Tomcat源码剖析|多图分析Tomcat启动时的start流程(含容器内应用启动流程)
Tomcat源码剖析——启动
本文解析源码来自于Tomcat8.5.33
本文引用参考文献为《Tomcat架构解析-刘光瑞》
注:此文为连载文章,可以参考前序文章《类加载器》《初始化》,以及后续文章《处理请求》
文章目录
-
- Tomcat源码剖析——启动
-
- 前言
- 源码分析
-
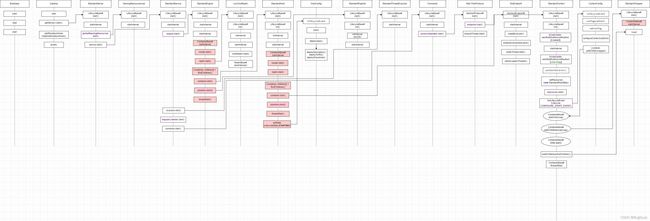
- 流程图
- 代码分析
-
- 1. Bootstrap.main()
- 2. Catalina.start()
- 3. StandardServer#LifecycleBase.start()
- 4. StandardServer.startInternal()
- 5. StandardService.startInternal()
- 6. StandardThreadExecutor.startInternal()
- 7. StandardEngine.startInternal()
- 8. StandardEngine#ContainerBase.startInternal()
- 9.StandardHost.startInternal()
- 10. StandardContext.startInternal()
- 11.ContextConfig.lifecycleEvent()
- 12. StandardWrapper#LifecycleBase.start()
- 13. StandardWrapper.load()
- 14. HostConfig.lifecycleEvent()
- 15. Connector.startInternal()
- 16. Http11NioProtocol.start()
- 总结
前言
上文我们已经分析了,Tomcat在初始化后,部分组件已经调用了init()方法。接下来就是Web应用的加载启动了。
Catalina对Web应用的加载主要由StandardHost,HostConfig,StandardContext,ContextConfig,StandWrapper这五个类完成。
源码分析
流程图
代码分析
1. Bootstrap.main()
在初始化完组件后,再调用start()启动加载Web应用;实际上是通过反射,调用catalina.start();见方法2;
// Bootstrap.class
public static void main(String args[]) {
// ...
try {
if (command.equals("start")) {
daemon.setAwait(true);
// 加载
daemon.load(args);
// 启动
daemon.start();
if (null == daemon.getServer()) {
System.exit(1);
}
}
} catch(e){}
// ...
}
public void start() throws Exception {
if (catalinaDaemon == null) {
init();
}
// 反射调用catalina.start()
Method method = catalinaDaemon.getClass().getMethod("start", (Class [])null);
method.invoke(catalinaDaemon, (Object [])null);
}
2. Catalina.start()
我们可以看到,这里去调用了StandardServer.start(),见方法3,然后主线程阻塞等待。
// Catalina.class
public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
return;
}
// Register shutdown hook
// 注册关闭回调
if (useShutdownHook) {
// ...
}
if (await) {
// 主线程在这里wait
await();
stop();
}
}
3. StandardServer#LifecycleBase.start()
同样,server的start()方法交由生命周期父类去完成。然后调用子类实现的startInternal(),见方法4;
// StandardServer#LifecycleBase
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
if (LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP.equals(state) || LifecycleState.STARTING.equals(state) ||
LifecycleState.STARTED.equals(state)) {
return;
}
// 未初始化的组件进行初始化
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
init();
} else if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.INITIALIZED) &&
!state.equals(LifecycleState.STOPPED)) {
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT);
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
// 调用子类启动
startInternal();
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.FAILED)) {
// This is a 'controlled' failure. The component put itself into the
// FAILED state so call stop() to complete the clean-up.
stop();
} else if (!state.equals(LifecycleState.STARTING)) {
// Shouldn't be necessary but acts as a check that sub-classes are
// doing what they are supposed to.
invalidTransition(Lifecycle.AFTER_START_EVENT);
} else {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTED, null, false);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// This is an 'uncontrolled' failure so put the component into the
// FAILED state and throw an exception.
handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.startFail", toString());
}
}
4. StandardServer.startInternal()
这里StandardServer启动了全局资源(globalNamingResources定义了服务器的全局JNDI资源);
然后对所有的Service进行启动,见方法5。
// StandardServer.class
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
fireLifecycleEvent(CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
globalNamingResources.start();
// Start our defined Services
synchronized (servicesLock) {
for (Service service : services) {
// 启动Service
service.start();
}
}
}
5. StandardService.startInternal()
Service这里启动了他的下层容器:
StandardEngine引擎;见方法7;
StandardThreadExecutor 线程池;见方法6;
connector连接器;见方法15;
// StandardService.class
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
// 启动引擎
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
// 启动线程池
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor: executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
// 启动Mapper监听器
mapperListener.start();
// 启动连接器
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector: connectors) {
try {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardService.connector.startFailed",
connector), e);
}
}
}
}
6. StandardThreadExecutor.startInternal()
这里 tomcat自己封装维护了一个线程池。
首先它定义了一个队列TaskQueue,他是LinkedBlockingQueue的封装,由于LinkedBlockingQueue是无界队列,为了线程池仍然有机会创建新的线程,因此重写offer()方法,让他变得”有界“;offer()返回false,会创建救济线程去处理;
定义了一个核心数(minSpareThreads)默认25,最大线程数(maxThreads)默认100,保活时间6s的线程池。我们可以在server.xml中进行配置:
<Executor name="tomcatThreadPool" namePrefix="catalina-exec-"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="4"/>
然后触发状态为启动;
这里体现的设计模式:结构型 - 外观(Facade) 外观模式(Facade pattern),它提供了一个统一的暴露接口org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.ResizableExecutor;
public interface ResizableExecutor extends Executor {
/**
* Returns the current number of threads in the pool.
*
* @return the number of threads
*/
public int getPoolSize();
public int getMaxThreads();
/**
* Returns the approximate number of threads that are actively executing
* tasks.
*
* @return the number of threads
*/
public int getActiveCount();
public boolean resizePool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize);
public boolean resizeQueue(int capacity);
}
具体源码如下:
// StandardThreadExecutor.class
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Tomcat 实现了自定义的的任务队列,重写了 offer 方法,使得在任务队列长度无限制的情况下,线程池仍然有机会创建新的线程。
taskqueue = new TaskQueue(maxQueueSize);
// 线程名称tomcat-exec-
// daemon=true 线程都是守护线程
// getThreadPriority() 默认5个
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(namePrefix,daemon,getThreadPriority());
// getMinSpareThreads() 核心线程数,默认配置25
// getMaxThreads() 最大线程数, 默认配置100
// maxIdleTime 保活时间,默认60000ms
executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(getMinSpareThreads(), getMaxThreads(), maxIdleTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,taskqueue, tf);
executor.setThreadRenewalDelay(threadRenewalDelay);
if (prestartminSpareThreads) {
executor.prestartAllCoreThreads();
}
taskqueue.setParent(executor);
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
7. StandardEngine.startInternal()
这是我们启动的第一个容器,他启动的时候就打了个日志,主要逻辑交给了父类ContainerBase容器去实现的;见方法8
// StandardEngine.class
@Override
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Log our server identification information
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardEngine.start", ServerInfo.getServerInfo()));
}
// Standard container startup
// 调用ContainerBase#startInternal()
super.startInternal();
}
8. StandardEngine#ContainerBase.startInternal()
引擎这里做了如下事情:
-
集群,安全域启动;
-
启动子容器;通过创建线程
startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(container)), 调用的是container.start(), 这里的container实际上就是第二个登场的容器——StandardHost见方法9; -
启动管道;
-
设置Engine状态为STARTING,此时会触发START_EVENT生命周期事件。 EngineConfig监听该事件,打了个启动日志;
-
启动Engine层级的后台任务处理;
// ContainerBase
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
// 集群配置启动
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
// 安全域启动
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
// 启动子容器
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
// 通过线程进行启动
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
// 启动管道
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
/*
*StandardEngine:
* 设置Engine状态为STARTING,此时会触发START_EVENT生命周期事件。
* EngineConfig监听该事件,打了个启动日志
*/
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
/*
* StandardEngine:
* 启动Engine层级的后台任务处理:Cluster后台任务处理(包括部署变更检测,心跳),Realm后台任务处理
* Pipeline中Value的后台任务处理
*/
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}
9.StandardHost.startInternal()
这里的StandardHost给管道里增加了一个错误报告Value(ErrorReportValve),然后调用父类ContainerBase容器方法;
Host的父类这里做了如下事情:
-
集群,安全域启动;
-
启动子容器;通过创建线程
startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(container)), 调用的是container.start()见方法10, 这里的container实际上就是第三个登场的容器——StandardContext; -
启动管道;
-
设置Host状态为STARTING,此时会触发START_EVENT生命周期事件。HostConfig监听该事件:扫描Web部署目录,对于部署描述文件,WAR包,目录会自动创建StandardContext实例添加到Host并启动;见方法14;
-
启动Host层级的后台任务处理:Cluster后台任务处理(包括部署变更检测,心跳),Realm后台任务处理,Pipeline中Value的后台任务处理(某些Value通过后台任务实现定期处理功能, 如StuckThreadDetectionValue用于定时检测耗时请求并输出);
因此我们可以看出,Host创建子容器是有两种途径:
- 通过server.xml配置的< Context />节点;
- 通过直接部署应用,在HostConfig中去扫描创建;见方法10;
// StandardHost
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Set error report valve
// 给Pipleline增加org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve 错误页面
String errorValve = getErrorReportValveClass();
if ((errorValve != null) && (!errorValve.equals(""))) {
try {
boolean found = false;
Valve[] valves = getPipeline().getValves();
for (Valve valve : valves) {
if (errorValve.equals(valve.getClass().getName())) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
if(!found) {
Valve valve =
(Valve) Class.forName(errorValve).getConstructor().newInstance();
getPipeline().addValve(valve);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
log.error(sm.getString(
"standardHost.invalidErrorReportValveClass",
errorValve), t);
}
}
// 调用父类方法
super.startInternal();
}
// StandardHost#ContainerBase
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
// 集群配置启动
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
// 安全域启动
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
// 启动子容器context 【途径1】
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
// 启动管道
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
/*
*StandardHost:
* 设置Host状态为STARTING,此时会触发START_EVENT生命周期事件。
* HostConfig监听该事件,扫描Web部署目录,对于部署描述文件,WAR包,目录会自动创建StandardContext实例,
* 添加到Host并启动
*/
// 启动子容器context 【途径2】
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
/*
* StandardHost:
* 启动Host层级的后台任务处理:Cluster后台任务处理(包括部署变更检测,心跳),Realm后台任务处理,
* Pipeline中Value的后台任务处理(某些Value通过后台任务实现定期处理功能,
* 如StuckThreadDetectionValue用于定时检测耗时请求并输出)
*/
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}
10. StandardContext.startInternal()
context就是一个Web应用了,他的启动非常的复杂,具体步骤如下(已和代码注释同步):
这块就当了解吧,有兴趣的去看《Tomcat架构解析-刘光瑞》书P62页,反正我是晕了,关注我下述的几个方法;方法11,方法12,方法13吧;
- 发布正在启动的JMX通知,可以通过添加NotificationListener来监听Web应用的启动;
- 处理工作目录;
- 初始化当前Context使用的WebResourceRoot并启动。WebResourceRoot维护了Web应用所有的资源集合(Class文件,Jar包以及其他资源文件),主要用于类加载和按照路径查找资源文件;
- 创建Web应用类加载器,WebappLoader继承LifecycleMBeanBase,其启动时创建Web应用类加载器; (WebappClassLoader)。此外,该类还提供了background-Process,用于Context后台处理。当检测到Web应用的类文件,Jar包发生变更时,重新加载Context;
- 设置默认的Cookie处理器;
- 设置字符集映射,该映射主要用于根据Locale获取字符集编码;
- 启动Web应用类加载器(WebappLoader.start),此时才真正创建WebappClassLoader实例;
- 启动安全组件;
- 发布CONFIGURE_START_EVENT事件,ContextConfig监听该事件以完成Servlet的创建;见方法11;
- 启动Context子节点(Wrapper);见方法12;
- 启动Context维护的Pipeline;
- 创建会话管理器 Manager contextManager;
- 如果配置了集群组件,则由集群组件创建,否则使用StandardManager,在集群环境下,需要将会话管理器注册到集群组件;
- 将Context的WEB资源集合添加到ServletContext属性;
- 创建实例管理器,用于创建对象实例,如Servlet,Filter;
- 将Jar包扫描器添加到ServletContext属性;
- 合并ServletContext初始化参数和Context组件中的ApplicationParameter(前提是配置可覆盖);
- 启动添加到当前Context的ServletContainerInitializer;
- 实例化监听器(时间监听器和生命周期监听器);
- 检测未覆盖的HTTP方法的安全约束;
- 启动会话管理器;
- 实例化FilterConfig、Filter、并调用Filter.init初始化;
- 对于loadOnStartup>=0的Wrapper,调用wrapper.load();见方法13;
- 该方法负责实例化Servlet,并调用Servlet.init进行初始化;
- 启动后台定时处理线程;只有当backgroundProcessorDelay>0时启动:用于监护守护文件的变更等;当backgroundProcessorDelay<=0时,标识Context的后台任务由上级容器(Host)调度;
- 发布正在运行的JMX通知;
- 调用WebResourceRoot.gc()释放资源;
- // 启动成功设置STARTED;
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if(log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Starting " + getBaseName());
}
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
// 发布正在启动的JMX通知,可以通过添加NotificationListener来监听Web应用的启动
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting",
this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
setConfigured(false);
boolean ok = true;
// Currently this is effectively a NO-OP but needs to be called to
// ensure the NamingResources follows the correct lifecycle
if (namingResources != null) {
namingResources.start();
}
// Post work directory
// 处理工作目录
postWorkDirectory();
// Add missing components as necessary
if (getResources() == null) { // (1) Required by Loader
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Configuring default Resources");
}
// 初始化当前Context使用的WebResourceRoot并启动。WebResourceRoot维护了Web应用所有的
// 资源集合(Class文件,Jar包以及其他资源文件),主要用于类加载和按照路径查找资源文件
try {
/*
* WebResourceRoot[StandardRoot]
* 表示组成Web应用的所有资源的集合,在WebResourceRoot中,一个Web应用的资源又可以按照
* 分类划分为多个集合,当查找资源时,按照指定顺序处理;
*/
setResources(new StandardRoot(this));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.resourcesInit"), e);
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
resourcesStart();
}
// 创建Web应用类加载器,WebappLoader继承LifecycleMBeanBase,其启动时创建Web应用类加载器
// (WebappClassLoader)。此外,该类还提供了background-Process,用于Context后台处理。
// 当检测到Web应用的类文件,Jar包发生变更时,重新加载Context
if (getLoader() == null) {
WebappLoader webappLoader = new WebappLoader();
webappLoader.setDelegate(getDelegate());
setLoader(webappLoader);
}
// An explicit cookie processor hasn't been specified; use the default
// 默认的Cookie处理器
if (cookieProcessor == null) {
cookieProcessor = new Rfc6265CookieProcessor();
}
// Initialize character set mapper
// 设置字符集映射,该映射主要用于根据Locale获取字符集编码
getCharsetMapper();
// Validate required extensions
boolean dependencyCheck = true;
try {
dependencyCheck = ExtensionValidator.validateApplication
(getResources(), this);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.extensionValidationError"), ioe);
dependencyCheck = false;
}
if (!dependencyCheck) {
// do not make application available if dependency check fails
ok = false;
}
// Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable
String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming");
if ((useNamingProperty != null)
&& (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) {
useNaming = false;
}
if (ok && isUseNaming()) {
if (getNamingContextListener() == null) {
NamingContextListener ncl = new NamingContextListener();
ncl.setName(getNamingContextName());
ncl.setExceptionOnFailedWrite(getJndiExceptionOnFailedWrite());
addLifecycleListener(ncl);
setNamingContextListener(ncl);
}
}
// Standard container startup
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Processing standard container startup");
}
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
try {
if (ok) {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
Loader loader = getLoader();
// 启动Web应用类加载器(WebappLoader.start),此时才真正创建WebappClassLoader实例
if (loader instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
}
// since the loader just started, the webapp classloader is now
// created.
if (loader.getClassLoader() instanceof WebappClassLoaderBase) {
WebappClassLoaderBase cl = (WebappClassLoaderBase) loader.getClassLoader();
cl.setClearReferencesRmiTargets(getClearReferencesRmiTargets());
cl.setClearReferencesStopThreads(getClearReferencesStopThreads());
cl.setClearReferencesStopTimerThreads(getClearReferencesStopTimerThreads());
cl.setClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread(getClearReferencesHttpClientKeepAliveThread());
cl.setClearReferencesObjectStreamClassCaches(getClearReferencesObjectStreamClassCaches());
cl.setClearReferencesThreadLocals(getClearReferencesThreadLocals());
}
// By calling unbindThread and bindThread in a row, we setup the
// current Thread CCL to be the webapp classloader
unbindThread(oldCCL);
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Initialize logger again. Other components might have used it
// too early, so it should be reset.
logger = null;
getLogger();
// 启动安全组件
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if(null != realm) {
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Place the CredentialHandler into the ServletContext so
// applications can have access to it. Wrap it in a "safe"
// handler so application's can't modify it.
CredentialHandler safeHandler = new CredentialHandler() {
@Override
public boolean matches(String inputCredentials, String storedCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().matches(inputCredentials, storedCredentials);
}
@Override
public String mutate(String inputCredentials) {
return getRealmInternal().getCredentialHandler().mutate(inputCredentials);
}
};
context.setAttribute(Globals.CREDENTIAL_HANDLER, safeHandler);
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
// 发布CONFIGURE_START_EVENT事件,ContextConfig监听该事件以完成Servlet的创建
fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT, null);
// Start our child containers, if not already started
for (Container child : findChildren()) {
// 启动Context子节点
if (!child.getState().isAvailable()) {
child.start();
}
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
// 启动Context维护的Pipeline
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
// Acquire clustered manager
// 创建会话管理器
Manager contextManager = null;
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager == null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.cluster.noManager",
Boolean.valueOf((getCluster() != null)),
Boolean.valueOf(distributable)));
}
// 如果配置了集群组件,则由集群组件创建,否则使用StandardManager
// 在集群环境下,需要将会话管理器注册到集群组件
if ((getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
try {
contextManager = getCluster().createManager(getName());
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("standardContext.clusterFail", ex);
ok = false;
}
} else {
contextManager = new StandardManager();
}
}
// Configure default manager if none was specified
if (contextManager != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("standardContext.manager",
contextManager.getClass().getName()));
}
setManager(contextManager);
}
if (manager!=null && (getCluster() != null) && distributable) {
//let the cluster know that there is a context that is distributable
//and that it has its own manager
getCluster().registerManager(manager);
}
}
if (!getConfigured()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.configurationFail"));
ok = false;
}
// We put the resources into the servlet context
if (ok) {
// 将Context的WEB资源集合添加到ServletContext属性
getServletContext().setAttribute
(Globals.RESOURCES_ATTR, getResources());
// 创建实例管理器,用于创建对象实例,如Servlet,Filter
if (getInstanceManager() == null) {
javax.naming.Context context = null;
if (isUseNaming() && getNamingContextListener() != null) {
context = getNamingContextListener().getEnvContext();
}
Map<String, Map<String, String>> injectionMap = buildInjectionMap(
getIgnoreAnnotations() ? new NamingResourcesImpl(): getNamingResources());
setInstanceManager(new DefaultInstanceManager(context,
injectionMap, this, this.getClass().getClassLoader()));
}
getServletContext().setAttribute(
InstanceManager.class.getName(), getInstanceManager());
InstanceManagerBindings.bind(getLoader().getClassLoader(), getInstanceManager());
// 将Jar包扫描器添加到ServletContext属性
// Create context attributes that will be required
getServletContext().setAttribute(
JarScanner.class.getName(), getJarScanner());
// Make the version info available
getServletContext().setAttribute(Globals.WEBAPP_VERSION, getWebappVersion());
}
// Set up the context init params
// 合并ServletContext初始化参数和Context组件中的ApplicationParameter(前提是配置可覆盖)
mergeParameters();
// Call ServletContainerInitializers
// 启动添加到当前Context的ServletContainerInitializer
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer, Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializers.entrySet()) {
try {
entry.getKey().onStartup(entry.getValue(),
getServletContext());
} catch (ServletException e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.sciFail"), e);
ok = false;
break;
}
}
// Configure and call application event listeners
if (ok) {
// 实例化监听器(时间监听器和生命周期监听器)
if (!listenerStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Check constraints for uncovered HTTP methods
// Needs to be after SCIs and listeners as they may programmatically
// change constraints
// 检测未覆盖的HTTP方法的安全约束
if (ok) {
checkConstraintsForUncoveredMethods(findConstraints());
}
try {
// Start manager
// 启动会话管理器
Manager manager = getManager();
if (manager instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
}
} catch(Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.managerFail"), e);
ok = false;
}
// Configure and call application filters
if (ok) {
// 实例化FilterConfig、Filter、并调用Filter.init初始化
if (!filterStart()) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.filterFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
if (ok) {
// 对于loadOnStartup>=0的Wrapper,调用wrapper.load()
// 该方法负责实例化Servlet,并调用Servlet.init进行初始化
if (!loadOnStartup(findChildren())){
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.servletFail"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Start ContainerBackgroundProcessor thread
// 启动后台定时处理线程
// 只有当backgroundProcessorDelay>0时启动:用于监护守护文件的变更等
// 当backgroundProcessorDelay<=0时,标识Context的后台任务由上级容器(Host)调度
super.threadStart();
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
// Set available status depending upon startup success
if (ok) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Starting completed");
}
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed", getName()));
}
startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
// 发布正在运行的JMX通知
if (ok && (this.getObjectName() != null)) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// The WebResources implementation caches references to JAR files. On
// some platforms these references may lock the JAR files. Since web
// application start is likely to have read from lots of JARs, trigger
// a clean-up now.
// 调用WebResourceRoot.gc()释放资源
getResources().gc();
// Reinitializing if something went wrong
if (!ok) {
setState(LifecycleState.FAILED);
// Send j2ee.object.failed notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.object.failed",
this.getObjectName(), sequenceNumber.getAndIncrement());
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
} else {
// 启动成功设置STARTED
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
}
}
11.ContextConfig.lifecycleEvent()
解析web.xml;创建Weapper(Servlet),Filter,ServletContextListerner等一系列Web容器相关对象,完成Web容器的初始化;
具体流程与代码注释已同步:
- 根据web.xml部署应用,Web应用中的配置优先级最高,其次Host级,最后为容器级;
- 应用程序注解配置 在实例化相关接口时可以进行JNDI资源依赖注入;
- 基于解析完的Web容器,检测Web应用部署描述中使用的安全角色名,当发现使用了未定义的角色时,提示警告同时将未定义的角色添加到Context安全角色列表中;
- 当Context需要进行安全认证,但是没有指定具体的Authenticator时,根据服务器配置西东创建默认实例;
// ContextConfig.class
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
// ...
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.CONFIGURE_START_EVENT)) {
configureStart();
}
// ...
}
protected synchronized void configureStart() {
// Called from StandardContext.start()
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("contextConfig.start"));
}
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(sm.getString("contextConfig.xmlSettings",
context.getName(),
Boolean.valueOf(context.getXmlValidation()),
Boolean.valueOf(context.getXmlNamespaceAware())));
}
// Web容器的初始化
// 根据web.xml部署应用,Web应用中的配置优先级最高,其次Host级,最后为容器级
webConfig();
// 关闭jsp启动报错
context.addServletContainerInitializer(new JasperInitializer(), null);
if (!context.getIgnoreAnnotations()) {
// 应用程序注解配置 在实例化相关接口时可以进行JNDI资源依赖注入
applicationAnnotationsConfig();
}
if (ok) {
// 基于解析完的Web容器,检测Web应用部署描述中使用的安全角色名
// 当发现使用了未定义的角色时,提示警告同时将未定义的角色添加到Context安全角色列表中
validateSecurityRoles();
}
// Configure an authenticator if we need one
if (ok) {
// 当Context需要进行安全认证,但是没有指定具体的Authenticator时,
// 根据服务器配置创建默认实例
authenticatorConfig();
}
// Dump the contents of this pipeline if requested
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Pipeline Configuration:");
Pipeline pipeline = context.getPipeline();
Valve valves[] = null;
if (pipeline != null) {
valves = pipeline.getValves();
}
if (valves != null) {
for (Valve valve : valves) {
log.debug(" " + valve.getClass().getName());
}
}
log.debug("======================");
}
// Make our application available if no problems were encountered
if (ok) {
context.setConfigured(true);
} else {
log.error(sm.getString("contextConfig.unavailable"));
context.setConfigured(false);
}
}
// 根据web.xml部署应用,Web应用中的配置优先级最高,其次Host级,最后为容器级
protected void webConfig() {
WebXmlParser webXmlParser = new WebXmlParser(context.getXmlNamespaceAware(),
context.getXmlValidation(), context.getXmlBlockExternal());
Set<WebXml> defaults = new HashSet<>();
defaults.add(getDefaultWebXmlFragment(webXmlParser));
// 解析默认配置,生成WebXml对象
WebXml webXml = createWebXml();
// Parse context level web.xml
// 解析Web应用的web.xml文件
InputSource contextWebXml = getContextWebXmlSource();
if (!webXmlParser.parseWebXml(contextWebXml, webXml, false)) {
ok = false;
}
ServletContext sContext = context.getServletContext();
// Ordering is important here
// Step 1. Identify all the JARs packaged with the application and those
// provided by the container. If any of the application JARs have a
// web-fragment.xml it will be parsed at this point. web-fragment.xml
// files are ignored for container provided JARs.
// 扫描Web应用所有的jar包,如果包含Web-fragment.xml,则解析文件并创建WebXml对象;
Map<String,WebXml> fragments = processJarsForWebFragments(webXml, webXmlParser);
// Step 2. Order the fragments.
// 按照Servlet规范将Webxml对象进行排序,并将排序结果对应的JAR文件名列表
// 设置到ServletContext属性中,属性名为orderedLibs,这决定了Filter等的执行顺序
Set<WebXml> orderedFragments = null;
orderedFragments =
WebXml.orderWebFragments(webXml, fragments, sContext);
// Step 3. Look for ServletContainerInitializer implementations
// 查找ServletContainerInitializer实现,并创建实例,查找范围分为两部分
// Web应用下的包:如果orderedLibs不为空,仅搜索该属性包含的包,否则搜索WEB-INF/lib下所有的包
// 容器包:搜索所有包(优先加载,因此配置生效优先级最低)
if (ok) {
// 初始化typeInitializerMap和initializerClassMap两个映射(用于后续注解检测)
// typeInitializerMap表示:类对应的ServletContainerInitializer集合
// initializerClassMap表示:每个ServletContainerInitializer对应的类的集合
processServletContainerInitializers();
}
if (!webXml.isMetadataComplete() || typeInitializerMap.size() > 0) {
// Steps 4 & 5.
// 处理WEB-INF/classes下的注解,以及JAR包内的注解
processClasses(webXml, orderedFragments);
}
if (!webXml.isMetadataComplete()) {
// Step 6. Merge web-fragment.xml files into the main web.xml
// file.
// 将所有的web-fragment.xml合并到主WebXml中
if (ok) {
ok = webXml.merge(orderedFragments);
}
// Step 7. Apply global defaults
// Have to merge defaults before JSP conversion since defaults
// provide JSP servlet definition.
// 默认WebXml合并到主WebXml
webXml.merge(defaults);
// Step 8. Convert explicitly mentioned jsps to servlets
// 配置JspServlet
if (ok) {
convertJsps(webXml);
}
// Step 9. Apply merged web.xml to Context
// 使用主WebXml配置当前StandardContext
if (ok) {
configureContext(webXml);
}
} else {
webXml.merge(defaults);
convertJsps(webXml);
configureContext(webXml);
}
if (context.getLogEffectiveWebXml()) {
log.info("web.xml:\n" + webXml.toXml());
}
// Always need to look for static resources
// Step 10. Look for static resources packaged in JARs
if (ok) {
// Spec does not define an order.
// Use ordered JARs followed by remaining JARs
Set<WebXml> resourceJars = new LinkedHashSet<>(orderedFragments);
for (WebXml fragment : fragments.values()) {
if (!resourceJars.contains(fragment)) {
resourceJars.add(fragment);
}
}
processResourceJARs(resourceJars);
// See also StandardContext.resourcesStart() for
// WEB-INF/classes/META-INF/resources configuration
}
// Step 11. Apply the ServletContainerInitializer config to the
// context
if (ok) {
for (Map.Entry<ServletContainerInitializer,
Set<Class<?>>> entry :
initializerClassMap.entrySet()) {
if (entry.getValue().isEmpty()) {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), null);
} else {
context.addServletContainerInitializer(
entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
}
}
12. StandardWrapper#LifecycleBase.start()
我们看,StandardWrapper需要先调用init()初始化再调用startInternal();
// StandardWrapper#LifecycleBase
public final synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
// ...
// 未初始化的组件进行初始化
if (state.equals(LifecycleState.NEW)) {
// 先调用
init();
}
try {
setStateInternal(LifecycleState.STARTING_PREP, null, false);
// 调用子类启动
startInternal();
// ...
} catch (Throwable t) {
handleSubClassException(t, "lifecycleBase.startFail", toString());
}
}
这里初始化就是创建了创建单个线程的线程池,并初始化MBean;
// StandardWrapper#ContainerBase.initInternal()
@Override
protected void initInternal() throws LifecycleException {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> startStopQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
// 创建单个线程的线程池,最大存活时间10s,可超时
startStopExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
getStartStopThreadsInternal(),
getStartStopThreadsInternal(), 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
startStopQueue,
new StartStopThreadFactory(getName() + "-startStop-"));
startStopExecutor.allowCoreThreadTimeOut(true);
super.initInternal();
}
start()这里,由于wrapper是最底层容器了,所以不会再有子容器,启动完成;
// StandardWrapper.class
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Send j2ee.state.starting notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification = new Notification("j2ee.state.starting",
this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
// Start up this component
// 调用父类容器的方法ContainerBase
super.startInternal();
setAvailable(0L);
// Send j2ee.state.running notification
if (this.getObjectName() != null) {
Notification notification =
new Notification("j2ee.state.running", this.getObjectName(),
sequenceNumber++);
broadcaster.sendNotification(notification);
}
}
// ContainerBase
protected synchronized void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// Start our subordinate components, if any
logger = null;
getLogger();
// 集群配置启动
Cluster cluster = getClusterInternal();
if (cluster instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
}
// 安全域启动
Realm realm = getRealmInternal();
if (realm instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
// 这里就没有子容器了最底层容器了
Container children[] = findChildren();
List<Future<Void>> results = new ArrayList<>();
for (Container child : children) {
results.add(startStopExecutor.submit(new StartChild(child)));
}
MultiThrowable multiThrowable = null;
for (Future<Void> result : results) {
try {
result.get();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"), e);
if (multiThrowable == null) {
multiThrowable = new MultiThrowable();
}
multiThrowable.add(e);
}
}
if (multiThrowable != null) {
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("containerBase.threadedStartFailed"),
multiThrowable.getThrowable());
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
// 启动管道
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle) {
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our thread
threadStart();
}
13. StandardWrapper.load()
Tomcat在web.xml中默认定义了两个Servlet:DefaultServlet,JspServlet,这两个默认下会存在于所有Web应用容器中;
当load-on-startup>=0时,调用StandardWrapper.load(),加载Servlet;其流程如下:
- 创建Servlet实例,如果添加了JNDI资源注解,将进行依赖注入;
- 读取MultipartConfig配置,以用于multipart/form-data请求处理,包含临时文件存储路径、上传文件最大字节数、请求最大字节数、文件大小阈值;
- 读取ServletSecurity()注解配置,添加Servlet安全;
- 调用servlet.init()进行Servlet初始化;
// StandardWrapper
public synchronized void load() throws ServletException {
// 加载Server
instance = loadServlet();
if (!instanceInitialized) {
// 加载Servlet
initServlet(instance);
}
if (isJspServlet) {
// ...加载JSP配置
}
}
// 创建Servlet实例load()
public synchronized Servlet loadServlet() throws ServletException {
// 默认org.apache.catalina.servlets.DefaultServlet
Servlet servlet;
try {
long t1=System.currentTimeMillis();
InstanceManager instanceManager = ((StandardContext)getParent()).getInstanceManager();
try {
// 创建Servlet实例,如果添加了JNDI资源注解,将进行依赖注入;
servlet = (Servlet) instanceManager.newInstance(servletClass);
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
// 读取MultipartConfig配置,以用于multipart/form-data请求处理,
// 包含临时文件存储路径、上传文件最大字节数、请求最大字节数、文件大小阈值;
if (multipartConfigElement == null) {
MultipartConfig annotation =
servlet.getClass().getAnnotation(MultipartConfig.class);
if (annotation != null) {
multipartConfigElement =
new MultipartConfigElement(annotation);
}
}
// Special handling for ContainerServlet instances
// Note: The InstanceManager checks if the application is permitted
// to load ContainerServlets
if (servlet instanceof ContainerServlet) {
((ContainerServlet) servlet).setWrapper(this);
}
classLoadTime=(int) (System.currentTimeMillis() -t1);
if (servlet instanceof SingleThreadModel) {
if (instancePool == null) {
instancePool = new Stack<>();
}
singleThreadModel = true;
}
// 调用servlet.init()进行Servlet初始化;
initServlet(servlet);
fireContainerEvent("load", this);
loadTime=System.currentTimeMillis() -t1;
} finally {
if (swallowOutput) {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
if (getServletContext() != null) {
getServletContext().log(log);
} else {
out.println(log);
}
}
}
}
return servlet;
}
// 调用servlet.init()进行Servlet初始化;
private synchronized void initServlet(Servlet servlet)
throws ServletException {
// Call the initialization method of this servlet
try {
if( Globals.IS_SECURITY_ENABLED) {
boolean success = false;
try {
Object[] args = new Object[] { facade };
SecurityUtil.doAsPrivilege("init",
servlet,
classType,
args);
success = true;
} finally {
if (!success) {
SecurityUtil.remove(servlet);
}
}
} else {
servlet.init(facade);
}
instanceInitialized = true;
} catch (UnavailableException f) {
unavailable(f);
throw f;
} catch (ServletException f) {
// If the servlet wanted to be unavailable it would have
// said so, so do not call unavailable(null).
throw f;
} catch (Throwable f) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(f);
getServletContext().log(sm.getString("standardWrapper.initException", getName()), f);
// If the servlet wanted to be unavailable it would have
// said so, so do not call unavailable(null).
throw new ServletException
(sm.getString("standardWrapper.initException", getName()), f);
}
}
14. HostConfig.lifecycleEvent()
当HostConfig收到Lifecycle.START_EVENT事件,就去调用start()方法;start()内部调用deployApps()方法,这里才是实际创建context的地方;
简述deployApps()的实现目标:通过Context描述文件部署,Web目录部署,War包部署;
-
Context描述文件部署
Tomcat支持通过一个独立的Context的xml文件配置启动Web应用;该配置文件的位置由Host的xmlBase属性指定。如果未指定,默认为$CATALINA_BASE/conf/< Engine名称>/< Host名称>,即默认路径为Tomcat目录下
D:\tomcat8.5\conf\Catalina\localhost;<Context docBase="test/testMyApp" path="/testMyApp" reloadable="false"> <WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xmlWatchedResource> Context>上述配置中docBase指向web应用的物理路径,path指向请求路径后缀;
-
Web目录部署
以目录的形式发布并部署Web应用;将所有资源,jar包,描述文件(WEB-INF/web.xml)的目录复制到Host指定的appBase(就是
D:\tomcat8.5\webapps)目录下即可完成部署; -
War包部署
tomcat会对war包进行处理,和Web目录部署类似,在Host指定的appBase(就是
D:\tomcat8.5\webapps)目录下的所有符合条件的WAR(不在deployIgnore的过滤规则,文件名不为META-INF和WEB-INF,以war作为扩展名的文件),由线程池完成部署;
public class HostConfig implements LifecycleListener {
// 事件监听处理逻辑
public void lifecycleEvent(LifecycleEvent event) {
// ...
// Process the event that has occurred
if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT)) {
check();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.BEFORE_START_EVENT)) {
beforeStart();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.START_EVENT)) {
// 看这里
start();
} else if (event.getType().equals(Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT)) {
stop();
}
}
// 启动
public void start() {
// .... host的deployOnStartup属性为true
if (host.getDeployOnStartup()) {
deployApps();
}
}
// 三种创建context的途径
protected void deployApps() {
File appBase = host.getAppBaseFile();
File configBase = host.getConfigBaseFile();
String[] filteredAppPaths = filterAppPaths(appBase.list());
// Deploy XML descriptors from configBase
// Context描述文件部署
deployDescriptors(configBase, configBase.list());
// Deploy WARs
deployWARs(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
// Deploy expanded folders
deployDirectories(appBase, filteredAppPaths);
}
}
15. Connector.startInternal()
这里面是协议处理器protocolHandler.start();见方法16;
// Connector.class
protected final ProtocolHandler protocolHandler;
@Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
// ...
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
try {
protocolHandler.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
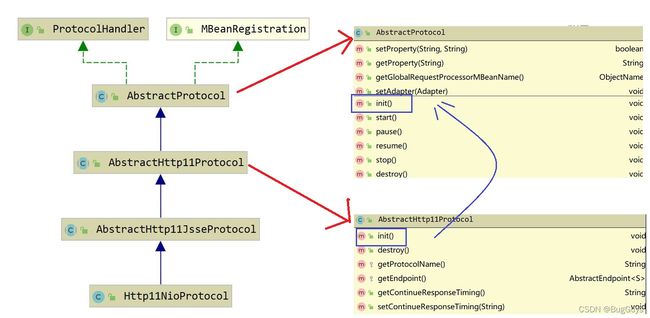
16. Http11NioProtocol.start()
我们再来看看这个处理器的类图;
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" />
protocolHandler只是个接口,根据我们的配置,其实现类是Http11NioProtocol;Http11NioProtocol.start()实际上是调用父类AbstractProtocol.start();
// AbstractProtocol
public void start() throws Exception {
if (getLog().isInfoEnabled()) {
getLog().info(sm.getString("abstractProtocolHandler.start", getName()));
}
// 监听器启动
endpoint.start();
// Start timeout thread
asyncTimeout = new AsyncTimeout();
Thread timeoutThread = new Thread(asyncTimeout, getNameInternal() + "-AsyncTimeout");
int priority = endpoint.getThreadPriority();
if (priority < Thread.MIN_PRIORITY || priority > Thread.MAX_PRIORITY) {
priority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY;
}
timeoutThread.setPriority(priority);
timeoutThread.setDaemon(true);
timeoutThread.start();
}
AbstractProtocol.start()中启动了NioEndpoint,这里是调用了父类方法AbstractEndpoint.start();
这里的执行流程:
- 申请128个缓存池nioChannels,在Bytebuffer缓存中,每个通道持有一组缓冲区(两个,除了SSL持有四个);
- 构造线程池处理SocketProcessor,对socket进行读写封装成request对象然后做业务处理;
- 初始化poller默认是两个poller,主要循环扫描PollerEvent队列是否存在待处理请求;
- 启动Acceptor 默认使用一单线程处理连接;
// NioEndpoint#AbstractEndpoint
public final void start() throws Exception {
// 在初始化的时候已经调用过bind(),bindState已经变成BOUND_ON_INIT状态
if (bindState == BindState.UNBOUND) {
bind();
bindState = BindState.BOUND_ON_START;
}
// 直接执行这里
startInternal();
}
// NioEndpoint
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
// 申请nioChannel 默认128个,申请了系统内存io读写直接使用系统内存的效率比堆内存好快很多
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
// Create worker collection
// 构造线程池处理SocketProcessor,对socket进行读写封装成request对象然后做业务处理
if (getExecutor() == null) {
createExecutor();
}
initializeConnectionLatch();
// Start poller threads
// 初始化poller默认是两个poller
// poller主要循环扫描PollerEvent队列是否存在待处理请求
// 如果存在PollerEvent待处理,进行请求解析封装
// 启动Executor线程进行请求读处理
pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()];
for (int i=0; i<pollers.length; i++) {
pollers[i] = new Poller();
Thread pollerThread = new Thread(pollers[i], getName() + "-ClientPoller-"+i);
pollerThread.setPriority(threadPriority);
pollerThread.setDaemon(true);
pollerThread.start();
}
//启动Acceptor 默认使用一单线程处理连接
startAcceptorThreads();
}
}
总结
经过初始化和启动后,Service去启动连接(Connector)和容器(Container);连接这里根据配置文件创建socket并进行监听连接处理,见方法15;容器这里,关于Context的创建(Web服务的加载)有两种渠道,第一种就是Host根据配置文件创建Context,第二种就是通过HostConfig监听器去创建Context(Context描述文件部署,Web目录部署,War包部署)可以见方法14;Context创建启动后(见方法10),我们根据配置load-on-startup>=0去初始化Servlet(见方法13),Servlet的创建就是通过反射去实例化相应的实现类;
以上就是启动的全部流程,推荐阅读《Tomcat架构解析-刘光瑞》第三章,下一篇我们将分析Connector和Container之间的关系——请求处理;