图的基本操作--邻接表类型
本文作者:韩申权
作者博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/hsqdboke
转载请注明出处,侵权必究,保留最终解释权!
程序2
/* 邻接表的结点类型 */
typedef struct arc
{int adjvex;
struct arc *next;}ArcNode;
typedef struct VexNode
{int vertex;
ArcNode *firstarc;
}VerNode;
typedef VerNode AdjList[MAXNODE];
/* 建立图的邻接表 */
void CreatAdjlist(AdjList GL)
/* 从初始点v出发深度优先遍历邻接表GL表示的图 */
void DfsAdjlist(AdjList GL,int v)
/*从初始点v出发广度优先遍历邻接表GL表示的图*/
void BfsAdjlist(AdjList GL,int v)
例如:
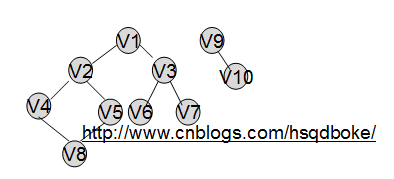
//2012年5月23日9:52:20 //图的邻接表进行图的基本操作 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<string.h> #define MAX_V 20 //定义最多有20个顶点 #define OVERFLOW -1 typedef int QElemType; int p=1,q=1; int visited[MAX_V]; typedef struct arc { int adjvex; struct arc *next; }ArcNode; typedef struct VexNode { char vertex[10]; ArcNode *firstarc; }VerNode; typedef VerNode AdjList[MAX_V+1]; void CreateG(AdjList g,int v,int e)//创建图的链表 { int i,x; ArcNode *p=NULL,*q=NULL; printf("请输入顶点的信息:"); for(i=1;i<=v;i++) { scanf("%s",g[i].vertex); g[i].firstarc=NULL; } for(i=1;i<=v;i++) { printf("请输入与结点%d相邻的结点的序号,并以0结束:",i);//稍做处理 以0结束 scanf("%d",&x); p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); q=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex=x; p->next=NULL; g[i].firstarc=p; q=p; if(x) { while(1) { scanf("%d",&x); p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p->adjvex=x; p->next=NULL; q->next=p; q=p; if(!x)break; } } } } int FAV(AdjList g,int vc)//vc为当前顶点返回第一个邻接点 { if(g[vc].firstarc->adjvex!=0)return g[vc].firstarc->adjvex; else return 0; } int NAV(AdjList g,int vc,int w)//返回其邻接点w的下一个邻接点 { ArcNode *p=NULL; if(g[vc].firstarc->adjvex==w)return g[vc].firstarc->next->adjvex; else { p=(ArcNode*)malloc(sizeof(ArcNode)); p=g[vc].firstarc; while(p) { if(p->next->adjvex==w)return p->next->next->adjvex; p=p->next; } } return 0; } void visit(AdjList g,int v) { if(p) { printf("%s",g[v].vertex); p=0; } else printf("->%s",g[v].vertex); } void visit1(AdjList g,int v) { if(q) { printf("%s",g[v].vertex); q=0; } else printf("->%s",g[v].vertex); } void DFS(AdjList g,int v) //DFS { int w; visited[v]=1; visit(g,v); for(w=FAV(g,v);w;w=NAV(g,v,w)) if(!visited[w])DFS(g,w); } void DFSTraverse(AdjList g,int n,int v)//从第n个顶点开始的DFS { int i; memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); printf("从初始点%d进行DFS的结果为:\n",n); DFS(g,n); for(i=1;i<=v;i++) { if(!visited[i])DFS(g,i); } printf("\n"); } //BFS函数的需要的函数 typedef struct QNode { QElemType data; struct QNode *next; }QNode,*Queuep; typedef struct { Queuep front; Queuep rear; }LinkQueue; void InitQueue(LinkQueue *Q) //初始队列 { Q->front=Q->rear=(Queuep)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if(!Q->front)exit(OVERFLOW); Q->front->next=NULL; } void EnQueue(LinkQueue *Q,QElemType e)//队尾插入元素 { Queuep p; p=(Queuep)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if(!p)exit(OVERFLOW); p->data=e; p->next=NULL; Q->rear->next=p; Q->rear=p; } void DeQueue(LinkQueue *Q,QElemType *e)//删除队首元素 { Queuep p; p=Q->front->next; *e=p->data; Q->front->next=p->next; if(Q->rear==p)Q->rear=Q->front; free(p); } int QueueEmpty(LinkQueue *Q)//判空 { if(Q->front==Q->rear)return 1; else return 0; } void BFSTraverse(AdjList g,int n,int v) { int i,w,u; LinkQueue Q; memset(visited,0,sizeof(visited)); printf("从初始点%d进行BFS的结果为:\n",n); InitQueue(&Q); EnQueue(&Q,n); visited[n]=1; visit1(g,n); while(!QueueEmpty(&Q)) { DeQueue(&Q,&u); for(w=FAV(g,u);w;w=NAV(g,u,w)) if(!visited[w]) { visited[w]=1; visit1(g,w); EnQueue(&Q,w); } } for(i=1;i<=v;i++) { if(!visited[i]) { EnQueue(&Q,i); visited[i]=1; visit1(g,i); while(!QueueEmpty(&Q)) { DeQueue(&Q,&u); for(w=FAV(g,u);w;w=NAV(g,u,w)) if(!visited[w]) { visited[w]=1; visit1(g,w); EnQueue(&Q,w); } } } } printf("\n"); } int main() { int n,e,v; AdjList g; printf("请输入图的顶点数和边数:"); scanf("%d%d",&v,&e); printf("请输入从第几个顶点开始遍历:"); scanf("%d",&n); CreateG(g,v,e); DFSTraverse(g,n,v); printf("\n"); BFSTraverse(g,n,v); return 0; }

本文作者:韩申权
作者博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/hsqdboke
转载请注明出处,侵权必究,保留最终解释权!