via: https://github.com/DT42/BerryNet
This project turns Raspberry Pi 3 into an intelligent gateway with deep learning running on it. No internet connection is required, everything is done locally on the Raspberry Pi 3 itself. At DT42, we believe that bringing deep learning to edge devices is the trend towards the future. It not only saves costs of data transmission and storage but also makes devices able to respond according to the events shown in the images or videos without connecting to the cloud.
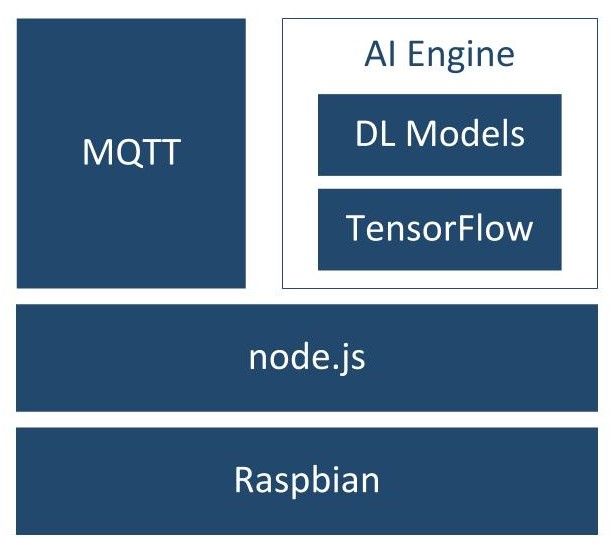
Figure 1 shows the software architecture of the project, we use Node.js, MQTT and an AI engine to analyze images or video frames with deep learning. So far, there are two supported AI engines, the classification engine and the object detection engine. Figure 2 shows the differences between classification and object detection.
One of the application of this intelligent gateway is to use the camera to monitor the place you care about. For example, Figure 3 shows the analyzed results from the camera hosted in the DT42 office. The frames were captured by the IP camera and they were submitted into the AI engine. The output from the AI engine will be shown in the dashboard. We are working on the Email and IM notification so you can get a notification when there is a dog coming into the meeting area with the next release.
AI Engines
The current supported AI Engines leverage work from the following projects:
- TensorFlow
- TensorFlow on RPi3 (Sam is looking for donation)
- Darknet
- Darkflow
The current supported classification model is Inception v3[1] and the detection model is TinyYOLO[2].
Installation
$ git clone https://github.com/DT42/BerryNet.git
$ cd BerryNet
$ ./configure
Start and Stop BerryNet
BerryNet is managed by systemd. You can manage BerryNet via berrynet-manager:
$ berrynet-manager [start | stop | status | log]
Configuration
All the configurations are in config.js.
-
Choose AI Engine.
- Two types of AI engines currently: object classifier and object detector.
-
Configure IP camera's snapshot access interface.
- Please refer to IP camera setup for more details.
MQTT topics.
Dashboard
Open dashboard on RPi3 (with touch screen)
Open browser and enter the URL:
http://localhost:8080/index.html#source=dashboard.json
The default dashboard configuration file will be loaded.
Open dashboard on browser from any computer
Open browser and enter the URL:
http://
Click the data sources, and change MQTT broker's IP address to the gateway's IP.
For more details about dashboard configuration (e.g. how to add widgets), please refer to freeboard project.
Provide Image Input
To capture an image via configured IP camera
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m snapshot_ipcam
To capture an image via board-connected camera (RPi camera or USB webcam)
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m snapshot_boardcam
To provide a local image
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/localImage -m
To start and stop streaming from board-connected camera
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m stream_boardcam_start
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m stream_boardcam_stop
To start and stop streaming from Nest IP camera
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m stream_nest_ipcam_start
$ mosquitto_pub -h localhost -t berrynet/event/camera -m stream_nest_ipcam_stop
Enable Data Collector
You might want to store the snapshot and inference results for data analysis.
To enable data collector, you can set the storage directory path in config.js:
config.storageDirPath = '';
and restart BerryNet.
Use Your Data To Train
The original instruction of retraining YOLOv2 model see github repository of darknet
In the current of BerryNet, TinyYolo is used instead of YOLOv2.
The major differences are:
- Create file yolo-obj.cfg with the same content as in
tiny-yolo.cfg - Download pre-trained weights of darknet reference model,
darknet.weights.12, for the convolutional layers (6.1MB)
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/0B-oZJEwmkAObMzAtc2QzZDhyVGM?usp=sharing
The rest parts are the same as retraining YOLO.
If you use LabelMe to annotate data, utils/xmlTotxt.py can help convert the xml format to the text format that darknet uses.
Discussion
Please refer to the Google Group for questions, suggestions, or any idea discussion.
-
Inception v3 https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.00567.pdf ↩
-
TinyYOLO https://pjreddie.com/media/files/papers/YOLO9000.pdf ↩