->getList();
stk.emplace(lst.begin(), lst.end());
}
return false;
}
};
3、队列问题
- 主要为了解决广度优先遍历问题;
- 树:层序遍历
- 图:无权图的最短路径
3.1、队列与树
- 于树而言,广度优先遍历就是层序遍历。
102. 二叉树的层序遍历
- 根据队列中现存的一层数量来做;也可以que中存节点+层数;
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root) return {};
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*> my_que;
my_que.push(root);
while(!my_que.empty())
{
int _size =my_que.size();
vector<int> _vec;
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
TreeNode* temp = my_que.front();
my_que.pop();
_vec.push_back(temp->val);
if(temp->left) my_que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) my_que.push(temp->right);
}
res.push_back(_vec);
}
return res;
}
};
107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II
- 层序遍历的,反转一下。。。;
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
vector<vector<int>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> my_que;
bool _bo =false;
my_que.push(root);
while(!my_que.empty())
{
int _size = my_que.size();
vector<int> _vec;
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
TreeNode* temp = my_que.front();
my_que.pop();
_vec.push_back(temp->val);
if(temp->left) my_que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) my_que.push(temp->right);
}
if(_bo)
res.push_back({_vec.rbegin(),_vec.rend()});
else
res.push_back(_vec);
_bo = !_bo;
}
return res;
}
199. 二叉树的右视图
- 还是层序,每次压入层序最后的;
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> m_que;
m_que.push(root);
while(!m_que.empty())
{
int _size = m_que.size();
TreeNode* temp;
for(int i=0;i<_size;i++)
{
temp = m_que.front();
m_que.pop();
if(temp->left) m_que.push(temp->left);
if(temp->right) m_que.push(temp->right);
}
res.push_back(temp->val);
}
return res;
}
- 也可以深度优先,先右子树,然后新的深度,就压入;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int deep)
{
if(!root) return;
if(deep == res.size())
res.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right,deep+1);
dfs(root->left,deep+1);
}
vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root,0);
return res;
}
};
3.2、队列与图
- 于图而言,广度优先遍历可以求得无权图最短路径问题;
279. 完全平方数 无法使用贪心
- 动态规划 //链接:【C++】【学习笔记】【动态规划问题】
int numSquares(int n) {
vector<int> dp(n+1,0);
dp[0] = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
dp[i] = i;
for(int j=1;j*j<=i;j++)
dp[i] = min(dp[i],dp[i-j*j]+1);
}
return dp.back();
}
- 转换思想,转换成为图论的问题;
- 对图的广度优先遍历bfs
- 其中,visit作为优化,防止冗余计算;(也就是这条路已经被更短的计算过了。更长的就不要计算了)(同时不怕错过这个节点,因为之前计算过这个节点)
int numSquares(int n) {
queue<pair<int,int>> aux;
vector<bool> visit(n+1,false);
aux.push({n,0});
visit[n] = true;
while(!aux.empty())
{
auto [num,step] = aux.front();
aux.pop();
for( int i=1;;i++)
{
int temp = num-i*i;
if(temp==0) return step+1;
if(temp<0) break;
if(visit[temp]) continue;
aux.push({temp,step+1});
visit[temp] = true;
}
}
return 0;
}
127. 单词接龙
- 根据上面的题,这个题很明显可以作为图论的问题;
- 同样也是每次换一个字母,然后根据换的字母在里面bfs寻找最短路径
int ladderLength(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> m_hash;
unordered_set<string> m_hash2;
for(auto& it:wordList)
m_hash.insert(it);
if(m_hash.find(endWord)==m_hash.end()) return 0;
int len = beginWord.size();
queue<pair<string,int>> aux;
aux.push({beginWord,1});
while(!aux.empty())
{
auto [str,step] = aux.front();
aux.pop();
for(int i =0;i<len;i++)
{
char its = str[i]-'a';
string temp_str = str;
for(int j=0;j<25;j++)
{
its++;
its%=26;
temp_str[i] = its+'a';
if(m_hash.find(temp_str)!=m_hash.end()&&(m_hash2.find(temp_str)==m_hash.end()))
{
// cout<
if(temp_str ==endWord)
return step+1;
else
{
aux.push({temp_str,step+1});
m_hash2.insert(temp_str);
}
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
126. 单词接龙 II //***
- 重点在于记录层数;记录每个单词最进的层数,高于这个层数再碰到这个单词就不用管;这样的剪枝才能过;否则都超时;
vector<vector<string>> findLadders(string beginWord, string endWord, vector<string>& wordList) {
unordered_set<string> m_list_hash;
unordered_map<string,int> m_list_map;
for (auto& it : wordList)
{
m_list_hash.insert(it);
m_list_map[it] = wordList.size();
}
if (m_list_hash.find(endWord) == m_list_hash.end()) return {};
vector<vector<string>> res;
queue<tuple<string, vector<string>>> aux;
aux.push({ beginWord,{beginWord} });
int len = beginWord.size();
while (!aux.empty())
{
auto[temp_str, _vec] = aux.front();
aux.pop();
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++)
{
string str = temp_str;
char ch_temp = str[j] - 'a';
for (int i = 0; i < 25; i++)
{
ch_temp = (ch_temp + 1) % 26;
str[j] = ch_temp + 'a';
if (m_list_hash.find(str) != m_list_hash.end() && m_list_map[str]>=_vec.size())
{
m_list_map[str] = _vec.size();
if (str == endWord)
{
// cout << str << " " << _vec.size() << endl;
_vec.push_back(str);
res.push_back(_vec);
break;
}
else
{
auto temp_vec = _vec;
temp_vec.push_back(str);
aux.push({ str,temp_vec});
}
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
3.2、优先队列 :堆
- 优先队列问题,通常涉及到堆;
- 堆的实现,可以使用数组模拟一棵树;常用!
【C++】【 lambda使用】priority_queue 与 sort 对 lambda的使用; lambda的多种使用和声明;
347. 前 K 个高频元素 要求时间复杂度小于O(nlogn)
- k个优先队列O(nlogk);(排序可以使用greater,然后先存频率)
vector<int> topKFrequent(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
unordered_map<int,int> m_hash;
auto comp = [](const pair<int,int>&a,const pair<int,int>&b){return a.second>b.second;};
priority_queue<pair<int,int>,vector<pair<int,int>>,decltype(comp)> my_que(comp);
for(auto &it:nums)
m_hash[it]++;
for(auto it:m_hash)
{
if(my_que.size()<k)
my_que.push({it.first,it.second});
else if(it.second>my_que.top().second)
{
my_que.pop();
my_que.push({it.first,it.second});
}
}
vector<int> res;
while(!my_que.empty())
{
res.push_back(my_que.top().first);
my_que.pop();
}
return res;
}
- 快排思想,基于快排的每次只需要对一遍继续partition,时间复杂度为O(2n);平均复杂度下优于快排;
23. 合并K个升序链表
- 优先队列,把所有节点都塞进去,一个一个出来;相当于都取出来,然后根据val排序
- 优先队列,塞所有头节点进去,出来一个进去一个;(更优、用上了排序的条件)
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
ListNode dummy_head(-1);
ListNode* cur = &dummy_head;
int len = lists.size();
auto comp = [](ListNode* a,ListNode* b){return a->val>b->val;};
priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,decltype(comp)> m_que(comp);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
if(lists[i])
m_que.push(lists[i]);
while(!m_que.empty())
{
cur->next = m_que.top();
cur = cur->next;
m_que.pop();
if(cur->next)
m_que.push(cur->next);
}
cur->next = nullptr;
return dummy_head.next;
}
六、二叉树与递归 - 链接
【C++】【学习笔记】【二叉树与递归详解与例题】前驱后继问题;染色法递归遍历;最近公共祖先(LCA) 问题
六、二叉树与递归
1、二叉树天然递归结构
2、递归的终止条件 与 递归结构
2、较复杂的递归逻辑
3、二叉搜索树中的问题
七、递归和回溯 - 链接
【C++】【学习笔记】【递归与回溯问题详解与例题】排列问题;组合问题;二维平面回溯;flood fill问题;搜索问题(八皇后);
七、递归和回溯
1、回溯
2、回溯应用 - 排列问题
2、回溯应用 - 组合问题
3、回溯应用 - 二维平面
4、回溯应用 - floodfill算法 问题
4、回溯应用 - 搜索问题 - 八皇后
八、动态规划问题 - 链接
【C++】【学习笔记】【动态规划问题详解与例题】记忆化搜索与暴力穷举思想 ;0-1 背包问题;子序列问题;
九、动态规划问题
1、参考练习题
2、记忆化搜索与暴力穷举思想的重要性
3、0-1 背包问题
4、0-1 背包问题- 变种
5、0-1 背包问题- 例题
6、 最长上升子序列
7、 最长上升子序列 -例题
8、 最长公共子序列 LCS
9、 动态规划找出具体解1、子序列问题的具体解
2、0 - 1 背包问题具体解
九、贪心算法
- 贪心算法与排序是分不开的
1、贪心算法基础
455. 分发饼干
- 贪心用最大饼干给最大需求的小朋友;
class Solution {
public:
int findContentChildren(vector<int>& g, vector<int>& s) {
sort(s.begin(),s.end(),greater<int>());
sort(g.begin(),g.end(),greater<int>());
int res =0;
for(int i=0,j = 0;i<g.size()&& j<s.size();i++)
if(s[j]>=g[i])
{
j++;
res++;
}
return res;
}
};
392. 判断子序列
- 双指针方法;与贪心有什么关系呢;下面就是这个题的贪心地方
- 如果是匹配一个较短字符串 s ,对于 s中每一个char 都优先匹配最先遇到的;
- 因为假设有两处可以匹配,匹配后一处的情况其实是匹配前一处情况的子集,直接扫描一遍
- 贪心算法必须具备后无效性,也就是不必考虑前面的影响,只需考虑当前的状态。
- 这里有讲后续贪心的方法:(预处理,取最近的元素)
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/is-subsequence/solution/javati-jie-he-hou-xu-tiao-zhan-by-lil-q/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSubsequence(string s, string t) {
int i=0;
for(int j=0;j<t.size()&&i<s.size();j++)
if(t[j] == s[i])
i++;
if(i ==s.size()) return true;
return false;
}
};
2、贪心算法与动态规划
435. 无重叠区间 最长上升子序列;
- DP 为 当前节点处所能构成的最长不重叠区间;
class Solution {
public:
int eraseOverlapIntervals(vector<vector<int>>& intervals) {
if(intervals.size()<2) return 0;
sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end());
vector<int> dp(intervals.size(),0);
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<dp.size();i++)
{
int temp = 0;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
if(intervals[i][0]>=intervals[j][1])
temp = max(dp[j] +1,temp);
else
temp = max(dp[j],temp);
dp[i] = temp;
}
return intervals.size()-dp.back();
}
};
- 贪心思路:排序按照结尾从小到大排 ;
- 每次选择结尾最早的,且和前一个区间不重叠的区间;选择一个,结果可以++;并把前一个更新为现在这个;
- 其实就是贪心的选择了最适合的,而不是动态规划;
3、贪心选择性质
-
在求解一个最优化的问题中,贪心的选择了一组内容以后,不会影响剩下子问题的求解;
-
最小生成树和最短路径都使用了贪心算法;贪心只是其中的一步;
剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子 剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II 343. 整数拆分
十、改错题
找错误
#include 参考
liuyubobo的课
【C++】【学习笔记】【动态规划问题】玩转算法面试-- Leetcode真题分门别类讲解;0-1 背包问题;子序列问题;