Binding 使用多个源
以下三个都是与多源组合相关。
CompositeCollection
MSDN上的说明:启用要以单个列表形式显示的多个集合和项。可以解理为把多个源组合在一起,然后以列表形式显示。
<Window Background="Cornsilk" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml" xmlns:c="clr-namespace:SDKSample" x:Class="SDKSample.Window1" Title="CompositeCollections" SizeToContent="WidthAndHeight"> <Window.Resources> <c:GreekGods x:Key="GreekGodsData"/> <XmlDataProvider x:Key="GreekHeroesData" XPath="GreekHeroes/Hero"> <x:XData> <GreekHeroes xmlns=""> <Hero Name="Jason" /> <Hero Name="Hercules" /> <Hero Name="Bellerophon" /> <Hero Name="Theseus" /> <Hero Name="Odysseus" /> <Hero Name="Perseus" /> </GreekHeroes> </x:XData> </XmlDataProvider> <DataTemplate DataType="{x:Type c:GreekGod}"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding Path=Name}" Foreground="Gold"/> </DataTemplate> <DataTemplate DataType="Hero"> <TextBlock Text="{Binding XPath=@Name}" Foreground="Cyan"/> </DataTemplate> </Window.Resources> <StackPanel> <TextBlock FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Center">Composite Collections Sample</TextBlock> <ListBox Name="myListBox" Height="300" Width="200" Background="White"> <ListBox.ItemsSource> <CompositeCollection> <CollectionContainer Collection="{Binding Source={StaticResource GreekGodsData}}" /> <CollectionContainer Collection="{Binding Source={StaticResource GreekHeroesData}}" /> <ListBoxItem Foreground="Red">Other Listbox Item 1</ListBoxItem> <ListBoxItem Foreground="Red">Other Listbox Item 2</ListBoxItem> </CompositeCollection> </ListBox.ItemsSource> </ListBox> </StackPanel> </Window>
此例中使用的源有后台定义的集合GreekGodsData和XmlDataProvider(GreekHeroesData),以及两个ListBoxItem
CollectionContainer是必须的,保存要用在 CompositeCollection 中的现有集合结构,如 ObservableCollection<(Of <(T>)>) 或 DataSet。
显示效果图:
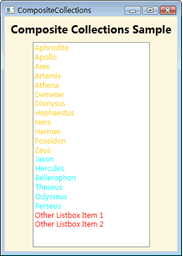
MultiBinding
MultiBinding把几个绑定组合在一起,然后根据Converter,返回出Binding需要的对象。
MultiBinding在实际中是很有用的,因为我们经常需要根据给定的多个值算出所需的内容。
比如根据宽高画出一个箭头(仅做示例):
…
<Polygon.Resources> <local:PointConvert x:Key="pointConvert"/> </Polygon.Resources> <Polygon.Points> <MultiBinding Converter="{StaticResource pointConvert}"> <Binding ElementName="control" Path="Width"/> <Binding ElementName="control" Path="Height"/> </MultiBinding> </Polygon.Points>
…
public class PointConvert : IMultiValueConverter { public object Convert(object[] values, Type targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { if (values.Length == 2) { double width = double.Parse(values[0].ToString()); double height = double.Parse(values[1].ToString()); if (double.NaN.Equals(width)) { width = 100; } if (double.NaN.Equals(height)) { height = 40; } PointCollection pc = new PointCollection(7); Point p = new Point(0, height / 4); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(0, height * 3 / 4); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(width * 3 / 4, height * 3 / 4); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(width * 3 / 4, height); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(width, height / 2); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(width * 3 / 4, 0); pc.Add(p); p = new Point(width * 3 / 4, height / 4); pc.Add(p); return pc; } return Binding.DoNothing; } public object[] ConvertBack(object value, Type[] targetType, object parameter, CultureInfo culture) { throw new NotSupportedException(); } }
Converter要继承于IMultiValueConverter, ConvertBack在目标绑到源时发生,在OneWay,OneTime模式下是不会被调用的,TwoWay或OnwWayToSource才会被调用。
PriorityBinding
和MultiBinding有点像,相同的是多个源,不同的是多个源绑定到一个对象,而MultiBinding是根据多个源算出一个值。顾名思义,每个源返回时间不同时使用此类可获得比较好的用户体验。
MSDN上的例子是,定义了三个源,最慢的需要5秒才返回,中间的需要3秒返回,最快的不需等待。所以在顺序上需要先绑最慢的,其次慢的,最快的。请遵守这个顺序,否则消耗时间还是累加的。
而且需要把除最后一个Binding外的其他Binding设置为IsAsync="True"
<Window.Resources> <c:AsyncDataSource SlowestDP="Slowest Value" SlowerDP="Slower Value" FastDP="Fast Value" x:Key="AsyncDS" /> </Window.Resources> <StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Center" VerticalAlignment="Center" DataContext="{Binding Source={StaticResource AsyncDS}}"> <TextBlock FontSize="18" FontWeight="Bold" Margin="10" HorizontalAlignment="Center">Priority Binding</TextBlock> <TextBlock Background="Honeydew" Width="100" HorizontalAlignment="Center"> <TextBlock.Text> <PriorityBinding FallbackValue="defaultvalue"> <Binding Path="SlowestDP" IsAsync="True"/> <Binding Path="SlowerDP" IsAsync="True"/> <Binding Path="FastDP" /> </PriorityBinding> </TextBlock.Text> </TextBlock> </StackPanel>
public class AsyncDataSource { private string _fastDP; private string _slowerDP; private string _slowestDP; public AsyncDataSource() { } public string FastDP { get { return _fastDP; } set { _fastDP = value; } } public string SlowerDP { get { // This simulates a lengthy time before the // data being bound to is actualy available. Thread.Sleep(3000); return _slowerDP; } set { _slowerDP = value; } } public string SlowestDP { get { // This simulates a lengthy time before the // data being bound to is actualy available. Thread.Sleep(5000); return _slowestDP; } set { _slowestDP = value; } } }
Word打开大文档时,对于字数和页数的统计也是类似,先是小一些的值,然后慢慢算到正确的值。