LeakCanary源码分析
LeakCanary使用
LeakCanary是一个用于Android的内存泄漏检测库.本文从如下四点分析源码
- 检查哪些内存泄漏
- 检查内存泄漏的时机
- 如何判定内存泄漏
- 如何分析内存泄漏(只有一点点,可能跟没有一样)
- 内存泄漏误报
1.检查哪些内存泄漏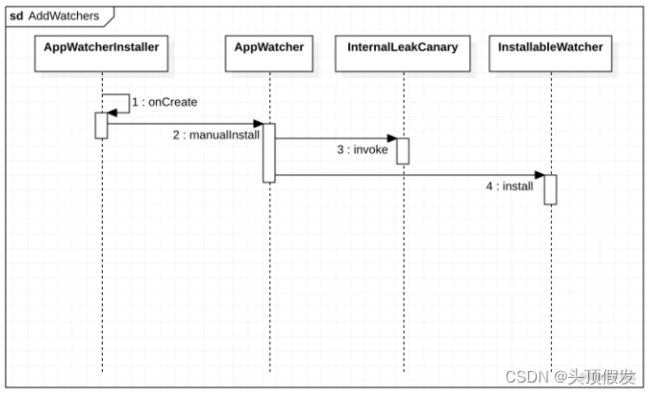
AppWatcherInstaller继承于ContentProvider,调用时机是介于Application的attachBaseContext(Context)和 onCreate() 之间.通过这种方式初始化.
方法2manualInstall实现了默认参数watchersToInstall,通过这个方法我们看到Activity,FragmentAndViewModel,RootView,Service四个观察者
fun appDefaultWatchers(
application: Application,
reachabilityWatcher: ReachabilityWatcher = objectWatcher
): List {
return listOf(
ActivityWatcher(application, reachabilityWatcher),
FragmentAndViewModelWatcher(application, reachabilityWatcher),
RootViewWatcher(reachabilityWatcher),
ServiceWatcher(reachabilityWatcher)
)
} 2.检查内存泄漏的时机
2.1 ActivityWatcher
activity触发OnDestory检查是否回收Activity实例
private val lifecycleCallbacks =
object : Application.ActivityLifecycleCallbacks by noOpDelegate() {
override fun onActivityDestroyed(activity: Activity) {
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
activity, "${activity::class.java.name} received Activity#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}2.2 FragmentAndViewModelWatcher
fragment触发onFragmentDestroyed或onFragmentViewDestroyed检查是否可以回收Fragment实例
viewModel触发onClear检查是否可以回收ViewModel实例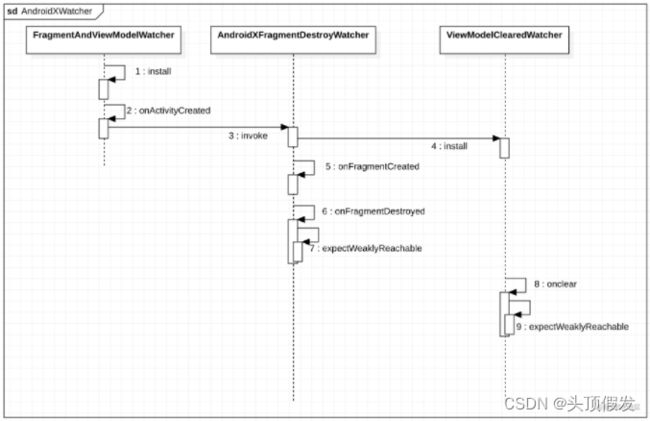
2.2.1 检查哪些Fragment
由于Android现在有三种Fragment
androidx.fragment.app
android.app.fragment
android.support.v4.app.Fragment
leakCanary通过反射先去检查是否引入上面三种Fragment,如果有就反射创建对应的watcher加入到 fragmentDestroyWatchers中
private fun getWatcherIfAvailable(
fragmentClassName: String,
watcherClassName: String,
reachabilityWatcher: ReachabilityWatcher
): ((Activity) -> Unit)? {
return if (classAvailable(fragmentClassName) &&
classAvailable(watcherClassName)
) {
val watcherConstructor =
Class.forName(watcherClassName).getDeclaredConstructor(ReachabilityWatcher::class.java)
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
watcherConstructor.newInstance(reachabilityWatcher) as (Activity) -> Unit
} else {
null
}
}2.2.2 Fragment内存泄漏检查时机
(1)application注册activity生命周期回调
(2)当监听到ctivity被创建时,获取该activity的对应的fragmentManager创建fragment的生命周期观察者
(3)当
onFragmentViewDestroyed/onFragmentDestroyed触发时,遍历集合然后检查是否可以回收Fragment实例
private val fragmentLifecycleCallbacks = object : FragmentManager.FragmentLifecycleCallbacks() {
override fun onFragmentViewDestroyed(
fm: FragmentManager,
fragment: Fragment
) {
val view = fragment.view
if (view != null) {
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
view, "${fragment::class.java.name} received Fragment#onDestroyView() callback " +
"(references to its views should be cleared to prevent leaks)"
)
}
}
override fun onFragmentDestroyed(
fm: FragmentManager,
fragment: Fragment
) {
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
fragment, "${fragment::class.java.name} received Fragment#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}2.2.3 检查哪些ViewModel内存泄漏
既然fragment/activity被销毁了,fragment/activity对象被回收了,那么fragment/activity绑定的所有viewmodel实例也应该销毁,所以leakCanary增加了viewmodel的内存检查
(1)监听当activity被创建时,绑定一个间谍viewmodel实例
//AndroidXFragmentDestroyWatcher
override fun invoke(activity: Activity) {
if (activity is FragmentActivity) {
val supportFragmentManager = activity.supportFragmentManager
supportFragmentManager.registerFragmentLifecycleCallbacks(fragmentLifecycleCallbacks, true)
ViewModelClearedWatcher.install(activity, reachabilityWatcher)
}
}(2)监听当fragment被创建时,绑定一个间谍viewmodel实例
//AndroidXFragmentDestroyWatcher##fragmentLifecycleCallbacks
override fun onFragmentCreated(
fm: FragmentManager,
fragment: Fragment,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
) {
ViewModelClearedWatcher.install(fragment, reachabilityWatcher)
}2.2.4 ViewModel内存泄漏检查时机
(1)利用反射获得fragment/activity绑定的viewModel集合
(2)当leakcanary绑定的viewmodel生命周期走到onCleared时,就去检查所有viewmodel实例是否可以回收(这边就是为啥作者取名叫spy)
//ViewModelClearedWatcher
override fun onCleared() {
viewModelMap?.values?.forEach { viewModel ->
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
viewModel, "${viewModel::class.java.name} received ViewModel#onCleared() callback"
)
}
}2.3 RootViewWatcher
view触发onViewDetachedFromWindow检查是否回收View实例
利用Curtains获得视图变化,检查所有被添加到phoneWindow上面的,windowLayoutParams.title为Toast或者是Tooltip,或者除PopupWindow之外的所有view.
//RootViewWatcher
rootView.addOnAttachStateChangeListener(object : OnAttachStateChangeListener {
val watchDetachedView = Runnable {
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
rootView, "${rootView::class.java.name} received View#onDetachedFromWindow() callback"
)
}
override fun onViewAttachedToWindow(v: View) {
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_PHONE
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(watchDetachedView)
}
override fun onViewDetachedFromWindow(v: View) {
mainHandler.post(watchDetachedView)
}
})2.4 ServiceWatcher
service触发onDestroy检查是否回收Service实例
private fun onServiceDestroyed(token: IBinder) {
servicesToBeDestroyed.remove(token)?.also { serviceWeakReference ->
serviceWeakReference.get()?.let { service ->
reachabilityWatcher.expectWeaklyReachable(
service, "${service::class.java.name} received Service#onDestroy() callback"
)
}
}
}3.如何判定内存泄漏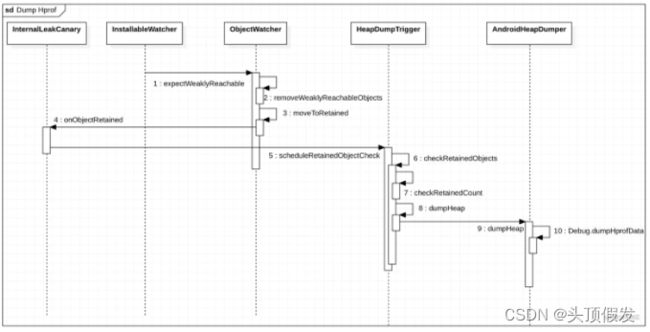
ReferenceQueue : 引用队列,在检测到适当的可到达性更改后,垃圾回收器将已注册的引用对象添加到该队列中
(1)将待检查对象加入到weakReference和watchedObjects中
@Synchronized override fun expectWeaklyReachable(
watchedObject: Any,
description: String
) {
if (!isEnabled()) {
return
}
removeWeaklyReachableObjects()
val key = UUID.randomUUID()
.toString()
val watchUptimeMillis = clock.uptimeMillis()
val reference =
KeyedWeakReference(watchedObject, key, description, watchUptimeMillis, queue)
SharkLog.d {
"Watching " +
(if (watchedObject is Class<*>) watchedObject.toString() else "instance of ${watchedObject.javaClass.name}") +
(if (description.isNotEmpty()) " ($description)" else "") +
" with key $key"
}
watchedObjects[key] = reference
checkRetainedExecutor.execute {
moveToRetained(key)
}
}(6)执行GC后,遍历ReferenceQueue,删除watchedObjects集合中保存的对象
private fun removeWeaklyReachableObjects() {
// WeakReferences are enqueued as soon as the object to which they point to becomes weakly
// reachable. This is before finalization or garbage collection has actually happened.
var ref: KeyedWeakReference?
do {
ref = queue.poll() as KeyedWeakReference?
if (ref != null) {
watchedObjects.remove(ref.key)
}
} while (ref != null)
}(3)判断watchedObjects长度是否发生改变,如果改变就认为内存泄漏
private fun checkRetainedCount(
retainedKeysCount: Int,
retainedVisibleThreshold: Int,
nopeReason: String? = null
): Boolean {
val countChanged = lastDisplayedRetainedObjectCount != retainedKeysCount
...
if (retainedKeysCount < retainedVisibleThreshold) {
if (applicationVisible || applicationInvisibleLessThanWatchPeriod) {
if (countChanged) {
onRetainInstanceListener.onEvent(BelowThreshold(retainedKeysCount))
}
showRetainedCountNotification(
objectCount = retainedKeysCount,
contentText = application.getString(
R.string.leak_canary_notification_retained_visible, retainedVisibleThreshold
)
)
scheduleRetainedObjectCheck(
delayMillis = WAIT_FOR_OBJECT_THRESHOLD_MILLIS
)
return true
}
}
return false
}(10) 当检查到5次内存泄漏就会生成hprof文件
override fun dumpHeap(): DumpHeapResult {
...
val durationMillis = measureDurationMillis {
Debug.dumpHprofData(heapDumpFile.absolutePath)
}
...
}4.如何分析内存泄漏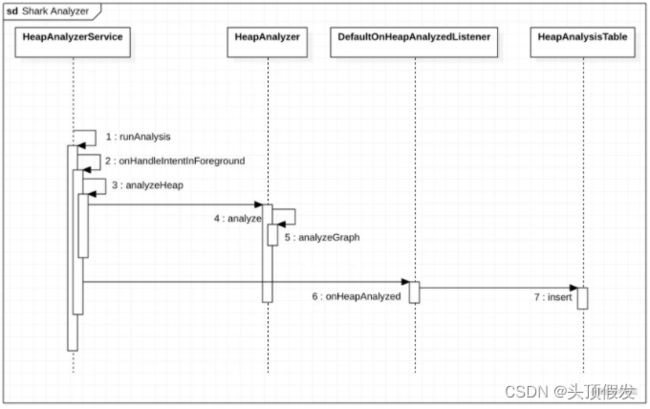
利用Shark分析工具分析hprof文件
(8)这里通过解析hprof文件生成heapAnalysis对象.SharkLog打印并存入数据库
override fun onHeapAnalyzed(heapAnalysis: HeapAnalysis) {
SharkLog.d { "\u200B\n${LeakTraceWrapper.wrap(heapAnalysis.toString(), 120)}" }
val db = LeaksDbHelper(application).writableDatabase
val id = HeapAnalysisTable.insert(db, heapAnalysis)
db.releaseReference()
...
}5.内存泄漏误报
Java虚拟机的主流垃圾回收器采取的是可达性分析算法, 可达性算法是通过从GC root往外遍历,如果从root节点无法遍历该节点表明该节点对应的对象处于可回收状态. 反之不会回收.
public class MainActivity2 extends FragmentActivity {
Fragment mFragmentA;
Fragment mFragmentB;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
mFragmentA = new FragmentA();
mFragmentB = new FragmentB();
findViewById(R.id.buttona).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
replaceFragment(mFragmentA);
}
});
findViewById(R.id.buttonb).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
replaceFragment(mFragmentB);
}
});
}
private void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment) {
getSupportFragmentManager().beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.container, fragment).commit();
}
}以fragment为例,leakcanary认为fragment走onDestory了,就应该释放fragment.但是这种情况真的是内存泄漏么?
├─ com.example.MainActivity2 instance
│ Leaking: NO (Activity#mDestroyed is false)
│ ↓ MainActivity2.mFragmentA
│ ~~~~~~~~~~
╰→ com.example.FragmentA instance
Leaking: YES (ObjectWatcher was watching this because com.example.FragmentA
received Fragment#onDestroy() callback and Fragment#mFragmentManager is null)
key = 216c8cf8-2cdb-4509-84e9-8404afefffeb
watchDurationMillis = 3804
retainedDurationMillis = -1
key = eaa41c88-bccb-47ac-8fb7-46b27dec0356
watchDurationMillis = 6113
retainedDurationMillis = 1112
key = 77d5f271-382b-42ec-904b-1e8a6d4ab097
watchDurationMillis = 7423
retainedDurationMillis = 2423
key = 8d79952f-a300-4830-b513-62e40cda8bba
watchDurationMillis = 15771
retainedDurationMillis = 10765
13858 bytes retained by leaking objects
Signature: f1d17d3f6aa4713d4de15a4f465f97003aa7根据堆栈信息,leakcanary认为fragmentA走了onDestory应该要回收这个fragmentA对象,但是发现还被MainActivity2对象持有无法回收,然后判定是内存泄漏. 放在我们这个逻辑里面,fragment不释放是对的. 只不过这种实现不是内存最佳罢了.