Java 优化:读取配置文件 “万能方式“ 跨平台,动态获取文件的绝对路径
Java 优化:读取配置文件 “万能方式” 跨平台,动态获取文件的绝对路径
每博一文案
往事不会像烟雾似的飘散,将永远像铅一般沉重地浇铸在心灵的深处。
不过,日常生活的纷繁不会让人专注地沉湎于自己的痛苦
不幸,即使人的心灵伤痕累累,也还得要去为现实中的生存和发展而挣扎。
—————— 《平凡世界》
每个人的生活同样也是一个世界,即使最平凡的人,也得要为他那个世界的存在而战斗。从这个意义
上说,在这些平凡的世界里,也没有一天是平静的。
—————— 《平凡世界》
文章目录
- Java 优化:读取配置文件 "万能方式" 跨平台,动态获取文件的绝对路径
-
- 每博一文案
- 1. 优化方式一:返回一个文件的绝对路径
-
- 1.1 情况一
- 1.2 情况二
- 2. 优化方式二:返回一个 InputStream 字节输入流
- 3. 优化方式三:java.util 包下提供了一个资源绑定器
- 4. 总结:
- 5. 最后:
我们知道在 Java 中读取一些配置文件信息,是在开发中十分常用的要求。
例如:这里我们使用 JDBC 实例:连接MySQL 数据库,读取连接数据库的 用户名,密码 。
如下是一个名为 jdbc.properties 的配置文件信息,以及存在目录
package blogs.blogs8;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream f = null;
try {
// 创建字节输入流对象
// 在IDEA 中的默认相对路径是在 src 同级目录下的
f = new FileInputStream("src/blogs/blogs8/jdbc.properties");
// 创建Map集合中的 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(f);
// 通过 key 读取对应的键值对
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
System.out.println(user);
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(password);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭IO资源
if(f == null) {
try {
f.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
说明:
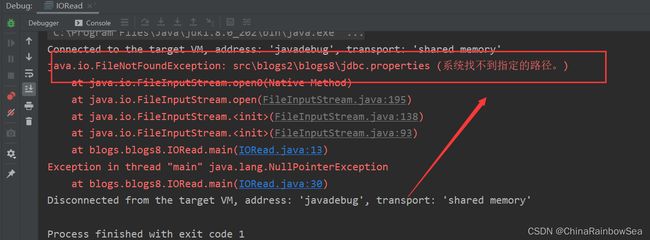
上述的读取文件的方式,我们可以看到是 “完全没有问题的” 可以读取到对应的配置信息,但是存在一个缺点:就是移除性差。src 中是在 IDEA 这个编译器中体现的,如果是在其它的编译器中运行的时候,很大的可能会报错,原因是:这里我们使用的相对路径是,在 IDEA中的,IDEA 中的默认相对路径是 在 project 下的也就是 src 的同级目录。但是其它的系统,或者编译器就可能不是这个和 IDEA 中默认相对路径了。运行程序时,就有可能会报错:如下:找不到指定的文件。
上述这种方式:如果我们不写相对路径,而是写绝对路径的话,也是存在一个问题的。那就是因为该绝对路径是写死了的,不是动态获取的,该路径在 Windows 操作系统中是存在盘符的,所以写绝对路径的时候是需要带上盘符(E盘,D盘的),但是如果该程序是运行在其他操作系统中的话,比如 Linux 操作系统中是没有盘符的说法的。所以就会出问题。无法跨平台。
1. 优化方式一:返回一个文件的绝对路径
接下来说一种比较通用的一种路径:即使代码换位置了,这样的代码编写的方式仍然是通用的。因为该文件的路径是动态获取的。
在Windows中的话,就以该系统的文件规则,动态获取到的绝对路径是带盘符的,而 Linux系统中就以该系统的文件规则,获取到的绝对路径是不带盘符的。 这就可以跨平台了。
注意: 使用该方式的前提是:所读取的文件必须是在 类路径 下才行。如果不是在类路径下,运行程序时是会报错:系统找不到指定的路径。
什么是类路径 ?
类路径也是一种特殊的相对路径,只不过它相对的是class文件。在 IDEA 中的类路径是在 src 目录下的。重点记住它
该方式的核心代码:
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("db.properties").getPath();
/*
解释:
Thread.currentThread() 当前线程对象
getContextClassLoader() 是线程对象的方法,可以获取到当前线程的类加载对象
getResource() 获取资源:这是类加载器对象的方法,当前线程的类加载器默认从类的根路径下加载资源。
getPath() 获取当文件的绝对路径
*/
1.1 情况一
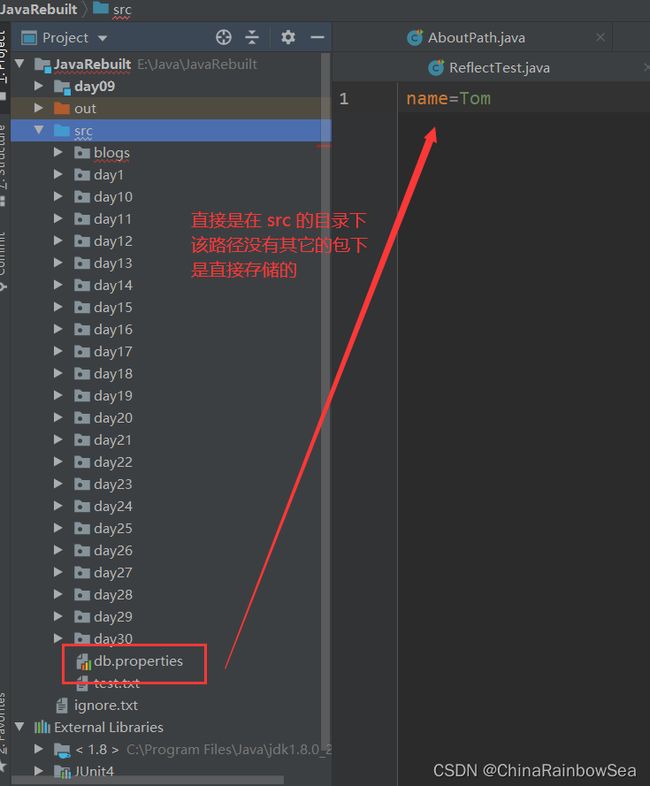
所读取的文件是直接存放在 src 的目录下的,该文件的并没有其它的的包。如下图所示:可以直接写文件名 + 文件名的后缀即可。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("db.properties").getPath();
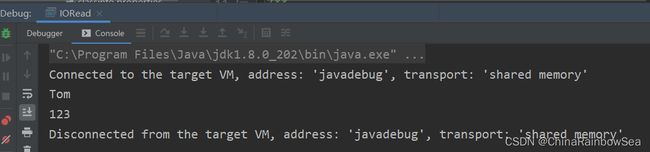
System.out.println(path); // 返回该文件的绝对路径:
}
}
通过该方式获取到指定文件的绝对路径,再将该绝对路径,作为参数,创建FileInputStream字节输入流对象
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream f = null;
try {
// 获取到该配置文件的的绝对路径
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("db.properties").getPath();
// 通过该获取的文件的绝对路径创建 字节输入流对象
f = new FileInputStream(path);
// 创建Map集合中的 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(f);
// 通过 key 读取对应的键值对
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
System.out.println(user);
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(password);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭IO资源
if (f != null) {
try {
f.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
也是可以读取到文件中是在 src 目录下。
1.2 情况二
当所读取的文件,是在 src 目录下,但是该 src 目录下还有其他的包(目录),则不可以直接写 “文件名+ 文件后缀名”了,而是需要写明该 src 包(目录)下的 相对路径:如下图所示的文件:该路径名应该是:blogs/blogs8/jdbc.properties
举例:
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream f = null;
try {
// 获取到该配置文件的的绝对路径,如下src目录下还有目录(包),需要指定 src目录下/包下的哪个文件。
String path = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource("blogs/blogs8/jdbc.properties").getPath();
// 通过该获取的文件的绝对路径创建 字节输入流对象
f = new FileInputStream(path);
// 创建Map集合中的 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(f);
// 通过 key 读取对应的键值对
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
System.out.println(user);
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(password);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭IO资源
if (f != null) {
try {
f.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2. 优化方式二:返回一个 InputStream 字节输入流
上述方式一:我们需要通过 :new 一个 FileInputStream 字节输入流对象的方式,这里我们直接通过指定的文件名的,直接返回一个 InputStream 字节输入流 ,不需要 new 。
同样的:该读取的文件必须是在类路径下才行,这里的IDEA的类路径是 src 目录下
核心代码如下:
// 直接以流的形式返回。
InputStream resourceAsStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().
getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
举例:
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Properties;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 直接在 src目录下没有包含任何子目录,可以直接写文件名+ 后缀,而如果有子目录,需要指明子目录下的文件名+后缀名
InputStream inputStream = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
// 创建 Properties 集合对象,通过流获取指定配置文件中的键值对信息
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
System.out.println(user);
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
System.out.println(password);
// 关闭IO资源
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3. 优化方式三:java.util 包下提供了一个资源绑定器
上述两个方式可以获取到任意文件的信息。
但是以下这个方式三:就只能获取到 类路径下的以 .properties 后缀的配置文件信息了。
java.util 包下提供了一个资源绑定器,便于获取属性.properties 配置文件中的内容。
该资源绑定器:只能绑定 xxx.properties 配置文件 ,并且这个文件必须在 类路径下,这里的 IDEA 是 src 目录下。
并且在写路径的时候,路径后面的扩展名不能写,写了会报错: ``。因为既然只能读取 properteis 后缀的文件,那就不用再多余的写文件后缀名了。
如果在 src 目录下的子目录中的文件,需要指明是 src 下的哪个子目录下的文件,同样不要写文件后缀名,不然报错。
举例:
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class IORead {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourceBundle resourceBundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("db");
String user = resourceBundle.getString("user");
System.out.println(user);
String password = resourceBundle.getString("password");
System.out.println(password);
}
}
4. 总结:
- 原始的方式:写相对路径的话,无法跨编译器;因为不同的编译器默认相对的路径是不同的。写绝对路径的话,无法跨平台,因为不同操作系统的文件规则是不一样的,比如 Windows系统中的绝对路径是带盘符(D盘,C盘),Linux 系统中的文件规则是不带盘符的。当在J Windows 操作系统中编写的绝对路径的Java程序,移植到到 Linux 操作系统中就会报错。
- 静态获取的绝对路径 和 动态获取绝对路径。
- 上述的三种优化方式,都是动态获取绝对路径的,但是都是基于 类路径下的文件才行的,不同所读取的文件不在 类路径下 是无法动态获取到对应绝对路径的。
- 上述 :优化方式1,优化方式2 可以动态获取到 类路径下的任意文件信息。但是 优化方式三:只能获取到 类路径下的以
.properties后缀的配置文件信息了。 - 注意:优化方式三:不可以写文件后缀名,直接写文件名就可以了。因为资源绑定器,就只能绑定
xxx.properties配置文件 ,并且这个文件必须在 类路径下。 - 如果类路径下,比如:IDEA 中的 src 目录就是类路径,文件是直接在 src 类路径下没有包含子目录的话,可以直接写
文件名+文件后缀名,如果文件是在 src 目录下含有的子目录下,则需要指明 类路径 src 下的哪个子目录的文件。
5. 最后:
限于自身水平,其中存在的错误,希望大家给予指教,韩信点兵——多多益善 。谢谢大家,后会有期 ,江湖再见 !!!