【SpringMVC】 一文掌握 》》》 @RequestMapping注解
![]()
个人简介:Java领域新星创作者;阿里云技术博主、星级博主、专家博主;正在Java学习的路上摸爬滚打,记录学习的过程~
个人主页:.29.的博客
学习社区:进去逛一逛~
@RequestMapping注解
- 一、SpringMVC环境准备
-
- 1.`相关Maven依赖`:
- 2.`配置web.xml文件`:
- 3.`创建请求控制器`:
- 4.`创建SpringMVC的XML配置文件`:
- 二、 @RequestMapping注解 功能
-
- 功能案例
- 功能小结
- 三、@RequestMapping注解 位置说明
- 四、@RequestMapping注解 属性
-
- ⚪value属性
- ⚪method属性
- ⚪params属性
- ⚪headers属性
- 五、ant风格的路径
- 六、路径中占位符的使用
一、SpringMVC环境准备
1.相关Maven依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvcartifactId>
<version>5.3.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logbackgroupId>
<artifactId>logback-classicartifactId>
<version>1.2.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servletgroupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-apiartifactId>
<version>3.1.0version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleafgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
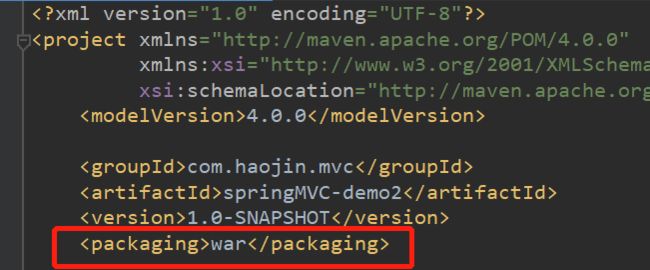
同时记得将打包方式改为war包(web工程需要的方式):
2.配置web.xml文件:
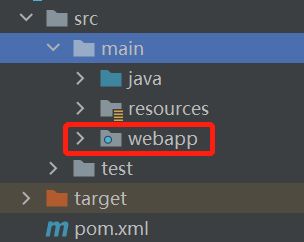
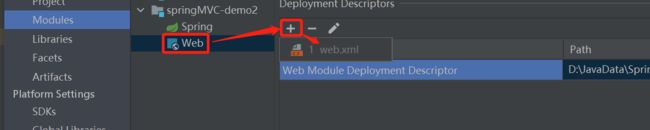
项目结构中创建web.xml配置文件:
(这里创建时需要注意目录是否正确 – src\main\webapp\WEB-INF\web.xml)
配置web.xml文件:
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:springMVC.xmlparam-value>
init-param>
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
servlet-mapping>
web-app>
3.创建请求控制器:
由于前端控制器对浏览器发送的请求进行了统一的处理,但是具体的请求有不同的处理过程,因此需要创建处理具体请求的类,即请求控制器
请求控制器中每一个处理请求的方法成为控制器方法
因为SpringMVC的控制器由一个POJO(普通的Java类)担任,因此需要通过@Controller注解将其标识为一个控制层组件,交给Spring的IoC容器管理,此时SpringMVC才能够识别控制器的存在
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-04 17:17
*/
@Controller
public class RequestMappingController {
}
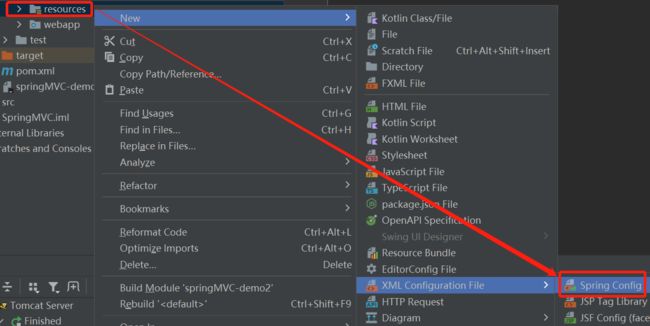
4.创建SpringMVC的XML配置文件:
XML配置文件内容:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.haojin.java.controller"/>
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
bean>
property>
bean>
property>
bean>
beans>
二、 @RequestMapping注解 功能
从注解名称上我们可以看到,@RequestMapping注解的作用就是将请求和处理请求的控制器方法关联起来,建立映射关系。
SpringMVC 接收到指定的请求,就会来找到在映射关系中对应的控制器方法来处理这个请求。
功能案例
实现对index.html页面的访问 + 通过超链接跳转指定页面:
1.index.html页面:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>这里是.29.的主页h1>
<a th:href="@{/target}">跳转进入专栏a>
body>
html>
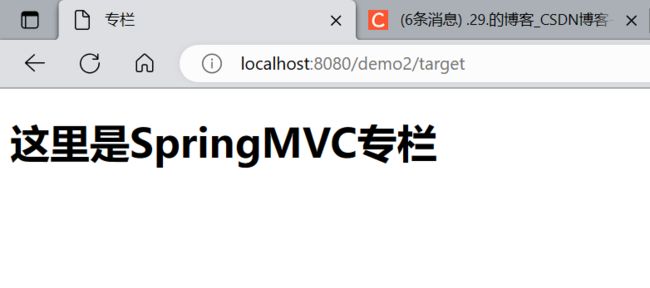
2.指定页面target.html:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>专栏title>
head>
<body>
<h1>这里是SpringMVC专栏h1>
body>
html>
3.请求控制器中创建处理请求的方法:
- @RequestMapping注解:处理请求和控制器方法之间的映射关系
- @RequestMapping注解的value属性可以通过请求地址匹配请求,/表示的当前工程的上下文路径
- localhost:8080/springMVC/
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-04 16:07
*/
@Controller
public class testController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping(value="/target")
public String target(){
return "target";
}
}
4.效果:
功能小结
浏览器发送请求,若请求地址符合前端控制器的url-pattern,该请求就会被前端控制器DispatcherServlet处理。前端控制器会读取SpringMVC的核心配置文件,通过扫描组件找到控制器,将请求地址和控制器中@RequestMapping注解的value属性值进行匹配,若匹配成功,该注解所标识的控制器方法就是处理请求的方法。处理请求的方法需要返回一个字符串类型的视图名称,该视图名称会被视图解析器解析,加上前缀和后缀组成视图的路径,通过Thymeleaf对视图进行渲染,最终转发到视图所对应页面
三、@RequestMapping注解 位置说明
-
@RequestMapping标识一个类:设置映射请求的请求路径的初始信息
-
@RequestMapping标识一个方法:设置映射请求请求路径的具体信息
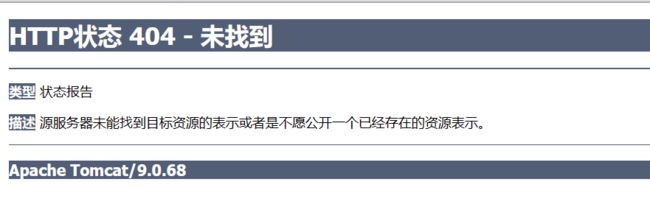
当我们同时使用@RequestMapping标识请求控制类和其中的请求方法,但是请求路径只设置了具体信息,而不包含初始信息时,就会出现找不到资源的错误。
请求控制类:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-04 17:17
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/one") //在类上标识@RequestMapping注解
public class RequestMappingController {
//当前请求路径应当是:/one/testRequestMapping
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRequestMapping")
public String success(){
return "success";
}
}
访问的主页面:
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>这里是.29.的主页h1>
<a th:href="@{/target}">跳转进入专栏(测试@RequestMapping 功能)a> <br>
<a th:href="@{/testRequestMapping}">测试@RequestMapping 标识位置a> <br>
body>
html>
就会发现找不到对应资源:
四、@RequestMapping注解 属性
⚪value属性
-
@RequestMapping注解的value属性通过请求的请求地址 匹配请求映射;
-
@RequestMapping注解的value属性是一个字符串类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求;
-
@RequestMapping注解的value属性必须设置,至少通过请求地址匹配请求映射;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-04 17:17
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/one") //在类上标识@RequestMapping注解
public class RequestMappingController {
//当前请求路径应当是:/one/testRequestMapping
@RequestMapping(value = "/testRequestMapping")
public String success(){
return "success";
}
//value属性可以匹配多个请求地址所对应的请求,其中一个请求路径映射匹配即可
@RequestMapping(
value = {"/test","/test2","test3"},
)
public String success2(){
return "success";
}
}
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>主页title>
head>
<body>
<h1>这里是.29.的主页h1>
<a th:href="@{/target}">跳转进入专栏(测试@RequestMapping 功能)a> <br>
<a th:href="@{/one/testRequestMapping}">测试@RequestMapping 标识位置a> <br>
<a th:href="@{/one/test}">测试@RequestMapping value属性a> <br>
body>
html>
⚪method属性
-
@RequestMapping注解的method属性通过请求的请求方式(get或post)匹配请求映射;
-
@RequestMapping注解的method属性是一个RequestMethod类型的数组,表示该请求映射能够匹配多种请求方式的请求;
-
若当前请求的请求地址满足请求映射的value属性,但是请求方式不满足method属性,则浏览器报错405:Request method ‘POST’ not supported
使用方式:
@RequestMapping(
value = "请求路径1",
method = RequestMethod.GET
)
@RequestMapping(
value = {"请求路径1","请求路径2"},
method = {RequestMethod.GET,RequestMethod.POST}
)
注意:
1、对于处理指定请求方式的控制器方法,SpringMVC中提供了@RequestMapping的派生注解
处理get请求的映射–>@GetMapping
处理post请求的映射–>@PostMapping
处理put请求的映射–>@PutMapping
处理delete请求的映射–>@DeleteMapping
2、常用的请求方式有get,post,put,delete
但是目前浏览器只支持get和post,若在form表单提交时,为method设置了其他请求方式的字符串(put或delete),则按照默认的请求方式get处理
⚪params属性
-
@RequestMapping注解的params属性通过请求的请求参数匹配请求映射
-
@RequestMapping注解的params属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求参数和请求映射的匹配关系
-
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足params属性,此时页面会报 错误400
使用方式:
“param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数
“!param”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带param请求参数
“param=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数且param=value
“param!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数但是param!=value
@RequestMapping(
value = {"请求路径1", "请求路径2"},
params = {"username","!sex","age=18","password!=123456"}
)
注:html页面中路径携带的参数,使用()括起来:
<a th:href="@{/test(username='admin',password=123,age=18)">测试@RequestMapping的params属性-->/testa>
⚪headers属性
-
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性通过请求的请求头信息匹配请求映射
-
@RequestMapping注解的headers属性是一个字符串类型的数组,可以通过四种表达式设置请求头信息和请求映射的匹配关系
-
若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
使用方式:
“header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
“!header”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
“header=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
“header!=value”:要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
请求头信息是用Map集合存储的,不知道请求头包含什么信息的可以浏览器搜索一下。
五、ant风格的路径
SpringMVC支持的ant风格路径 使用方式:
-
?:这里表示任意的单个字符; -
*:表示任意的0个或多个字符; -
**:表示任意的一层或多层目录;
注意:在使用**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式;
@RequestMapping("/a?a/test")
@RequestMapping("/a*a/test")
@RequestMapping("/**/test")
六、路径中占位符的使用
SpringMVC路径中的占位符常用于RESTful风格中,当请求路径中将某些数据通过路径的方式传输到服务器中,就可以在相应的@RequestMapping注解的value属性中通过占位符{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参。
使用方式:
{xxx}表示传输的数据,在通过@PathVariable注解,将占位符所表示的数据赋值给控制器方法的形参
@RequestMapping("/testRest/{name}/{sex}/{age}")
public String testRest(@PathVariable("name") String name, @PathVariable("sex") String sex,@PathVariable("age") int age){
System.out.println("name:"+name+",sex:"+sex+",age:"+age);
return "success";
}
RESTful风格方式传递路径中的参数:
<a th:href="@{/testRest/.29./man/18}">测试路径中的占位符-->/testResta><br>