C/C++考试必考题目(含答案*仅供参考)
今天继续来分享几个C++经常考试的几道题目,大家快快拿去,赶紧做一下
目录
(小事一桩)约瑟夫问题
discreb
input
output
效果展示:
1、 猜价格游戏
2、 计算 N 以内的所有素数
3、 袋中取球
4、 乘法口诀表
5、 最大公约数和最小公倍数
7、 计算n 阶勒让德多项式
实验二 类与对象
1、 矩形
2、 圆形
3、 友元
4、 分数
1、 矩阵(一)
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
2、 矩阵(二)
3、 矩阵(三)
(小事一桩)约瑟夫问题
discreb
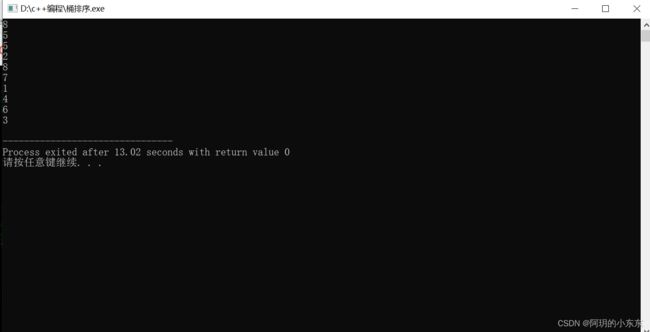
有 m 个人,其编号分别为 1~m。按顺序围成一个圈,现在给定一个数 n,从第一个人开始依次报数,报到 n 的人出圈,然后再从下一个人开始,继续从 1 开始依次报数,报到 n 的人再出圈,……如此循环,直到最后一个人出圈为止。
编程输出所有人出圈的顺序。
input
一行两个正整数 m 和 n,之间用一个空格隔开,1≤m<100,1≤n≤32767。
output
输出 m 行,每行一个正整数,表示依次出圈的人的编号。
#include
using namespace std;
int a[50];
int main()
{
int m,n,x,i,count = 0;
cin>>n>>m; //输入总人数n和出局要报的数m
x = n; //把n赋给x,避免使用时n被修改
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
a[i] = i; //将数组a中每一项按1-n排序
}
do {
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
//判断是否出局,已经出局的就不用报数了
if (a[i] != 0)
{
count++; //报数
}
if (count == m)
{
a[i] = 0;
count = 0;
x--;
cout< 0);//接着循环!!!
return 0;
} 效果展示:
1、 猜价格游戏
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 假定有一件商品,程序用随机数指定该商品的价格(1-1000的整数);
(2) 提示用户猜价格,并输入:若用户猜的价格比商品价格高或低,对用户作出相应的提示;
(3) 直到猜对为止,并给出提示
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
srand((int)time(0));
int price=rand()%1000+1;//产生1到1000的随机数
int l=1,r=1000;
while(1) {
cout<<"您可以猜一个价格,当前范围["<>guess;
if(guess>1000||guess<1||cin.fail()) {
cout<<"输入不合法,请重新输入"<price) {
cout<<"猜大了"<guess)
r=guess;//缩小范围
} else if(guess 效果展示:
猜小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[550,1000]的整数
600
青小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[600,1000]的整数
700
猜小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[700,1000]的整数
700颢蹦碍
大了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[700,800]的整数
750
倩小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[750,800]的整数
760
猜小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[760,800]的整数
780
青小了
您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[780,800]的整数
790
猜大了您可以猜一个价格,当前范围[780,790]的整数。786您猜对了,价格就是786
2、 计算 N 以内的所有素数
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 提示用户输入N;
(2) 计算出从2到N之间的所有素数;
(3) 将结果保存在一个文本文件中。
#include
#include
#include
#define N 1000000
using namespace std;
int prime[N],cnt,n;
void getPrime(){
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
if(!prime[i])prime[++cnt]=i;
for(int j=1;j<=cnt&&prime[j]<=N/i;j++){
prime[prime[j]*i]=1;
if(i%prime[j]==0)break;
}
}
}
int main(){
ofstream f("prime.txt");
cout<<"请输入n"<>n;
getPrime();
for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
f< 3、 袋中取球
编写C++程序完成以下功能(使用 enum):
(1) 袋子中有 red, yellow, blue, white, black 五种颜色的球多个;
(2) 一次从袋子里取出3个颜色不同的球,有几种取法;
(3) 将每种方法的所有取法输出到屏幕上。
#include
using namespace std;
enum ball{
red,yellow,blue,white,black
};
void output(int i){
switch(i){
case red:cout<<"red ";break;
case yellow:cout<<"yellow ";break;
case blue:cout<<"blue ";break;
case white:cout<<"white ";break;
case black:cout<<"black ";break;
}
}
int main(){
for(int i=red;i<=black;i++)
for(int j=i+1;j<=black;j++)
for(int k=j+1;k<=black;k++){
output(i);
output(j);
output(k);
cout< 效果展示:
red yellow bluered
yellow whitered yellow
blackred blue whitered
blue blackred white
blackyellow blue whiteyellow
blue blackvellow white
blackblue white black
4、 乘法口诀表
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 输出乘法口诀表;
(2) 显示格式如下所示。
1*1=1 1*2=2 1*3=3 1*4=4 1*5=5 1*6=6 1*7=7 1*8=8 1*9=9 2*2=4 2*3=6 2*4=8 2*5=10 2*6=12 2*7=14 2*8=16 2*9=18 3*3=9 3*4=12 3*5=15 3*6=18 3*7=21 3*8=24 3*9=27 4*4=16 4*5=20 4*6=24 4*7=28 4*8=32 4*9=36 5*5=25 5*6=30 5*7=35 5*8=40 5*9=45 6*6=36 6*7=42 6*8=48 6*9=54 7*7=49 7*8=56 7*9=63 8*8=64 8*9=72 9*9=81(累死了,看到这点个赞呗,感谢少爷~)
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i*7;j++)
cout<<" ";
for(int j=i;j<=9;j++)
cout< 5、 最大公约数和最小公倍数
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 提示用户输入两个无符号整数;
(2) 计算两者的最大公约数和最小公倍数,并输出
#include
#define uint unsigned int
using namespace std;
uint gcd(uint a,uint b){
return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;
}
int main(){
uint a,b;
cout<<"请输入两个无符号整数"<>a>>b;
cout< 7、 计算n 阶勒让德多项式
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 提示用户输入整数n和实数x;
(2) Pn(x),并输出结果
#include
using namespace std;
double p(int n,int x){
if(!n)return 1;
if(n==1)return x;
return ((2*n-1)*p(n-1,x)-(n-1)*p(n-2,x))/n;
}
int main(){
int n,x;
cout<<"请输入n、x"<>n>>x;
cout<<"Pn("<
实验二 类与对象
1、 矩形
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 定义一个Point类,其属性包括点的坐标,提供计算两点之间距离的方法;
(2) 定义一个矩形类,其属性包括左上角和右下角两个点,提供计算面积的方法;
(3) 创建一个矩形对象,提示用户输入矩形左上角和右下角的坐标;
(4) 观察矩形对象以及Point类成员的构造函数与析构函数的调用;
(5) 计算其面积,并输出。
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Point {
private:
int x,y;
public:
Point(int _x=0,int _y=0):x(_x),y(_y) {};
Point(Point &p):x(p.x),y(p.y) {};
~Point() {};
int disX(const Point &b) {
return b.x-x;
};
int disY(const Point &b) {
return b.y-y;
}
};
class Rectangle {
private:
Point a,b;
public:
Rectangle(Point _a,Point _b):a(_a),b(_b) {};
Rectangle(int ax=0,int ay=0,int bx=1,int by=1):a(ax,ay),b(bx,by) {}
Rectangle(Rectangle &r):a(r.a),b(r.b) {};
~Rectangle() {
cout<<"hh"<>ax>>ay>>bx>>by;
if(ax>bx||ay 实验问题
- 构造函数和析构函数写在哪?
写在public里(声明必须在..里,定义里外都可以)- 析构函数里面要写什么?
留空就可以了吧,如果有动态申请的内存就delete掉- 拷贝构造函数怎么写?
Point(Point &p){ x=p.x;y=p.y; };
或者
Point(Point &p):x(p.x),y(p.y){};- 编译错误提示 call of overloaded `Point()' is ambiguous
Point()构造时,Point(){};和Point(int _x=0,int _y=0):x(_x),y(_y){};都可以被调用,于是就被overloaded了。- 编译错误提示 In member function int Rectangle::area()':
int Point::x' is private
因为x是Point类的私有成员,不能在Rectangle类里面使用,关于x的计算函数都要写在Point类的public里。- 初始化时Rectangle myRectangle=Rectangle(ax,ay,bx,by);报错.
应该为Rectangle myRectangle(ax,ay,bx,by);- 析构函数怎么调用
不用显式调用,需要显式时:p.~Point();即可
2、 圆形
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 定义一个Point类,其属性包括点的坐标,提供计算两点之间距离的方法;
(2) 定义一个圆形类,其属性包括圆心和半径;
(3) 创建两个圆形对象,提示用户输入圆心坐标和半径,判断两个圆是否相交,并输出结果。
#include
#include
#define sqr(x) ((x)*(x))
using namespace std;
class Point{
private:
int x,y;
public:
Point(int x=0,int y=0):x(x),y(y){}
double dis(Point &b)const{
return sqrt(sqr(x-b.x)+sqr(y-b.y));
}
};
class Circle{
private:
Point c;
double r;
public:
Circle(int x=0,int y=0,double r=0):c(x,y),r(r){}
double dis(Circle &b)const{
return c.dis(b.c);
}
double getR()const{
return r;
}
};
int main(){
int x,y,r;
cout<<"请输入a 圆心坐标半径"<>x>>y>>r;
Circle a(x,y,r);
cout<<"请输入b 圆心坐标半径"<>x>>y>>r;
Circle b(x,y,r);
if(a.dis(b)<=a.getR()+b.getR())
cout<<"两圆相交"< 3、 友元
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 定义一个Boat和Car两个类,他们都具有私用属性——重量;
(2) 编写一个函数,计算两者的重量和。
double TotalWeight(Boat& b, Car& c);
#include
using namespace std;
class Car;
class Boat {
private:
double weight;
public:
Boat() {};
Boat(double w=0):weight(w) {};
~Boat() {};
friend double TotalWeight(Boat&,Car&);
};
class Car {
private:
double weight;
public:
Car() {};
Car(double w=0):weight(w) {};
~Car() {};
friend double TotalWeight(Boat&,Car&);
};
double TotalWeight(Boat& b,Car& c) {
return b.weight+c.weight;
}
int main() {
cout<<"请输入Boat、Car的重量"<>bw>>cw;
if(cin.fail()) {
cout<<"输入不合法"< 实验问题
- 什么时候需要用友元?
当一个函数要用到这个类时(可能还有其他类)的私有成员,但是它不是这个类独享的函数,调用时不需要通过对象或指针。- 友元函数定义在哪?
定义在主函数外面,类定义后面,要加上friend然后声明在类的公有属性里。
4、 分数
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 定义一个分数类,他们都具有私用属性——分子和分母;
(2) 定义分数类的构造函数和析构函数;
(3) 定义方法Set,设置分子和分母;
(4) 定义方法print,打印分数,格式如:2/7;
(5) 定义方法value,返回double型的分数值;
(6) 定义方法invert, 分子和分母交换。
#include
using namespace std;
class Fractions{
private:
int num,den;
public:
Fractions(int n=0,int d=0):num(n),den(d){}
~Fractions(){}
void set(int n,int d){
num=n;den=d;
}
void print(){
cout< 实验三 数组与指针
1、 矩阵(一)
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 假定矩阵大小为4×5(整型数组表示);
(2) 定义矩阵初始化函数,可以从cin中输入矩阵元素;
(3) 定义矩阵输出函数,将矩阵格式化输出到cout;
(4) 定义矩阵相加的函数,实现两个矩阵相加的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵中;
(5) 定义矩阵相减的函数,实现两个矩阵相减的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵中;
(6) 定义三个矩阵:A1、A2、A3;
(7) 初始化A1、A2;
(8) 计算并输出:A3 = A1加A2,A3 = A1减A2。
#include
#define ROW 4
#define COL 5
using namespace std;
class Matrix {
private:
int mat[ROW][COL];
public:
Matrix() {};
void init() {
cout<<"please input the Matrix(4 row and 5 col)"<>mat[i][j];
}
void output() {
cout<<"The Matrix:"< 2、 矩阵(二)
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 假定矩阵大小为4×5(整型);
(2) 矩阵空间采用new动态申请,保存在指针中;
(3) 定义矩阵初始化函数,可以从cin中输入矩阵元素;
(4) 定义矩阵输出函数,将矩阵格式化输出到cout;
(5) 定义矩阵相加的函数,实现两个矩阵相加的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵中;
(6) 定义矩阵相减的函数,实现两个矩阵相减的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵中;
(7) 动态申请三个矩阵:A1、A2、A3;
(8) 初始化A1、A2;
(9) 计算并输出A3 = A1加A2,A3 = A1减A2;
(10) 释放矩阵空间。
#include
#include
#include
const int row = 4;
const int col = 5;
using namespace std;
bool malloc_array(int **&a,int row,int col) {
a=new int *[row];
if(a==NULL) {
cout<<"error:no enough space"<> mat[i][j];
}
void output()
{
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++)
cout << mat[i][j] << "\t";
cout << endl;
}
}
void cal(Matrix &a, Matrix &b, int op)
{
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++)
mat[i][j] = a.mat[i][j] + b.mat[i][j] * op;
}
};
int main()
{
Matrix *A1 = new Matrix();
A1->input();
Matrix *A2 = new Matrix();
A2->input();
Matrix *A3 = new Matrix();
A3->cal(*A1, *A2, 1);
cout << "Matrix A1 + Matrix A2 =" << endl;
A3->output();
A3->cal(*A1, *A2, -1);
cout << "Matrix A1 - Matrix A2 =" << endl;
A3->output();
A1->~Matrix();
A2->~Matrix();
A3->~Matrix();
A1 = NULL;
A2 = NULL;
A3 = NULL;
return 0;
} 实验问题
- 动态分配内存?
定义:int **mat;
分配:
mat=new int *[ROW];
for(int i=0; i *(mat+i)=new int[COL];
加上判断是否分配成功- 释放空间?
for(int i=0;i delete [] *(mat+i);
delete [] mat;
3、 矩阵(三)
编写C++程序完成以下功能:
(1) 用类来实现矩阵,定义一个矩阵的类,属性包括:
- 矩阵大小,用 lines, rows(行、列来表示);
- 存贮矩阵的数组指针,根据矩阵大小动态申请(new)。
(2) 矩阵类的方法包括:
- 构造函数,参数是矩阵大小,需要动态申请存贮矩阵的数组;
- 析构函数,需要释放矩阵的数组指针;
- 拷贝构造函数,需要申请和复制数组;
- 输入,可以从cin中输入矩阵元素;
- 输出,将矩阵格式化输出到cout;
- 矩阵相加的函数,实现两个矩阵相加的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵类,但必须矩阵大小相同;
- 矩阵相减的函数,实现两个矩阵相减的功能,结果保存在另一个矩阵类,但必须矩阵大小相同。
(3) 定义三个矩阵:A1、A2、A3;
(4) 初始化A1、A2;
(5) 计算并输出A3 = A1加A2,A3=A1减A2;
(6) 用new动态创建三个矩阵类的对象:pA1、pA1、pA3;
(7) 初始化pA1、pA2;
(8) 计算并输出pA3=pA1加pA2,pA3=pA1减pA2;
(9) 释放pA1、pA1、pA3。
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
bool malloc_array(int **&a,int row,int col) {
a=new int *[row];
if(a==NULL) {
cout<<"error:no enough space"<>mat[i][j];
}
void output() {
for(int i=0; i>row>>col;
Matrix *pA1=new Matrix(row,col);
pA1->input();
cout<<"please input Matrix A2's row and col:"<>row>>col;
Matrix *pA2=new Matrix(row,col);
pA2->input();
Matrix *pA3=new Matrix(row,col);
if(pA3->cal(*pA1,* pA2,1)) {
cout<<"Matrix A1 + Matrix A2 ="<output();
pA3->cal(*pA1,* pA2,-1);
cout<<"Matrix A1 - Matrix A2 ="<output();
}
pA1->~Matrix();
pA2->~Matrix();
pA3->~Matrix();
pA1=NULL;
pA2=NULL;
pA3=NULL;
return 0;
} 实验问题
- line和row,不应该是row和col吗?
那就用row和col- 加减的函数基本一样,我可以写在一起吗?
其实用了乘法会降低速度,不过,这种同一级别的计算量,差别微小。- 拷贝函数怎么写
里面不能用memcpy(mat,b.mat,sizeof mat);- 遇到错误error: passing ‘const Matrix’ as ‘this’ argument discards qualifiers [-fpermissive] in call to ‘int Matrix::getRow()’
这是因为const型的Matrix参数要调用getRow,要在getRow的大括号前加上const。不过这个const型的Matrix参数我改回引用了。- 怎么释放
显式调用析构函数,再将指针指向NULL