【数据结构第三章】- 栈
目录
一、栈的定义和特点
二、顺序栈的表示和实现
2.1 - SeqStack.h
2.2 - SeqStack.c
2.3 - test.c
三、链栈的表示和实现
3.1 - LinkStack.h
3.2 - LinkStack.c
3.3 - test.c
一、栈的定义和特点
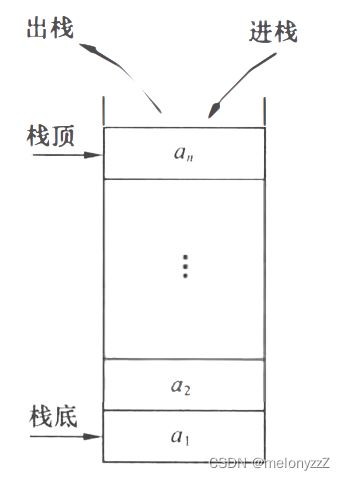
栈(stack)是限定仅在表尾进行插入或删除操作的线性表。因此,对栈来说,表尾端有其特殊含义,称为栈顶(top),相应地,表头端称为栈底(bottom)。不含元素的空表称为空栈。
假设栈 S = (a1, a2, ..., an),则称 a1 为栈底元素,an 为栈顶元素。栈中元素按照 a1, a2, ..., an 的次序进栈,退栈的第一个元素应为栈顶元素。换句话说,栈的修改是按后进先出的原则进行,如下图所示。因此,栈又称为后进先出(Last In First Out, LIFO)的线性表。
栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈;栈的删除操作叫做出栈。
在日常生活中,还要很多类似栈的例子。例如,洗干净的盘子总是逐个往上叠好放在已经洗好的盘子上面,而用时从上往下逐个取用。栈的特点正是上述实际应用的抽象。在程序设计中,如果需要按照保存数据时相反的顺序来使用数据,则可以利用栈来实现。
二、顺序栈的表示和实现
顺序栈是指利用顺序存储结构实现的栈,即利用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放自栈底到栈顶的数据元素。动态顺序栈的定义如下:
typedef struct SeqStack
{
DataType* data;
int top;
int capacity;
}SeqStack;
2.1 - SeqStack.h
#pragma once
#include
// 动态顺序栈
#define DEFAULT_CAPACITY 5 // 默认最大容量
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SeqStack
{
DataType* data;
int top;
int capacity;
}SeqStack;
// 基本操作
void SeqStackInit(SeqStack* pss); // 初始化
bool SeqStackEmpty(const SeqStack* pss); // 判断是否为空栈
void SeqStackPush(SeqStack* pss, DataType e); // 入栈
void SeqStackPop(SeqStack* pss); // 出栈
DataType SeqStackTop(const SeqStack* pss); // 返回栈顶元素
int SeqStackSize(const SeqStack* pss); // 返回栈的有效元素个数
void SeqStackDestroy(SeqStack* pss); // 销毁
2.2 - SeqStack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqStack.h"
#include
#include
// 初始化
void SeqStackInit(SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
pss->data = (DataType*)malloc(sizeof(DataType) * DEFAULT_CAPACITY);
if (NULL == pss->data)
{
perror("initialization failed!");
exit(-1);
}
pss->top = 0;
pss->capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
}
// 判断是否为空栈
bool SeqStackEmpty(const SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
return pss->top == 0; // 若为空栈,返回 true,否则返回 false
}
// 入栈
void SeqStackPush(SeqStack* pss, DataType e)
{
assert(pss);
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (pss->top == pss->capacity)
{
DataType* tmp = (DataType*)realloc(pss->data, sizeof(DataType) * 2 * pss->capacity);
if (NULL == tmp)
{
perror("realloc failed!");
return;
}
pss->data = tmp;
pss->capacity *= 2;
}
// 入栈
pss->data[pss->top++] = e;
}
// 出栈
void SeqStackPop(SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
assert(!SeqStackEmpty(pss)); // 前提是栈非空
// 出栈
--pss->top;
}
// 返回栈顶元素
DataType SeqStackTop(const SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
assert(!SeqStackEmpty(pss)); // 前提是栈非空
return pss->data[pss->top - 1];
}
// 返回栈的有效元素个数
int SeqStackSize(const SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
return pss->top;
}
// 销毁
void SeqStackDestroy(SeqStack* pss)
{
assert(pss);
free(pss->data);
pss->data = NULL;
pss->top = 0;
pss->capacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
}
2.3 - test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SeqStack.h"
#include
int main()
{
SeqStack s;
// 初始化
SeqStackInit(&s);
// 入栈:1 2 3 4
SeqStackPush(&s, 1);
SeqStackPush(&s, 2);
SeqStackPush(&s, 3);
SeqStackPush(&s, 4);
printf("当前栈中有效元素个数为:%d\n", SeqStackSize(&s)); // 4
// 出栈:4 3 2 1
while (!SeqStackEmpty(&s))
{
printf("%d ", SeqStackTop(&s));
SeqStackPop(&s);
}
printf("\n");
// 销毁
SeqStackDestroy(&s);
}
三、链栈的表示和实现
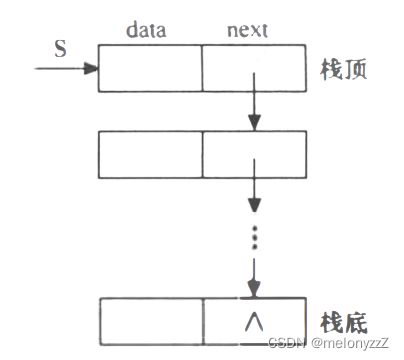
链栈是指采用链式存储结构实现的栈。通常链栈用单链表来表示,如下图所示。
由于栈的主要操作是在栈顶插入和删除,显然以链表的头部作为栈顶是最方便的。
链栈的定义如下:
typedef struct StackNode
{
DataType data;
struct StackNode* next;
}StackNode, *LinkStack;
3.1 - LinkStack.h
#pragma once
#include
#include
// 链栈
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct StackNode
{
DataType data;
struct StackNode* next;
}StackNode, *LinkStack;
// 基本操作
void LinkStackInit(LinkStack* pphead); // 初始化
bool LinkStackEmpty(const LinkStack phead); // 判断是否为空栈
void LinkStackPush(LinkStack* pphead, DataType e); // 入栈
void LinkStackPop(LinkStack* pphead); // 出栈
DataType LinkStackTop(const LinkStack phead); // 返回栈顶元素
int LinkStackSize(const LinkStack phead); // 返回栈的有效元素个数
void LinkStackDestroy(LinkStack* pphead); // 销毁
3.2 - LinkStack.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "LinkStack.h"
#include
#include
// 初始化
void LinkStackInit(LinkStack* pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
// 判断是否为空栈
bool LinkStackEmpty(const LinkStack phead)
{
return phead == NULL;
}
// 入栈
void LinkStackPush(LinkStack* pphead, DataType e)
{
assert(pphead);
StackNode* newnode = (StackNode*)malloc(sizeof(StackNode));
if (NULL == newnode)
{
perror("malloc failed!");
return;
}
newnode->data = e;
newnode->next = *pphead; // 将新结点插入栈顶
*pphead = newnode; // 修改头指针
}
// 出栈
void LinkStackPop(LinkStack* pphead)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(!LinkStackEmpty(*pphead)); // 前提是栈非空
StackNode* tmp = *pphead;
*pphead = (*pphead)->next;
free(tmp);
}
// 返回栈顶元素
DataType LinkStackTop(const LinkStack phead)
{
assert(!LinkStackEmpty(phead)); // 前提是栈非空
return phead->data;
}
// 返回栈的有效元素个数
int LinkStackSize(const LinkStack phead)
{
const StackNode* cur = phead;
int sz = 0;
while (cur != NULL)
{
++sz;
cur = cur->next;
}
return sz;
}
// 销毁
void LinkStackDestroy(LinkStack* pphead)
{
StackNode* cur = *pphead;
while (cur != NULL)
{
StackNode* tmp = cur;
cur = cur->next;
free(tmp);
}
*pphead = NULL;
}
3.3 - test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "LinkStack.h"
int main()
{
LinkStack phead;
// 初始化
LinkStackInit(&phead);
// 入栈:1 2 3 4
LinkStackPush(&phead, 1);
LinkStackPush(&phead, 2);
LinkStackPush(&phead, 3);
LinkStackPush(&phead, 4);
printf("当前栈中有效元素个数为:%d\n", LinkStackSize(phead)); // 4
// 出栈:4 3 2 1
while (!LinkStackEmpty(phead))
{
printf("%d ", LinkStackTop(phead));
LinkStackPop(&phead);
}
printf("\n");
// 销毁
LinkStackDestroy(&phead);
return 0;
}