自动驾驶感知——激光雷达物体检测算法
文章目录
- 1. 基于激光雷达的物体检测
-
- 1.1 物体检测的输入与输出
- 1.2 点云数据库
- 1.3 激光雷达物体检测算法
-
- 1.3.1 点视图
-
- 1.3.1.1 PointNet
- 1.3.1.2 PointNet++
- 1.3.1.3 Point-RCNN
- 1.3.1.4 3D-SSD
- 1.3.1.5 总结和对比
- 1.3.2 俯视图
-
- 1.3.2.1 VoxelNet
- 1.3.2.2 SECOND
- 1.3.2.3 PIXOR
- 1.3.2.4 AFDet
- 1.3.2.5 总结与对比
- 1.3.3 前视图
-
- 1.3.3.1 LaserNet
- 1.3.3.2 RangeDet
- 1.3.4 多视图融合 (俯视图+点视图)
-
- 1.3.4.1 PointPillar
- 1.3.4.2 SIENet
- 1.3.4.3 PV-CNN
- 1.3.5 多视图融合(俯视图+前视图)
-
- 1.3.5.1 MV3D
- 1.3.5.2 RSN
- 声明
1. 基于激光雷达的物体检测
1.1 物体检测的输入与输出
 输入
输入
❖ 点:X, Y, Z和反射强度R
❖ 点云:多个点的集合(无序的,非结构化的数据)
输出
❖ 目标的类别和置信度
❖ 目标的边框(BoundingBox)
中心点3D坐标,长宽高,旋转角度
❖目标的其它信息
速度,加速度等
算法
❖ 点云表示:点视图,俯视图,前视图
1.2 点云数据库
如下表所示:常见的点云数据库由KITTI、NuScenes、WOD等数据库。

1.3 激光雷达物体检测算法
为了直观,先将激光雷达物体检测的一些常用算法列出。
| 算法类别 | 算法 |
|---|---|
| 点视图 | PointNet/PointNet++,Point-RCNN,3D-SSD |
| 俯视图 | VoxelNet,SECOND,PIXOR,AFDet |
| 前视图 | LaserNet,RangeDet |
| 多视图融合 (俯视图+点视图) | PointPillar,SIENet,PV-CNN |
| 多视图融合(俯视图+前视图) | MV3D,RSN |
1.3.1 点视图
1.3.1.1 PointNet
Qi et al., Pointnet: Deep learning on point sets for 3d classification and segmentation, 2017.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.00593.pdf
PointNet有以下的用法:
-
识别/分类(Classification):对于给定的一帧点云,判断该 点云中物体所属的种类。
-
分割(segmentation):对于给定的一帧点云,将点云分成 若干个特定的、具有独特性质的区域。
核心思路:点云特征提取
- MLP(多个全连接层)提取点特征:n个点,特征由3维提升到1024维
- MaxPooling得到全局特征:1024维
端对端学习,对点云进行分类/语义分割
物体检测:Clustering得到候选 + PointNet分类
1.3.1.2 PointNet++
Qi et al., Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space, 2017.
论文地址:https://papers.nips.cc/paper/2017/file/d8bf84be3800d12f74d8b05e9b89836f-Paper.pdf
在物体检测方向进行扩展:Clustering+PointNet
- 用聚类的方式来产生多个候选点集,每个候选点集采用PointNet来提取点的特征
- 上述过程重复多次:上一层的点集经过全局特征提取后看作下一层的点(Set Abstraction,SA)
- 点特征具有较大的感受野,包含周围环境的上下文信息
PointNet和PointNet++中存在的问题
- 无法利用视觉领域成熟的检测框架,比如Faster-RCNN,YOLO等
- Clustering部分的计算复杂度较高,而且难以并行处理
- 两个改进方法:Point-RCNN和3D-SSD
1.3.1.3 Point-RCNN
Shi et al., PointRCNN: 3D Object Proposal Generation and Detection from Point Cloud, 2018
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1812.04244.pdf
PointRCNN是一个两步式目标检测网络,该网络第一步进行前景点分割,找出点云中所有的目标点;第二步利用前景点回归目标的准确边界框。该网络同时兼顾了检测的准确([email protected]=75.6%)与实时性(10FPS)。
点处理 + Faster RCNN
- PointNet++提取点特征,同时进行前景分割,以区分物体点和背景点
- 每个前景点生成一个3D候选框(PointNet++采用聚类生成候选)
- 对每个候选框内的点进行Pooling,最后输出候选框所属的类别,修正其位置和大小
运行速度瓶颈++中的Feature Propagation
- PointNet++需要将点集特征映射回原始点云(Feature Propagation), 因为聚类生成的点集无法很好的覆盖所有物体
- 全局搜索属于每个物体候选的点
1.3.1.4 3D-SSD
Yang et al., 3dssd: Point-based 3d single stage object detector, 2020
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2002.10187.pdf
提高聚类质量
- 同时考虑点与点之间在几何和特征空间的相似度
- 聚类的输出可以直接用来生成物体候选
避免重复计算
- 聚类算法输出每个cluster的中心和邻域点
- 避免全局搜索物体候选和点之间的匹配关系
1.3.1.5 总结和对比
❖ PointNet++的主要问题在于运行速度太慢
❖ 速度的瓶颈在于聚类过程中需要将点集特征映射回原始点云
❖ Point RCNN和3D-SSD的改进主要在于提高运行速度
1.3.2 俯视图
1.3.2.1 VoxelNet
Zhou and Tuzel, Voxelnet: End-to-end learning for point cloud based 3d object detection, 2018
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.06396.pdf
核心点:
- 特征学习网络(Feature Learning Network)
- 3D卷积网络 (Convolutional Middle Layers)
- 区域候选网络(Region Proposal Network)
VoxelNet中存在的问题
❖ 数据表示低效,大量空白区域
- KITTI数据库一般生成5K-8K个Voxel,只有0.5%的Voxel是非空的
- 改进方法:SECOND(采用稀疏卷积)
❖ 三维卷积计算量巨大
- 改进方法:PIXOR(3D网格压缩到2D)
1.3.2.2 SECOND
Yan et al., Second: Sparsely embedded convolutional detection, Sensors, 2018.
论文地址:https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/18/10/3337
稀疏卷积避免无效计算
- 中间层采用稀疏卷积
- 其余模块与VoxelNet类似
1.3.2.3 PIXOR
Yang et al., Pixor: Real-time 3d object detection from point clouds, CVPR, 2018
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.06326.pdf
PIXOR (ORiented 3D object detection from PIXel-wise neural network predictions)
❖ 手工设计高度维度的特征
❖ 3D->2D:高度维度变成特征通道
❖ 可以用2D卷积来提取特征

- Occupancy:L x W x H(H维度作为特征通道)
- Intensity:L x W x 1(H方向压缩为1维)
- In totalLxWx (H+1)
1.3.2.4 AFDet
Ge et al., Real-Time Anchor-Free Single-Stage 3D Detection with IoU-Awareness, 2021
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.12671.pdf
❖ 单阶段,无Anchor
❖ Waymo 3D物体检测 2021年度的获胜算法
❖ 算法方面的改进
- 轻量级的点云特征提取
- 扩大神经网络的感受野
- 额外的预测分支
1.3.2.5 总结与对比
❖ 俯视图
- 输入结构化数据,网络结构简单
- 对量化参数敏感:粗网格导致较大的信息损失,细网格导致较大的计算量 和内存使用量
❖ 点视图
- 没有量化损失,数据比较紧致
- 输入非结构化数据,网络结构复杂,并行处理困难,提取邻域特征困难
1.3.3 前视图
前视图的特点
❖ 优点
- 表示更为紧致,而且没有量化损失
- 每个像素上理论上都会有数据
❖ 问题
- 不同距离的物体尺度差别很大
- 2D特征与3D物体信息存在不一致性
1.3.3.1 LaserNet
Meyer et al., LaserNet: An Efficient Probabilistic 3D Object Detector for Autonomous Driving, 2019.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.08701.pdf
❖ 输入数据为多通道的前视图图像
❖ 卷积和下采样提取多尺度特征
❖ 每个像素都预测物体边框的分布(均值和方差)
❖ MeanShift聚类+NMS得到最终的输出
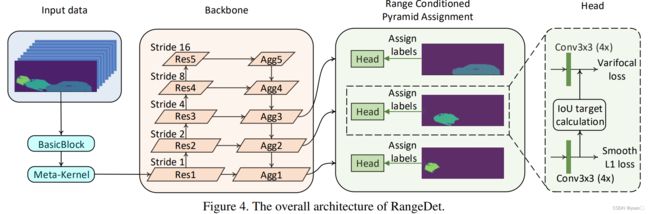
1.3.3.2 RangeDet
Fan et al., RangeDet: In Defense of Range View for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection, 2021
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.10039.pdf
核心点:
❖ Meta-Kernel Convolution
❖ Range Conditioned Pyramid
1.3.4 多视图融合 (俯视图+点视图)
❖ 基本思路
- 在较低分辨率的Voxel上提取邻域特征或者生成物体候选
- 在原始点云上提取点特征,忽略空白区域,保持空间分辨率
- Voxel特征与点特征结合
❖ 代表性方法
- PointPillar
- PV-CNN
- SIENet
1.3.4.1 PointPillar
Lang et al., PointPillars: Fast Encoders for Object Detection from Point Clouds, 2019.
论文地址:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/papers/Lang_PointPillars_Fast_Encoders_for_Object_Detection_From_Point_Clouds_CVPR_2019_paper.pdf
❖ 特征: PointNet提取点特征(点视图),然后进行Voxel量化(俯视图)
❖ 主干:Feature Pyramid Network
❖ 检测头:SSD
1.3.4.2 SIENet
Li et al., SIENet: Spatial Information Enhancement Network for 3D Object Detection from Point Cloud, 2021.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.15396.pdf
❖ 融合策略与PV-CNN相似
❖ 解决远处物体点云相对稀疏的问题
- 采用了一个附加分支,将物体候选框中的点集进行扩展
1.3.4.3 PV-CNN
Liu et al., Point-voxel CNN for efficient 3d deep learning, 2019.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1907.03739.pdf
❖Voxel分支:低分辨率的Voxel提取邻域特征,然后映射回每个点上
❖Point分支:利用MLP来提取点特征,没有量化损失,也避免空白区域的计算
❖两个分支的特征合并用于后续的物体检测
1.3.5 多视图融合(俯视图+前视图)
❖ 基本思路
- 融合俯视图和前视图下的特征
- 尽量避免空白区域的无效计算
❖ 代表性方法
- MV3D
- Range Sparse Net (RSN)
1.3.5.1 MV3D
Chen, et al., Multi-view 3d object detection network for autonomous driving, 2017
论文地址:https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/papers/Chen_Multi-View_3D_Object_CVPR_2017_paper.pdf
❖ BEV网格生成3D物体候选,再转换为不同视图下的候选
❖ 不同候选中进行ROI-Pooling
❖ 在候选层级上融合不同视图的特征
1.3.5.2 RSN
Sun, et al., RSN: Range Sparse Net for Efficient, Accurate LiDAR 3D Object Detection, 2021.
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.13365.pdf
两阶段检测器,目的在于提高检测距离的可扩展性
- 阶段1:前视图上进行前景分割,过滤背景点
- 阶段2:前景点量化为Voxel,稀疏卷积提取特征,稀疏的Grid上检测物体
- 稠密的前视图+稀疏的俯视图
声明
本人所有文章仅作为自己的学习记录,若有侵权,联系立删。本系列文章主要参考了清华大学、北京理工大学、深蓝学院、百度Apollo等相关课程。