手撕代码:VGG13实战CIFAR数据集,附:卷积神经网络CNN可视化学习
CNN基础实践
- VGG13实战
- 卷积神经网络CNN可视化学习
VGG13实战
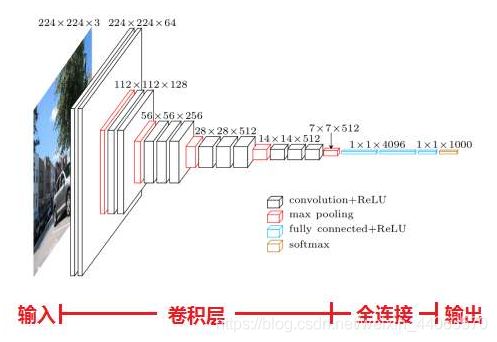
VGG模型是2014年ILSVRC竞赛的第二名,第一名是GoogLeNet。但是VGG模型在多个迁移学习任务中的表现要优于googLeNet。而且,从图像中提取CNN特征,VGG模型是首选算法。
“VGG”代表了牛津大学的Oxford Visual Geometry Group
特点:
- 小卷积核:作者将卷积核全部替换为3x3(极少用了1x1);
- 小池化核:相比AlexNet的3x3的池化核,VGG全部为2x2的池化核;
- 层数更深特征图更宽:基于前两点外,由于卷积核专注于扩大通道数、池化专注于缩小宽和高,使得模型架构上更深更宽的同时,计算量的增加放缓;
- 全连接转卷积:网络测试阶段将训练阶段的三个全连接替换为三个卷积,测试重用训练时的参数,使得测试得到的全卷积网络因为没有全连接的限制,因而可以接收任意宽或高为的输入。
引自百度百科:https://baike.baidu.com/item/VGG%20模型/22689655?fr=aladdin
代码如下
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, optimizers, datasets, Sequential
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2'
tf.random.set_seed(2345)
conv_layers = [ # 5 units of conv + max pooling
# unit 1 channel =64
layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Conv2D(64, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='same'),
# unit 2 channel =128
layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Conv2D(128, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='same'),
# unit 3 channel =256
layers.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Conv2D(256, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='same'),
# unit 4 channel =512
layers.Conv2D(512, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Conv2D(512, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='same'),
# unit 5 channel =512
layers.Conv2D(512, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Conv2D(512, kernel_size=[3, 3], padding="same", activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.MaxPool2D(pool_size=[2, 2], strides=2, padding='same')
]
def preprocess(x, y):
# [0~1]
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
return x,y
(x,y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.cifar100.load_data()
y = tf.squeeze(y, axis=1) # 根据sample输出的格式squeeze多余维度
y_test = tf.squeeze(y_test, axis=1)
print(x.shape, y.shape, x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y))
train_db = train_db.shuffle(1000).map(preprocess).batch(128)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test))
test_db = test_db.map(preprocess).batch(64)
# 测试sample的形状:(batchsize, h, w, channel)
sample = next(iter(train_db))
print('sample:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape,
tf.reduce_min(sample[0]), tf.reduce_max(sample[0]))
def main():
conv_net = Sequential(conv_layers)
# # 查看输出格式 [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 1, 1, 512]
# conv_net.build(input_shape=[None,32,32,3])
# x = tf.random.normal([4,32,32,3])
# out = conv_net(x)
# print(out.shape)
# 全连接层
fc_net = Sequential([
layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(100, activation=None),
])
# 将网络分为两部分,第一部分的输出即位为第二部分的输入
conv_net.build(input_shape=[None, 32, 32, 3])
fc_net.build(input_shape=[None, 512])
optimizer = optimizers.Adam(lr=1e-4)
# 网络两部分的参数放在一起 “+”运作原理:[1, 2] + [3, 4] => [1, 2, 3, 4]
variables = conv_net.trainable_variables + fc_net.trainable_variables
for epoch in range(50):
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(train_db):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# [b, 32, 32, 3] => [b, 1, 1, 512]
out = conv_net(x)
# flatten, => [b, 512] 打平送入全连接层
out = tf.reshape(out, [-1, 512])
# [b, 512] => [b, 100]
logits = fc_net(out)
# [b] => [b, 100]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=100)
# compute loss
loss = tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(y_onehot, logits, from_logits=True)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, variables) # Variables处理在line83
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, variables))
if step %100 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss))
# 测试部分
total_num = 0
total_correct = 0
for x,y in test_db:
out = conv_net(x)
out = tf.reshape(out, [-1, 512])
logits = fc_net(out)
prob = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=1)
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
total_correct += int(correct)
acc = total_correct / total_num
print(epoch, 'acc:', acc)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
卷积神经网络CNN可视化学习
此外,分享一个可视化CNN的网站,用chrome打开哟!
https://poloclub.github.io/cnn-explainer/
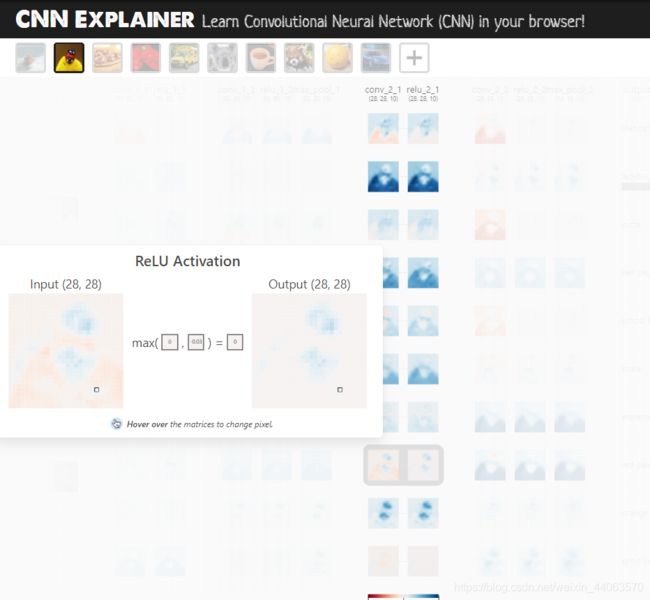
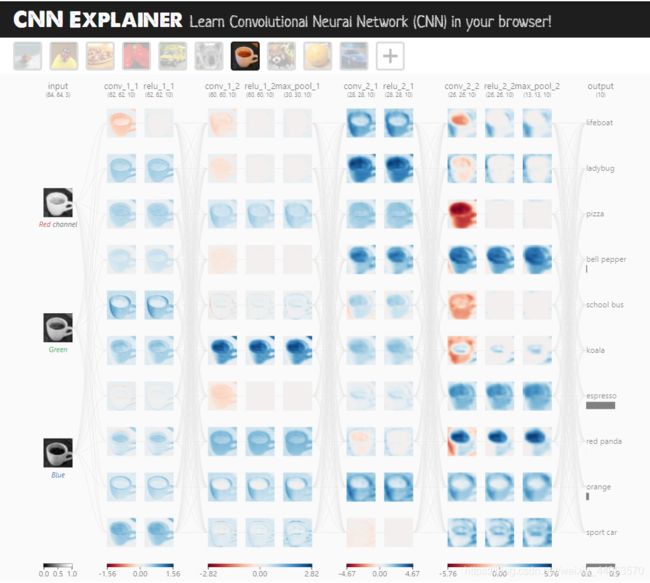 点击每个环节可以查看具体的过程的可视化,太牛逼了!
点击每个环节可以查看具体的过程的可视化,太牛逼了!
卷积层

ReLU激活
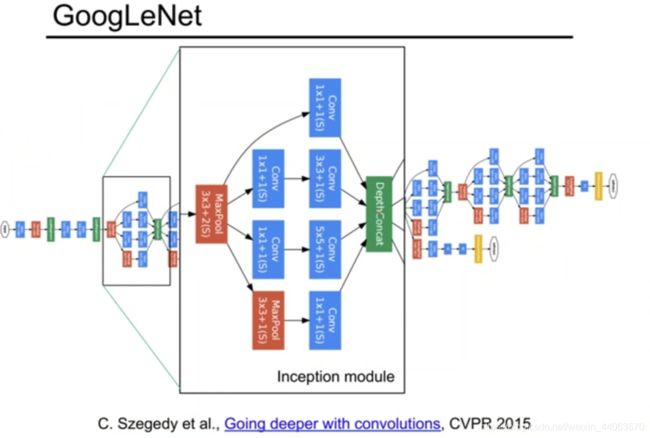
#GoogLeNet (Inception)简述
作为和VGG同时代的网络,在这里也放一张结构图以作对比。
GoogLeNet有Inception V1~V4四个版本的进化,
后来还融入SelectiveSearch等技术实现了目标检测任务,和FCN等技术融合实现图像分割等…
等待更进一步的学习再来补充吧。