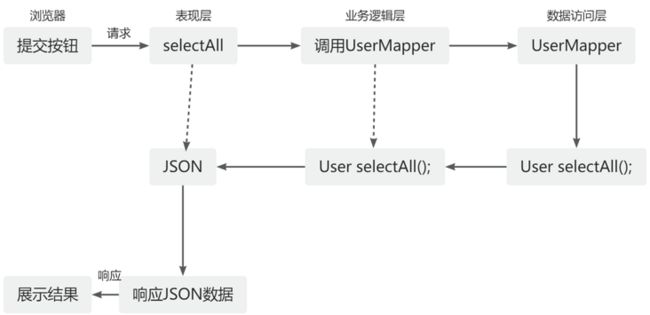
AJAX(Asynchronous JavaScript And XML 异步的JavaScript和XML)
Ajax 的作用:
1、与服务器进行数据交换:通过Ajax可以给服务器发送请求,并获取服务器响应的数据。
2、使用Ajax和服务器进行通信,就可以使用HTML来替换JSP页面
3、Ajax最重要的就是异步交换,可以在不重新加载整个页面的情况下,与服务器交换数据并更新部分网页的技术,比如,用户是否可校验。
同步:大伙按部就班,老老实实的等待请求服务器,服务器处理,响应客户端这个过程,一步一步走。
异步:可以在等待请求服务器,服务器处理,响应客户端的过程中做些别的事情(用户感知不到这个过程,一切都悄咪咪的进行)。
那Ajax究竟是怎么编写的呢?还是老规矩,给一个需求:通过URL传递数据,前端需要有两个输入框输入用户名和密码,用Ajax请求服务端。建一个数据库表(user),其中有两个字段,一个是Name字段一个是Password字段。提交,服务器接收,查询数据库。如果账号密码在数据库中存在,则提示成功,否则提示失败。传参的方式必须是post,参数不允许出现在url上。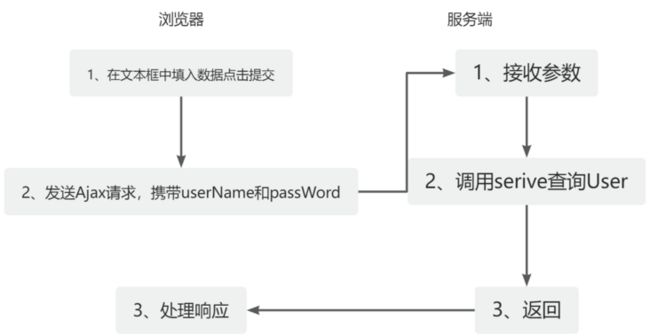
有了大致流程,我们就能开始动手啦!
1、在文本中填入数据点击提交
要校验用户的用户名和密码那肯定得先输入用户名和密码,还需要提交这个数据,那我们可以用form表单来实现这个功能。创建HTML,命名为ajax-demo.html:

表单是创建好了,那该怎么实现把数据提交到服务端上呢?可以看到我在表单里写了一个单击事件,执行fun()方法(onclick="fun()),这时就是我们这篇的主角Ajax上场啦!
2、发送Ajax请求,提交userName和passWord到服务端
在使用Ajax之前,我们先来了解一下Ajax的;两种请求方式:
GET 请求和 POST 请求。GET请求和POST请求的用法很相似,都可以通过URL来传递参数。但POST请求还具有requestBody,可以通过 setRequestHeader() 来添加 HTTP 头,通过send来传递参数。如需将请求发送到服务器,我们使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 open() 和 send() 方法。
open(method,url,async):method:请求的类型;GET 或 POST,url:文件在服务器上的位置
,async:true(异步)或 false(同步)。
send(string):string:仅用于 POST 请求,因为GET请求没有requestBody。
当然,想使用open和send方法之前,首先得创建一个XMLHttpRequest对象,因为这两种方法是XMLHttpRequest对象中的两种方法。
在了解完这两种请求之后,我们就继续完成这个需求吧。在这里我就使用POST向http://localhost:8080/addUser2发送请求。
function fun(){
const back = new XMLHttpRequest();
let name = {"userName":form1.userName.value,"passWord":form1.passWord.value}
userName="+name+"&&passWord="+psd;
let userName = JSON.stringify(name);
alert(userName);
back.open("POST","http://localhost:8080/addUser2");
//back.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");默认方法,固定格式
back.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/json;charset=UTF-8");//可以发送json格式字符串
back.send(userName);
}点击提交!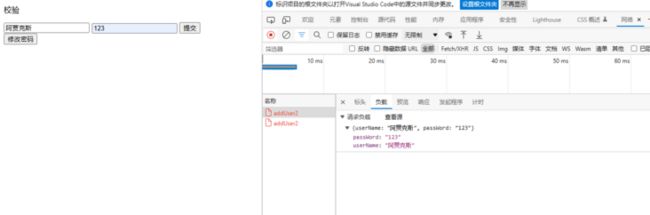
通过浏览器的开发者工具,我们能看到游览器以及成功的向服务端提交了一个JSON格式的数据(JSON.stringify()方法将name转换成了JSON格式),接下来就是着手准备服务端的接收了。
3、服务端接收参数
浏览器向服务器发送了post请求,由于这次POST请求添加了标头,所以在Servlet中request.getParameter()获取不了这个参数(如果没有添加标头,可以使用request.getParameter()获取浏览器提交的数据)。
创建DemoApplication。
public class DemoApplication {
@RequestMapping("/addUser2")
public People addUser2( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//String userName = request.getParameter("username");
//String passWord = request.getParameter("passWord");
String contentType = request.getContentType();
ServletInputStream is = request.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line=null;
String result="";
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line); //{"username":"阿贾克斯","password":"123"}
result =result + "\n" +line;
}
System.out.println(result);
return null;
}
}我们再次提交数据,来查看服务端是否收到了来自浏览器的数据。
执行!![]()
好像并没有符合预期呀,难不成是浏览器没有成功提交数据吗?我们开启浏览器的开发者工具查看网络: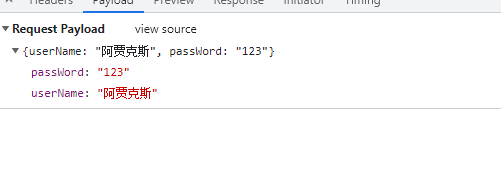
发现浏览器确实提交数据了,那为什么服务端没有收到来自浏览器提交的数据呢?
那我们再查看一下控制台: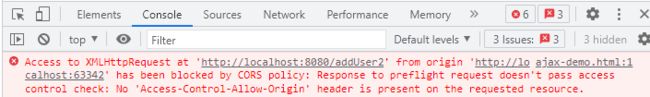
从“http://localhost:63342”访问“http://localhost:8080”的XMLHttpRequest已被CORS策略阻止。这是什么原因?这就不得不说一下跨域问题了。
跨域,指的是浏览器不能执行其他网站的脚本。它是由浏览器的同源策略造成的,是浏览器施加的安全限制。
所谓同源是指,域名,协议,端口均相同,只要有一个不同,就是跨域。
可以看到两个URL的端口并不相同(一个端口号是63342,另一个端口号是8080),所以发送了跨域请求,被阻止了。那该怎么顺利完成请求呢?那不如把ajax-demo.html写在servlet里吧,那端口号就一致了。
public class DemoApplication {
@GetMapping("/hello1")
public String hello1() {
String str ;
String htmlStr="";
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src/webapp/ajax-demo.html"));
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
htmlStr =htmlStr + "\n" +str;
}
System.out.print(htmlStr);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print("错误");
}
return htmlStr;
}
@RequestMapping("/addUser2")
public People addUser2( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//String userName = request.getParameter("username");
//String passWord = request.getParameter("passWord");
String contentType = request.getContentType();
ServletInputStream is = request.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line=null;
String result="";
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line); //{"username":"阿贾克斯","password":"123"}
result =result + "\n" +line;
}
System.out.println(result);
return null;
}
}通过读取文件的方式将ajax-demo.html成功的写在了servlet中,我们再执行一次看看效果是否符合预期。先执行程序,根据获得的URL在浏览器上输入。
这次再来试一试服务端能不能成功接收浏览器提交的数据: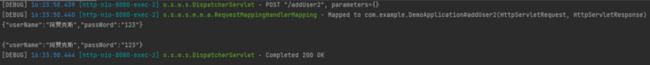
成功!
既然接收到了浏览器提交的数据,那就开始执行下一步。
4、查询数据库并与服务端接收到的数据进行比较,并且返回结果
首先创建数据库表user,并插入相关数据数据:
create table user(
username varchar(20) comment '用户',
password varchar(20) comment '密码'
) comment '账号表';
insert into user(username,password) values('阿贾克斯',123);然后使用MyBatis动态代理来实现查询数据库,关于MyBatis配置方面这里就不过多赘述了,想了解的可以看看之前的文章:https://segmentfault.com/a/11...
首先创建POJO类:
package com.example.pojo;
public class User {
private String userName;
private String passWord;
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassWord() {
return passWord;
}
public void setPassWord(String passWord) {
this.passWord = passWord;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"userName='" + userName + '\'' +
", passWord='" + passWord + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
然后添加UserMapper接口:
package com.example.mapper;
import com.example.pojo.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserMapper {
User selectAll(@Param("userName")String username, @Param("passWord")String password);
}
创建UserMapper.xml
前置工作完工,但在查询数据库之前,先得把服务端接收的JSON格式的数据提取到Object中,再通过Object赋值给变量:
创建People
package com.example;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonView;
public class People {
public interface WithoutPasswordView {};
@JsonView(WithoutPasswordView.class)
String userName ;
@JsonView(WithoutPasswordView.class)
String passWord ;
}
开始提取JSON,查询数据库!
public class DemoApplication {
@GetMapping("/hello1")
public String hello1() {
String str ;
String htmlStr="";
try {
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src/webapp/ajax-demo.html"));
while ((str = in.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
htmlStr =htmlStr + "\n" +str;
}
System.out.print(htmlStr);
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.print("错误");
}
return htmlStr;
}
@RequestMapping("/addUser2")
public People addUser2( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
//String userName = request.getParameter("username");
//String passWord = request.getParameter("passWord");
String contentType = request.getContentType();
ServletInputStream is = request.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String line=null;
String result="";
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line); //{"username":"阿贾克斯","password":"123"}
result =result + "\n" +line;
}
System.out.println(result);
//提取JSON中的值
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
People people = mapper.readValue(result,People.class);
String userName = people.userName;
String passWord = people.passWord;
//查询数据库
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2.获取SqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//3.获取Mapper接口的代理对象
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
//4.执行方法,数据库数据与userName、passWord做比较
User users =userMapper.selectAll(userName, passWord);
System.out.println(users);
//释放资源
sqlSession.close();
//如果users不为空,说明服务端接收的与数据库的一致
boolean flag = false;
if (users != null) {
flag = true;
} else {//说明服务端接收的数据和数据库的不一致
flag = false;
}
//返回一个Boolean
response.getWriter().write("" + flag);
return null;
}
}5、处理响应
function fun(){
const back = new XMLHttpRequest();
let name = {"userName":form1.userName.value,"passWord":form1.passWord.value}
userName="+name+"&&passWord="+psd;
let userName = JSON.stringify(name);
//处理响应
back.onload = function(){
//判断true 、false
if(this.responseText == "true"){
//密码账号正确
alert("密码账号正确");
}else{
//密码账号错误
alert("密码账号错误");
}
}
alert(userName);
back.open("POST","http://localhost:8080/addUser2");
//back.setRequestHeader("Content-type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");默认方法,固定格式
back.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/json;charset=UTF-8");//可以发送json格式字符串
back.send(userName);
}到这所有的步骤都结束了,执行来看看效果: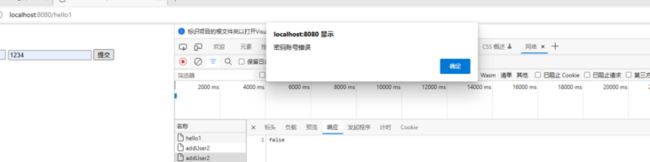
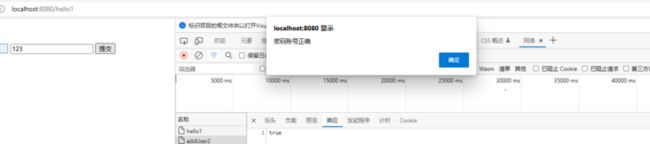
符合预期,成功完成需求。
数据传递的大概流程:
下期内容
再添加一个新的需求:新增一个修改密码的接口,前端再增加一个修改密码的页面,请求和返回都使用JSON,要求复用数据库连接,解决读取HTML文件硬编码问题。