GeoTools——JTS的相关介绍和操作
GeoTools——JTS的相关介绍(一)
JTS拓扑套件是GeoTools用于提供Geometry数据结构的实现,Geometry主要是指几何形状。
想要使用geoTools——JTS相关的操作可以导入以下的依赖
<properties>
<geotools.version>17.1</geotools.version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-geojson</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-geometry</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.vividsolutions</groupId>
<artifactId>jts</artifactId>
<version>1.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-epsg-hsql</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-jts-wrapper</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.geotools/gt-main -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-main</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.geotools</groupId>
<artifactId>gt-opengis</artifactId>
<version>${geotools.version}</version>
</dependency>
创建一个点
使用的是JTS GeometryFactory来创建一个全局的JTS :
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
Coordinate coord = new Coordinate(1, 1);
Point point = geometryFactory.createPoint(coord);
WKT规范定义的一种简单文本格式:
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader(geometryFactory);
Point point = (Point) reader.read("POINT (1 1)");
表示许多点(可能是构成围栏的围栏柱),可以使用MultiPoint。
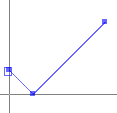
创建一个LineString
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
Coordinate[] coords =
new Coordinate[] {new Coordinate(0, 2), new Coordinate(2, 0), new Coordinate(8, 6) };
LineString line = geometryFactory.createLineString(coordinates);
LineString从WKT读取 :
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
LineString line = (LineString) reader.read("LINESTRING(0 2, 2 0, 8 6)");
可以使用MultiLineString表示多条线。
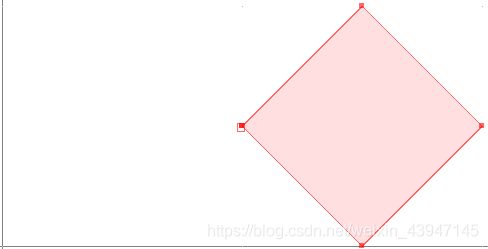
以下内容使多边形成为正方形:
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
Coordinate[] coords =
new Coordinate[] {new Coordinate(4, 0), new Coordinate(2, 2),
new Coordinate(4, 4), new Coordinate(6, 2), new Coordinate(4, 0) };
LinearRing ring = geometryFactory.createLinearRing( coords );
LinearRing holes[] = null; // use LinearRing[] to represent holes
Polygon polygon = geometryFactory.createPolygon(ring, holes );
从WKT读取多边形:
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory( null );
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader( geometryFactory );
Polygon polygon = (Polygon) reader.read("POLYGON((20 10, 30 0, 40 10, 30 20, 20 10))");
您也可以在其中创建一个多边形孔。并再次使用MultiPolygon表示由不同形状组成的单个几何。
创建CircularString
要创建一个CircularString(或一个CircularRing),请使用GeoTools CurvedGeometryFactory。设置时,CurvedGeometryFactory将在线性化过程中使用提供的公差:
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
CurvedGeometryFactory curvedFactory =
new CurvedGeometryFactory(geometryFactory, Double.MAX_VALUE);
CoordinateSequence coords =
PackedCoordinateSequenceFactory.DOUBLE_FACTORY.create(
new double[] {10, 14, 6, 10, 14, 10}, 2);
CircularString arc = (CircularString) curvedFactory.createCurvedGeometry(coords);
圆弧定义在通过点6,10的坐标10,14和14、10之间。该示例使用PackedCoordinateSequence允许直接使用双精度数组的数组。曲线支持仅限于2D坐标。CircularLineString在这种情况下返回 ,CircularRing如果从闭合环提供两个或更多曲线,则会产生闭环。
从WKT读取圆弧:
GeometryFactory geometryFactory = JTSFactoryFinder.getGeometryFactory();
CurvedGeometryFactory curvedfactory = new CurvedGeometryFactory(Double.MAX_VALUE);
WKTReader2 reader = new WKTReader2(curvedfactory);
CircularString arc = (CircularString) reader.read("CIRCULARSTRING(10 14,6 10,14 10)");
一个CompoundCurve(或封闭的CompoundRing)由CircularString和/或普通LineString成分组成的混合。
自定义曲线
JTS拓扑套件没有任何表示“曲线”或“圆”的结构-GeoTools将该扩展作为扩展。JTS使用的数学严格限于由直线(即线性)组成的几何。
GeoTools曲线的实现依赖于使用控制点来定义曲线,并在可能的最后时刻将其转换为直线。
曲线也可以通过一点数学来手工生成。
创建圆:
private static Geometry createCircle(double x, double y, final double RADIUS) {
GeometricShapeFactory shapeFactory = new GeometricShapeFactory();
shapeFactory.setNumPoints(32);
shapeFactory.setCentre(new Coordinate(x, y));
shapeFactory.setSize(RADIUS * 2);
return shapeFactory.createCircle();
}
即使GeometricShapeFactoryJTS提供了开箱即用的功能,没有什么花哨的代码。它在一个圆中创建一系列坐标。
另一种方法是使用Java的便捷Shape类之一创建曲线或形状对象,然后从该对象提取坐标以创建几何。
没有数学的弧:
private static Geometry createBezierCurve(Coordinate start,
Coordinate end,
Coordinate ctrlPoint1,
Coordinate ctrlPoint2
double smooth) {
Shape curve = new CubicCurve2D.Double(
start.x, start.y,
ctrlPoint1.x, ctrlPoint1.y,
ctrlPoint2.x, ctrlPoint2.y,
end.x, end.y);
//平滑参数的值决定线条的紧密程度
//点之间的线段近似光滑曲线
//(参见javadocs了解形状。Shape.getPathIterator)
PathIterator iter = curve.getPathIterator(null, smooth);
// a length 6 array is required for the iterator
double[] iterBuf = new double[6];
List<Coordinate> coords = new ArrayList<Coordinate>();
while (!iter.isDone()) {
iter.currentSegment(iterBuf);
coords.add(new Coordinate(buf[0], buf[1]);
iter.next();
}
GeometryFactory gf = new GeometryFactory();
return gf.createLineString(coords.toArray(new Coordinate[coords.size()]));
}
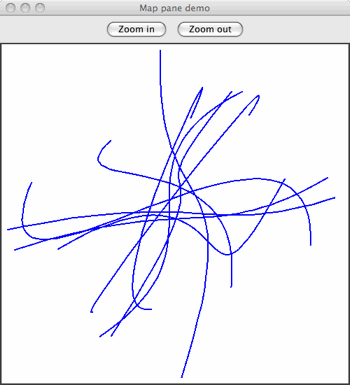
这是以此方式生成的一些随机定向和成形的曲线的示例……
有时您需要生成一条平滑曲线,以确保可以通过一组指定的点。这里尝试过的真实方法是使用样条函数。这将生成一组多项式(三次)曲线,每个曲线都拟合一部分数据,并平滑地与其相邻曲线连接。
花键:
public Geometry splineInterpolatePoints(double[] xPoints, double[] yPoints) {
/*
* 首先,使用。创建一个由段组成的LineString
* 输入点作为顶点。
*/
final int N = xPoints.length;
Coordinate[] coords = new Coordinate[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
coords[i] = new Coordinate(xPoints[i], yPoints[i]);
}
GeometryFactory gf = new GeometryFactory();
LineString line = gf.createLineString(coords);
/*
*现在我们使用GeoTools JTS实用程序类来平滑
*线。返回的几何图形将拥有所有的顶点
*的输入行加上跟踪样条的额外顶点
*曲线。第二个参数是“fit”参数,它
*可以在0(松散匹配)到1(最紧密匹配)的范围内。
*/
return JTS.smooth(line, 0.0);
}
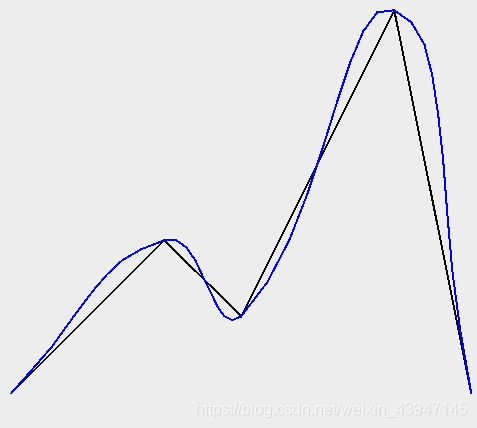
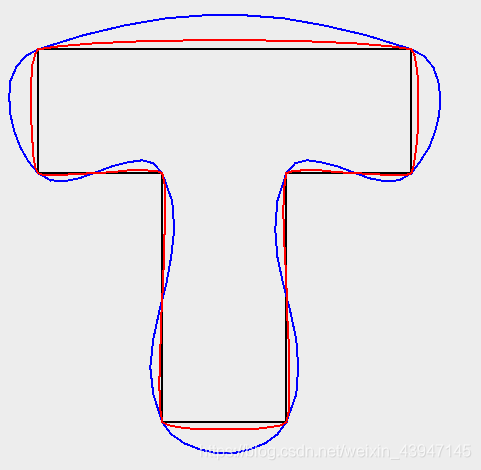
WKTReader reader = new WKTReader();
Geometry tShape = reader.read(
"POLYGON((10 0, 10 20, 0 20, 0 30, 30 30, 30 20, 20 20, 20 0, 10 0))");
Geometry tLoose = JTS.smooth(tShape, 0.0);
Geometry tTighter = JTS.smooth(tShape, 0.75);
这是结果图像: