单片机开发为啥对C++爱答不理?——不是C++不够好,是单片机太“穷”了
宋一平工作室
stm32单片机嵌入式硬件物联网c语言
单片机开发为啥对C++爱答不理?——不是C++不够好,是单片机太“穷”了你有没有过这种疑惑?C++明明听起来更“高级”——有类、有对象、有各种酷炫的语法,怎么到了单片机开发这儿,就成了没人待见的“外来户”?反倒是C语言这个看起来“老掉牙”的家伙,牢牢霸占着单片机的半壁江山。这事儿说起来挺有意思,不是C++不够优秀,而是单片机这“小身板”,实在消受不起C++的“豪华套餐”。今天咱们就用大白话唠唠:为
数据结构(十一)——B树
文章目录1.B树及其基本操作1.1概念1.2基本操作2.B+树的基本概念重点B树的基本特点B树的建立、插入和删除操作B+树的基本概念1.B树及其基本操作1.1概念B树又称多路平衡查找树,B树中所有节点的孩子个数的最大值称为B树的阶m。(1)性质一棵m阶B树或为空树,或为满足一下特性的m叉树:对任一节点,其所有子树高度相同。根节点的子树数∈[2,m],关键字数∈[1,m-1]。其他节点的子树数∈[[
数据结构——20.B树
爱看烟花的码农
数据结构数据结构
第一部分:核心理论精讲一、B树(B-Tree)1.为什么需要B树?当数据量非常大时,内存无法一次性装下,大部分数据需要存储在磁盘等外部存储器上。磁盘I/O(读/写)操作相比内存访问非常慢。为了减少磁盘I/O次数,我们需要一种特殊的树结构,它的每个节点可以存储大量信息,从而使得树的高度尽可能低。B树(一种多路平衡查找树)就是为此而设计的。2.B树的定义(m阶)一棵m阶B树是满足以下条件的m路查找树:
C++ --- list的简单实现
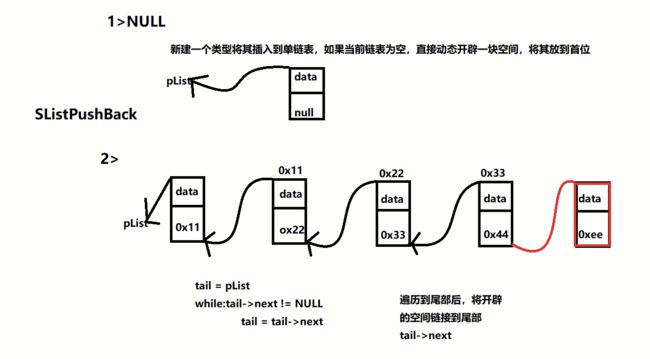
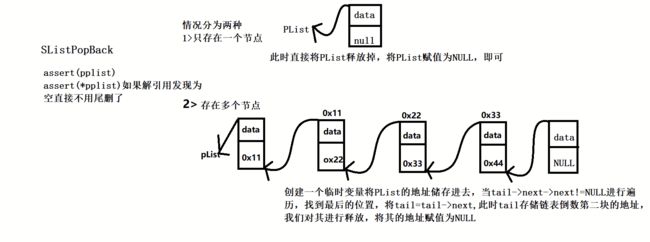
list的简单实现前言一、节点类二、迭代器类三、list类四、迭代器类的相关运算符重载1.解引用操作符2.成员访问操作符3.前置后置++/--4.==/!=运算符五、list类的相关构造和方法1.迭代器相关2.空初始化方法3.构造,析构函数相关4.赋值运算符重载5.尾插,头插,任意位置插6.尾删,头删,任意位置删除7.清空8.size方法六、总结前言本次实现的list结构是带头双向循环链表,节点结
【PTA数据结构 | C语言版】从顺序表 list 中删除第 i 个元素
秋说
PTA数据结构题目集数据结构c语言算法
本专栏持续输出数据结构题目集,欢迎订阅。文章目录题目代码题目请编写程序,将n个整数存入顺序表,对任一指定的第i个位置,将这个位置上的元素从顺序表中删除。注意:i代表位序,从1开始,不是数组下标。输入格式:输入首先在第一行给出正整数n(≤10^4);随后一行给出n个int范围内的整数,数字间以空格分隔;最后一行给出删除位序i,为int范围内的整数。输出格式:如果删除的位置不合法,则不能删除,在一行中
嵌入式C语言中void*的妙用与实战
隐身模式
C/C++c语言开发语言
嵌入式C语言中void*的工程应用详解在嵌入式开发中,void*指针无处不在,理解它的使用场景和注意事项,是写好通用接口和系统模块的关键。目录嵌入式C语言中`void*`的工程应用详解✳️一、什么是`void*`二、典型应用场景1.通用参数传递2.通用回调机制3.通用数据结构(链表、队列)4.封装模块接口(如SDK、HAL)⚠️三、使用`void*`的注意事项✅建议实践:四、实战案例:事件处理机制
C语言核心探秘:深入理解文件指针、stdin、stdout与stderr
web安全工具库
2025C++学习数据库笔记c语言c++学习开发语言
资料合集下载链接:https://pan.quark.cn/s/472bbdfcd014在C语言的编程世界里,输入和输出是程序与外部世界沟通的桥梁。无论是从文件中读取数据,还是将结果显示在屏幕上,我们都离不开I/O(Input/Output)操作。而这一切操作的核心,都围绕着一个重要的概念——文件指针(FilePointer)。今天,就让我们一起根据课堂的精华笔记,揭开文件指针的神秘面纱,并深入了
华为OD机试 2025B卷 - 字符串序列判定(C++&Python&JAVA&JS&C语言)
YOLO大师
华为od华为OD机试2025B卷华为OD2025B卷华为OD机试华为OD机考2025B卷
2025B卷目录点击查看:华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库+算法考点详解2025B卷100分题型题目描述:字符串序列判定/最后一个有效字符(本题分值100)输入两个字符串S和L,都只包含英文小写字母。S长度<=100,L长度<=500,000。判定S是否是L的有效子串。判定规则:S中的每个字符在L中都能找到(可以不连续),且S在L中字符的前后顺序与S中顺序要保持一致。(例如,S=”a
C++游戏开发需要具备哪些能力
星宇工作室
c++开发语言
1.C++语言基础:熟悉C++语法,包括变量、数据类型、控制结构(if,for,while等)、函数、类和对象等。理解C++的内存管理,包括堆和栈的区别、动态内存分配(new/delete)和智能指针的使用。掌握C++的高级特性,如模板、异常处理、STL(标准模板库)等。2.面向对象编程(OOP):理解面向对象的概念,如封装、继承和多态。能够设计和实现面向对象的系统。3.数据结构和算法:熟悉基本的
华为OD机试 2025B卷 - 小明减肥(C++&Python&JAVA&JS&C语言)
YOLO大师
华为odc++python华为OD2025B卷华为OD机试华为机试2025B卷华为OD机试2025B卷
2025B卷目录点击查看:华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库+算法考点详解2025B卷100分题型最新华为OD机试真题目录:点击查看目录华为OD面试真题精选:点击立即查看题目描述小明有n个可选运动,每个运动有对应卡路里,想选出其中k个运动且卡路里和为t。k,t,n都是给定的。求出可行解数量输入描述第一行输入ntk第一行输入每个运动的卡路里按照空格进行分割备注00,00输出描述求出可行解
一文讲清楚React Fiber
许先森森
Reactreact.jsjavascript前端ReactFiber
文章目录一文讲清楚ReactFiber1.基础概念1.1浏览器刷新率(帧)1.2JS执行栈1.3时间分片1.4链表2.ReactFiber是如何实现更新过程控制2.1任务拆分2.2挂起、恢复、终止2.2.1挂起2.2.2恢复2.2.3终止2.3任务具备优先级一文讲清楚ReactFiber1.基础概念1.1浏览器刷新率(帧)页面都是一帧一帧绘制出来的,浏览器大多是60Hz(60帧/s),每一帧耗时1
【华为OD机试真题 2025B卷】130、最多获得的短信条数、云短信平台优惠活动 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码解析(C++、Java、Py、C语言、JS)
KFickle
最新华为OD机试(C++JavaPyCJS)+OJ华为odc++javajavascript华为OD机试真题c语言最多获得的短信条数
文章目录一、题目题目描述输入输出样例1样例2二、代码与思路参考C++代码Java代码Python代码C语言代码JS代码订阅本专栏后即可解锁在线OJ刷题权限个人博客首页:KFickle专栏介绍:最新的华为OD机试真题,使用C++,Java,Python,C语言,JS五种语言进行解答,每个题目都包含解题思路,五种语言的解法,每日持续更新中,订阅后支持开通在线OJ测试刷题!!!一次订阅永久享受更新,有代
【华为OD机试真题 2025B卷】128、 判断一组不等式是否满足约束并输出最大差 | 机试真题+思路参考+代码解析(C++、Java、Py、C语言、JS)
KFickle
最新华为OD机试(C++JavaPyCJS)+OJ华为odc++java华为OD机试真题c语言javascript
文章目录一、题目题目描述输入输出样例1样例2二、代码与思路参考C++代码Java代码Python代码C语言代码JS代码订阅本专栏后即可解锁在线OJ刷题权限个人博客首页:KFickle专栏介绍:最新的华为OD机试真题,使用C++,Java,Python,C语言,JS五种语言进行解答,每个题目都包含解题思路,五种语言的解法,每日持续更新中,订阅后支持开通在线OJ测试刷题!!!一次订阅永久享受更新,有代
位运算符详解
在C语言中,位运算符(BitwiseOperators)用于对整数类型(如int,unsignedint,long,char等)的二进制位进行操作。这些操作比算术运算更底层,常用于嵌入式开发、驱动开发、图像处理、网络协议、加密等场景。下面是C语言中所有的位运算符及其详解:一、位运算符列表运算符名称功能说明&位与(AND)两个二进制位都为1,结果才为1``位或(OR)^位异或(XOR)两个二进制位不
【漏洞挖掘】——121、Xpath注入深入刨析
FLy_鹏程万里
【WEB渗透】XPath注入SQL注入Web渗透信息安全网络安全web渗透
基本介绍XPath即为XML路径语言,是W3CXSLT标准的主要元素,它是一种用来确定XML(标准通用标记语言的子集)文档中某部分位置的语言。它是一种用来在内存中导航整个XML树的语言,它的设计初衷是作为一种面向XSLT和XPointer的语言,后来独立成了一种W3C标准,XPath基于XML的树状结构,有不同类型的节点,包括元素节点,属性节点和文本节点,提供在数据结构树中找寻节点的能力,可用来在
【LeetCode 热题 100】21. 合并两个有序链表——(解法一)迭代法
xumistore
LeetCodeleetcode链表算法java
Problem:21.合并两个有序链表题目:将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。文章目录整体思路完整代码时空复杂度时间复杂度:O(M+N)空间复杂度:O(1)整体思路这段代码旨在解决一个基础且经典的链表问题:合并两个有序链表(MergeTwoSortedLists)。问题要求将两个已按升序排列的链表合并为一个新的、仍然保持升序的链表。该算法采
LeetCode-169-多数元素(完整代码C语言)
William国学
LeetCode刷题笔记算法数据结构leetcodec语言
LeetCode-169-多数元素(完整代码C语言)题目示例及提示代码1(C语言)(部分样例未通过)代码2(C语言)解读题目给定一个大小为n的数组,找到其中的多数元素。多数元素是指在数组中出现次数大于⌊n/2⌋的元素。你可以假设数组是非空的,并且给定的数组总是存在多数元素。来源:力扣(LeetCode)链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/majority-ele
【LeetCode 热题 100】142. 环形链表 II——快慢指针
xumistore
LeetCodeleetcode链表算法java
Problem:142.环形链表II题目:给定一个链表的头节点head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。如果链表无环,则返回null。文章目录整体思路完整代码时空复杂度时间复杂度:O(N)空间复杂度:O(1)整体思路这段代码旨在解决一个比“判断环形链表”更进阶的问题:环形链表II(LinkedListCycleII)。问题不仅要求判断链表中是否存在环,还要求找到环的入口节点。如果不存在环,则返回nu
Linux的Initrd机制
被触发
linux
Linux 的 initrd 技术是一个非常普遍使用的机制,linux2.6 内核的 initrd 的文件格式由原来的文件系统镜像文件转变成了 cpio 格式,变化不仅反映在文件格式上, linux 内核对这两种格式的 initrd 的处理有着截然的不同。本文首先介绍了什么是 initrd 技术,然后分别介绍了 Linux2.4 内核和 2.6 内核的 initrd 的处理流程。最后通过对 Lin
maven本地仓库路径修改
bitcarter
maven
默认maven本地仓库路径:C:\Users\Administrator\.m2
修改maven本地仓库路径方法:
1.打开E:\maven\apache-maven-2.2.1\conf\settings.xml
2.找到
XSD和XML中的命名空间
darrenzhu
xmlxsdschemanamespace命名空间
http://www.360doc.com/content/12/0418/10/9437165_204585479.shtml
http://blog.csdn.net/wanghuan203/article/details/9203621
http://blog.csdn.net/wanghuan203/article/details/9204337
http://www.cn
Java 求素数运算
周凡杨
java算法素数
网络上对求素数之解数不胜数,我在此总结归纳一下,同时对一些编码,加以改进,效率有成倍热提高。
第一种:
原理: 6N(+-)1法 任何一个自然数,总可以表示成为如下的形式之一: 6N,6N+1,6N+2,6N+3,6N+4,6N+5 (N=0,1,2,…)
java 单例模式
g21121
java
想必单例模式大家都不会陌生,有如下两种方式来实现单例模式:
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance=new Singleton();
private Singleton(){}
static Singleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
Linux下Mysql源码安装
510888780
mysql
1.假设已经有mysql-5.6.23-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
(1)创建mysql的安装目录及数据库存放目录
解压缩下载的源码包,目录结构,特殊指定的目录除外:
32位和64位操作系统
墙头上一根草
32位和64位操作系统
32位和64位操作系统是指:CPU一次处理数据的能力是32位还是64位。现在市场上的CPU一般都是64位的,但是这些CPU并不是真正意义上的64 位CPU,里面依然保留了大部分32位的技术,只是进行了部分64位的改进。32位和64位的区别还涉及了内存的寻址方面,32位系统的最大寻址空间是2 的32次方= 4294967296(bit)= 4(GB)左右,而64位系统的最大寻址空间的寻址空间则达到了
我的spring学习笔记10-轻量级_Spring框架
aijuans
Spring 3
一、问题提问:
→ 请简单介绍一下什么是轻量级?
轻量级(Leightweight)是相对于一些重量级的容器来说的,比如Spring的核心是一个轻量级的容器,Spring的核心包在文件容量上只有不到1M大小,使用Spring核心包所需要的资源也是很少的,您甚至可以在小型设备中使用Spring。
mongodb 环境搭建及简单CURD
antlove
WebInstallcurdNoSQLmongo
一 搭建mongodb环境
1. 在mongo官网下载mongodb
2. 在本地创建目录 "D:\Program Files\mongodb-win32-i386-2.6.4\data\db"
3. 运行mongodb服务 [mongod.exe --dbpath "D:\Program Files\mongodb-win32-i386-2.6.4\data\
数据字典和动态视图
百合不是茶
oracle数据字典动态视图系统和对象权限
数据字典(data dictionary)是 Oracle 数据库的一个重要组成部分,这是一组用于记录数据库信息的只读(read-only)表。随着数据库的启动而启动,数据库关闭时数据字典也关闭 数据字典中包含
数据库中所有方案对象(schema object)的定义(包括表,视图,索引,簇,同义词,序列,过程,函数,包,触发器等等)
数据库为一
多线程编程一般规则
bijian1013
javathread多线程java多线程
如果两个工两个以上的线程都修改一个对象,那么把执行修改的方法定义为被同步的,如果对象更新影响到只读方法,那么只读方法也要定义成同步的。
不要滥用同步。如果在一个对象内的不同的方法访问的不是同一个数据,就不要将方法设置为synchronized的。
将文件或目录拷贝到另一个Linux系统的命令scp
bijian1013
linuxunixscp
一.功能说明 scp就是security copy,用于将文件或者目录从一个Linux系统拷贝到另一个Linux系统下。scp传输数据用的是SSH协议,保证了数据传输的安全,其格式如下: scp 远程用户名@IP地址:文件的绝对路径
【持久化框架MyBatis3五】MyBatis3一对多关联查询
bit1129
Mybatis3
以教员和课程为例介绍一对多关联关系,在这里认为一个教员可以叫多门课程,而一门课程只有1个教员教,这种关系在实际中不太常见,通过教员和课程是多对多的关系。
示例数据:
地址表:
CREATE TABLE ADDRESSES
(
ADDR_ID INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
STREET VAR
cookie状态判断引发的查找问题
bitcarter
formcgi
先说一下我们的业务背景:
1.前台将图片和文本通过form表单提交到后台,图片我们都做了base64的编码,并且前台图片进行了压缩
2.form中action是一个cgi服务
3.后台cgi服务同时供PC,H5,APP
4.后台cgi中调用公共的cookie状态判断方法(公共的,大家都用,几年了没有问题)
问题:(折腾两天。。。。)
1.PC端cgi服务正常调用,cookie判断没
通过Nginx,Tomcat访问日志(access log)记录请求耗时
ronin47
一、Nginx通过$upstream_response_time $request_time统计请求和后台服务响应时间
nginx.conf使用配置方式:
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ''$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_r
java-67- n个骰子的点数。 把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为S。输入n,打印出S的所有可能的值出现的概率。
bylijinnan
java
public class ProbabilityOfDice {
/**
* Q67 n个骰子的点数
* 把n个骰子扔在地上,所有骰子朝上一面的点数之和为S。输入n,打印出S的所有可能的值出现的概率。
* 在以下求解过程中,我们把骰子看作是有序的。
* 例如当n=2时,我们认为(1,2)和(2,1)是两种不同的情况
*/
private stati
看别人的博客,觉得心情很好
Cb123456
博客心情
以为写博客,就是总结,就和日记一样吧,同时也在督促自己。今天看了好长时间博客:
职业规划:
http://www.iteye.com/blogs/subjects/zhiyeguihua
android学习:
1.http://byandby.i
[JWFD开源工作流]尝试用原生代码引擎实现循环反馈拓扑分析
comsci
工作流
我们已经不满足于仅仅跳跃一次,通过对引擎的升级,今天我测试了一下循环反馈模式,大概跑了200圈,引擎报一个溢出错误
在一个流程图的结束节点中嵌入一段方程,每次引擎运行到这个节点的时候,通过实时编译器GM模块,计算这个方程,计算结果与预设值进行比较,符合条件则跳跃到开始节点,继续新一轮拓扑分析,直到遇到
JS常用的事件及方法
cwqcwqmax9
js
事件 描述
onactivate 当对象设置为活动元素时触发。
onafterupdate 当成功更新数据源对象中的关联对象后在数据绑定对象上触发。
onbeforeactivate 对象要被设置为当前元素前立即触发。
onbeforecut 当选中区从文档中删除之前在源对象触发。
onbeforedeactivate 在 activeElement 从当前对象变为父文档其它对象之前立即
正则表达式验证日期格式
dashuaifu
正则表达式IT其它java其它
正则表达式验证日期格式
function isDate(d){
var v = d.match(/^(\d{4})-(\d{1,2})-(\d{1,2})$/i);
if(!v) {
this.focus();
return false;
}
}
<input value="2000-8-8" onblu
Yii CModel.rules() 方法 、validate预定义完整列表、以及说说验证
dcj3sjt126com
yii
public array rules () {return} array 要调用 validate() 时应用的有效性规则。 返回属性的有效性规则。声明验证规则,应重写此方法。 每个规则是数组具有以下结构:array('attribute list', 'validator name', 'on'=>'scenario name', ...validation
UITextAttributeTextColor = deprecated in iOS 7.0
dcj3sjt126com
ios
In this lesson we used the key "UITextAttributeTextColor" to change the color of the UINavigationBar appearance to white. This prompts a warning "first deprecated in iOS 7.0."
Ins
判断一个数是质数的几种方法
EmmaZhao
Mathpython
质数也叫素数,是只能被1和它本身整除的正整数,最小的质数是2,目前发现的最大的质数是p=2^57885161-1【注1】。
判断一个数是质数的最简单的方法如下:
def isPrime1(n):
for i in range(2, n):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
但是在上面的方法中有一些冗余的计算,所以
SpringSecurity工作原理小解读
坏我一锅粥
SpringSecurity
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
ConcurrentSessionFilter
WebAsyncManagerIntegrationFilter
HeaderWriterFilter
CsrfFilter
LogoutFilter
Use
JS实现自适应宽度的Tag切换
ini
JavaScripthtmlWebcsshtml5
效果体验:http://hovertree.com/texiao/js/3.htm
该效果使用纯JavaScript代码,实现TAB页切换效果,TAB标签根据内容自适应宽度,点击TAB标签切换内容页。
HTML文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
Hbase Rest API : 数据查询
kane_xie
RESThbase
hbase(hadoop)是用java编写的,有些语言(例如python)能够对它提供良好的支持,但也有很多语言使用起来并不是那么方便,比如c#只能通过thrift访问。Rest就能很好的解决这个问题。Hbase的org.apache.hadoop.hbase.rest包提供了rest接口,它内嵌了jetty作为servlet容器。
启动命令:./bin/hbase rest s
JQuery实现鼠标拖动元素移动位置(源码+注释)
明子健
jqueryjs源码拖动鼠标
欢迎讨论指正!
print.html代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<title>发票打印</title>
&l
Postgresql 连表更新字段语法 update
qifeifei
PostgreSQL
下面这段sql本来目的是想更新条件下的数据,可是这段sql却更新了整个表的数据。sql如下:
UPDATE tops_visa.visa_order
SET op_audit_abort_pass_date = now()
FROM
tops_visa.visa_order as t1
INNER JOIN tops_visa.visa_visitor as t2
ON t1.
将redis,memcache结合使用的方案?
tcrct
rediscache
公司架构上使用了阿里云的服务,由于阿里的kvstore收费相当高,打算自建,自建后就需要自己维护,所以就有了一个想法,针对kvstore(redis)及ocs(memcache)的特点,想自己开发一个cache层,将需要用到list,set,map等redis方法的继续使用redis来完成,将整条记录放在memcache下,即findbyid,save等时就memcache,其它就对应使用redi
开发中遇到的诡异的bug
wudixiaotie
bug
今天我们服务器组遇到个问题:
我们的服务是从Kafka里面取出数据,然后把offset存储到ssdb中,每个topic和partition都对应ssdb中不同的key,服务启动之后,每次kafka数据更新我们这边收到消息,然后存储之后就发现ssdb的值偶尔是-2,这就奇怪了,最开始我们是在代码中打印存储的日志,发现没什么问题,后来去查看ssdb的日志,才发现里面每次set的时候都会对同一个key
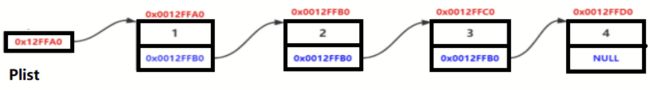
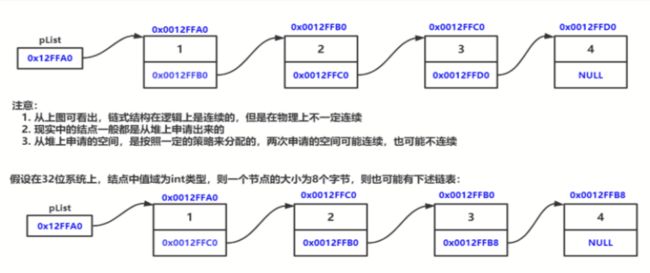
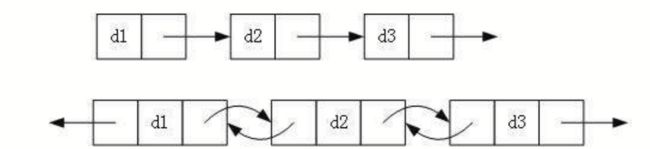
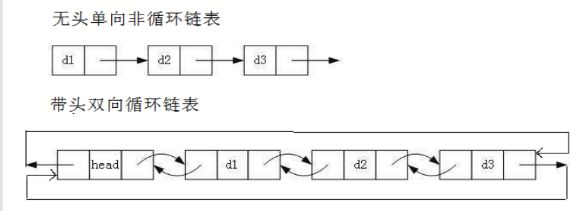
 链表的分类
链表的分类 单链表的实现
单链表的实现