基于近端策略优化的Proximal Policy Optimization(PPO)的无人机姿态控制系统的研究——简化版
基于近端策略优化的Proximal Policy Optimization(PPO)的无人机姿态控制系统的研究详细版订阅本博
https://blog.csdn.net/ccsss22/article/details/115423084
1.问题描述:
PPO算法是由OpenAI提出的,该算法是一种全新的策略梯度(Policy Gradient)算法,但是传统的策略梯度算法受到步长影响较大,而且很难选择出最优的步长参数,如果训练过程中,新策略和旧策略之间的差异过大将影响最终的学校效果。针对这个问题,PPO算法提出了一种新的目标函数,其可以通过多个训练步骤进行小批量的更新,从而解决了传统策略梯度算法中的步长选择问题。
2.部分程序:
python核心程序
"""
A simple version of Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) using single thread.
Based on:
1. Emergence of Locomotion Behaviours in Rich Environments (Google Deepmind): [https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.02286]
2. Proximal Policy Optimization Algorithms (OpenAI): [https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347]
View more on my tutorial website: https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials
Dependencies:
tensorflow r1.2
gym 0.9.2
"""
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import gym
EP_MAX = 1000
EP_LEN = 200
GAMMA = 0.9
A_LR = 0.0001
C_LR = 0.0002
BATCH = 32
A_UPDATE_STEPS = 10
C_UPDATE_STEPS = 10
S_DIM, A_DIM = 3, 1
METHOD = [
dict(name='kl_pen', kl_target=0.01, lam=0.5), # KL penalty
dict(name='clip', epsilon=0.2), # Clipped surrogate objective, find this is better
][1] # choose the method for optimization
class PPO(object):
def __init__(self):
self.sess = tf.Session()
self.tfs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, S_DIM], 'state')
# critic
with tf.variable_scope('critic'):
l1 = tf.layers.dense(self.tfs, 100, tf.nn.relu)
self.v = tf.layers.dense(l1, 1)
self.tfdc_r = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], 'discounted_r')
self.advantage = self.tfdc_r - self.v
self.closs = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.advantage))
self.ctrain_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(C_LR).minimize(self.closs)
# actor
pi, pi_params = self._build_anet('pi', trainable=True)
oldpi, oldpi_params = self._build_anet('oldpi', trainable=False)
with tf.variable_scope('sample_action'):
self.sample_op = tf.squeeze(pi.sample(1), axis=0) # choosing action
with tf.variable_scope('update_oldpi'):
self.update_oldpi_op = [oldp.assign(p) for p, oldp in zip(pi_params, oldpi_params)]
self.tfa = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, A_DIM], 'action')
self.tfadv = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1], 'advantage')
with tf.variable_scope('loss'):
with tf.variable_scope('surrogate'):
# ratio = tf.exp(pi.log_prob(self.tfa) - oldpi.log_prob(self.tfa))
ratio = pi.prob(self.tfa) / oldpi.prob(self.tfa)
surr = ratio * self.tfadv
if METHOD['name'] == 'kl_pen':
self.tflam = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, None, 'lambda')
kl = tf.distributions.kl_divergence(oldpi, pi)
self.kl_mean = tf.reduce_mean(kl)
self.aloss = -(tf.reduce_mean(surr - self.tflam * kl))
else: # clipping method, find this is better
self.aloss = -tf.reduce_mean(tf.minimum(
surr,
tf.clip_by_value(ratio, 1.-METHOD['epsilon'], 1.+METHOD['epsilon'])*self.tfadv))
with tf.variable_scope('atrain'):
self.atrain_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(A_LR).minimize(self.aloss)
tf.summary.FileWriter("log/", self.sess.graph)
self.sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
def update(self, s, a, r):
self.sess.run(self.update_oldpi_op)
adv = self.sess.run(self.advantage, {self.tfs: s, self.tfdc_r: r})
# adv = (adv - adv.mean())/(adv.std()+1e-6) # sometimes helpful
# update actor
if METHOD['name'] == 'kl_pen':
for _ in range(A_UPDATE_STEPS):
_, kl = self.sess.run(
[self.atrain_op, self.kl_mean],
{self.tfs: s, self.tfa: a, self.tfadv: adv, self.tflam: METHOD['lam']})
if kl > 4*METHOD['kl_target']: # this in in google's paper
break
if kl < METHOD['kl_target'] / 1.5: # adaptive lambda, this is in OpenAI's paper
METHOD['lam'] /= 2
elif kl > METHOD['kl_target'] * 1.5:
METHOD['lam'] *= 2
METHOD['lam'] = np.clip(METHOD['lam'], 1e-4, 10) # sometimes explode, this clipping is my solution
else: # clipping method, find this is better (OpenAI's paper)
[self.sess.run(self.atrain_op, {self.tfs: s, self.tfa: a, self.tfadv: adv}) for _ in range(A_UPDATE_STEPS)]
# update critic
[self.sess.run(self.ctrain_op, {self.tfs: s, self.tfdc_r: r}) for _ in range(C_UPDATE_STEPS)]
def _build_anet(self, name, trainable):
with tf.variable_scope(name):
l1 = tf.layers.dense(self.tfs, 100, tf.nn.relu, trainable=trainable)
mu = 2 * tf.layers.dense(l1, A_DIM, tf.nn.tanh, trainable=trainable)
sigma = tf.layers.dense(l1, A_DIM, tf.nn.softplus, trainable=trainable)
norm_dist = tf.distributions.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
params = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES, scope=name)
return norm_dist, params
def choose_action(self, s):
s = s[np.newaxis, :]
a = self.sess.run(self.sample_op, {self.tfs: s})[0]
return np.clip(a, -2, 2)
def get_v(self, s):
if s.ndim < 2: s = s[np.newaxis, :]
return self.sess.run(self.v, {self.tfs: s})[0, 0]
env = gym.make('Pendulum-v0').unwrapped
ppo = PPO()
all_ep_r = []
for ep in range(EP_MAX):
s = env.reset()
buffer_s, buffer_a, buffer_r = [], [], []
ep_r = 0
for t in range(EP_LEN): # in one episode
env.render()
a = ppo.choose_action(s)
s_, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
buffer_s.append(s)
buffer_a.append(a)
buffer_r.append((r+8)/8) # normalize reward, find to be useful
s = s_
ep_r += r
# update ppo
if (t+1) % BATCH == 0 or t == EP_LEN-1:
v_s_ = ppo.get_v(s_)
discounted_r = []
for r in buffer_r[::-1]:
v_s_ = r + GAMMA * v_s_
discounted_r.append(v_s_)
discounted_r.reverse()
bs, ba, br = np.vstack(buffer_s), np.vstack(buffer_a), np.array(discounted_r)[:, np.newaxis]
buffer_s, buffer_a, buffer_r = [], [], []
ppo.update(bs, ba, br)
if ep == 0: all_ep_r.append(ep_r)
else: all_ep_r.append(all_ep_r[-1]*0.9 + ep_r*0.1)
print(
'Ep: %i' % ep,
"|Ep_r: %i" % ep_r,
("|Lam: %.4f" % METHOD['lam']) if METHOD['name'] == 'kl_pen' else '',
)
plt.plot(np.arange(len(all_ep_r)), all_ep_r)
plt.xlabel('Episode');plt.ylabel('Moving averaged episode reward');plt.show()
————————————————
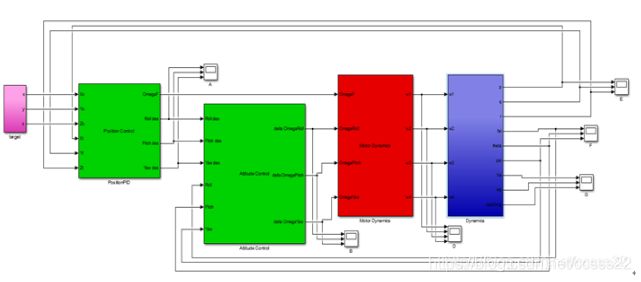
3.仿真结论:
A-05-0065