使用nginx反向代理解决请求接口跨域问题(前端)
首先,你既然想利用nginx去处理跨域了,那下载启动nginx,这种就不多说了,如果有对这块不明白的小伙伴,可以查看我的上一篇博客。
我们现在来模拟跨域。
先用node启一个服务:
let express = require('express');
let app = express();
app.get('/user', (req, res) => {
res.json({name: '旺柴'});
});
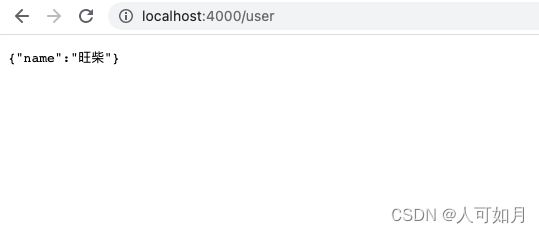
app.listen(4000);
//启动,node index.js
//输入 http://localhost:4000/user浏览器输入http://localhost:4000/user,就可以拿到数据了
接下来,写一个测试页面,我这边是用vue+axios发送的请求
安装 axios npm install axios
main.js中引入,并注册到vue的原型上,作为一个全局变量使用
import axios from 'axios'
Vue.prototype.$http = axios页面上发送请求
this.$http({
method: "get",
url: "http://localhost:4000/user", //这边先直接请求接口
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res, "res");
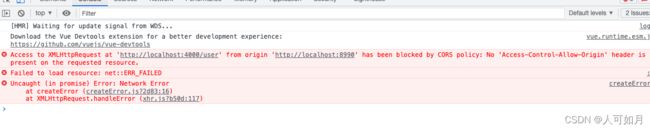
});然后启动项目,可以看到浏览器提示跨域
由于端口号不同,所以存在跨域问题
接下来,我们将本地项目部署在nginx上,利用nginx的反向代理来解决我们的跨域问题
打包之前,我们先将请求的接口地址改成同源的地址,也就是我们访问项目的地址
this.$http({
method: "get",
url: "http://localhost:8989/api/user", //真正的接口地址为 http://localhost:4000/user
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res, "res");
});将打包好的代码放到nginx相应的目录(这块不懂的小伙伴可以去看我上篇博客,里面有详细地址和说明)
打开nginx.conf 配置文件
#可以新添加一个server
server {
listen 8989;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html/dist;
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:4000/; //代理到真正的服务器地址
}
}
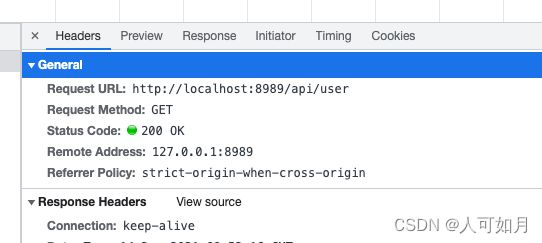
浏览器访问 http://localhost:8989/#/
成功拿到数据,之前的报错也没有了!
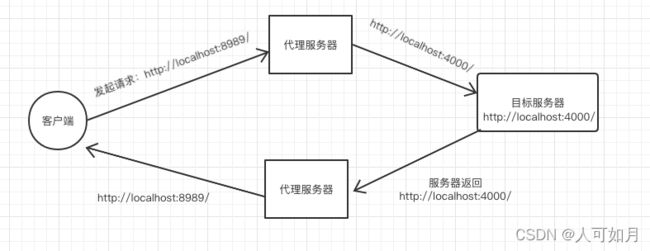
最后附上nginx反向代理原理示意图
vue项目里面本地开发的时候,我们也利用过代理解决跨域问题
this.$http({
method: "get",
url: "http://localhost:8989/api/user", //接口地址为 http://localhost:4000/user
}).then((res) => {
console.log(res, "res");
});vue.config.js
devServer: {
port: 8989, // 此处修改你想要的端口号,
proxy:{
'/api':{ //遇到有api的请求,代理服务器就会转发到真的的服务器上
target:'http://localhost:4000/', //后台接口域名,真正的服务器地址
changeOrigin:true,
pathRewrite:{
'^/api':'/' //路径重写,其实就是去掉我们上面加的api,因为我们实际接口中没有api这个路径
}
}
}
},