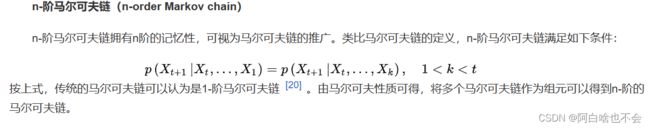阿白数模笔记之灰色-马尔科夫模型(Grey Markov model)
目录
前言(preface)
GM(1,1)
简介(brief introdution)
①级比检验(Grade ratio test)
②建立GM(1,1)模型
Ⅰ、邻值生成序列(Adjacent value generating sequence )
Ⅱ、回归分析(regression analysis)
Ⅲ、残差检验(Residual test)
Markov chain
① 转移概率矩阵(Transition probability matrix)
②状态分布向量(state vector)
③平稳分布向量(steady-state vector)
灰色马尔可夫模型(Grey Markov model)
①对y0建立GM(1,1)得到e1
Ⅰ、Grade ratio test
Ⅱ、Accumulative generation sequence
Ⅱ、Regression analysis&Residual test
②对abs(e1)建立GM(1,1)
Ⅰ、Grade ratio test
Ⅱ、Accumulative generation sequence
Ⅱ、Regression analysis&Residual test
③修正(revise)
Ⅰ、转移概率矩阵
Ⅱ、初始分布与预测
Ⅲ、修正效果
④总结(summary)
参考文章(Reference articles)
前言(preface)
在学习模拟退火算法时(Simulated Annealing,SA)发现了一个新名词——马尔科夫链(Markov chain),所以就先学习了Markov chain的相关知识,本文主要介绍GM(1,1),Markov chain,并将Grey Markov model应用到实例。
GM(1,1)
简介(brief introdution)
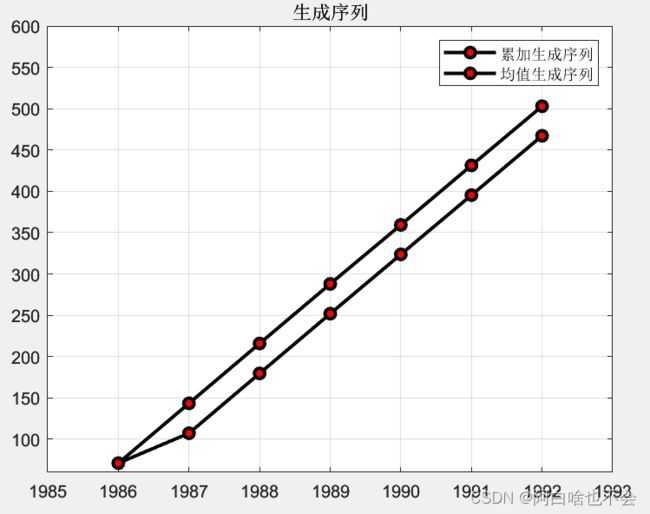
黑色未知,白色已知,而灰色是介于黑白之间的,意味着部分数据已知,而数据间有内在联系,但内在函数关系未知。GM(1,1)适用的情况大致满足以下条件:一、数据量少,二、短期预测,三、指数增长。下面是原数据和经过生成后的数据折线图,发现处理后的数据具有更明显的规律。
①级比检验(Grade ratio test)
%Grade ratio test
y0=[71.1,72.4,72.4,72.1,71.4,72.0,71.6];
[m,n]=size(y0);
k=0;
for i=2:n;
a=y0(i-1)/y0(i);
if exp(-2/(n+1))②建立GM(1,1)模型
Ⅰ、邻值生成序列(Adjacent value generating sequence )
%GM(1,1)
x=1986:1992;
y0=[71.1,72.4,72.4,72.1,71.4,72.0,71.6];
plot(x,y0,'-ok','markerfacecolor','r','linewidth',2);
axis([1985,1993,60,80]);
title('某城市1986-1992交通噪声平均声级');grid on
%累加生成数列
y1=zeros(size(y0));
for i=1:size(y0,2);
y1(i)=sum(y0(1:i));
end
figure,plot(x,y1,'-ok','markerfacecolor','r','linewidth',2);
axis([1985,1993,60,600]);
%均值生成数列
z1=zeros(size(y0));
for i=1:size(y0,2);
if i==1;
z1(i)=y1(i);
else
z1(i)=(y1(i)+y1(i-1))*0.5;
end
end
hold on
plot(x,z1,'-ok','markerfacecolor','r','linewidth',2);
axis([1985,1993,60,600]);
title('生成序列');
legend('累加生成序列','均值生成序列');grid onⅡ、回归分析(regression analysis)
fit1=polyfit(y1,y0,1);%拟合的一次函数
a1=fit1(1);u1=fit1(2);
%prediction
y11=zeros([1,1+n]);%n=size(y(0),2)
%y11是拟合后的累加生成序列
%y01用来储存时间步的预测值,y01(k+1)=y11(k+1)-y11(k)
y01=[y0(1),zeros([1,n])];
for k=0:n
y11(k+1)=(y0(1)+u1/a1)*exp(a1*k)-u1/a1; %求解微分方程后的函数
if k~=0
y01(k+1)=y11(k+1)-y11(k);
end
end
figure,plot(x,y0,'b*-');hold on
plot([x,1993],y01,'ro--');axis([1985,1993,60,80]);grid on
legend('actual','pred');title('Accumulative generation sequence')Ⅲ、残差检验(Residual test)
%Residual test
e1=abs((y0-y01(1,1:7)))./y0;
r11=length(e1(find(e1<0.1)));
r12=length(e1(find(e1<0.2)));
if r1==n
disp('The fitting effect of the model is very good')
elseif r2==n
disp('The fitting effect of the model is not bad' )
else
disp('GM(1,1) is not suitable to solve this problem')
end
output:
The fitting effect of the model is very goodMarkov chain
① 转移概率矩阵(Transition probability matrix)
动态规划算法中有个概念叫状态转移方程,就是说从前面 t-1 时刻的状态到 t时刻的状态的实现方式。Markov chain中的转移概率矩阵定义类似:(t-1)时刻处于状态 i,转移到状态 j 的概率为![]() ,则
,则![]() ,即每一行的和为1,称
,即每一行的和为1,称![]() 为转移概率矩阵
为转移概率矩阵
②状态分布向量(state vector)
![]() ,称为t时刻的状态分布向量,
,称为t时刻的状态分布向量,![]() ,一般取
,一般取![]() 为给定的初始分布,
为给定的初始分布,![]() ,其中P是转移概率矩阵
,其中P是转移概率矩阵
③平稳分布向量(steady-state vector)
对于一般的Markov chain ,当 t 足够大时,状态分布向量会收敛于某一特殊向量![]() ,即平稳分布向量,满足
,即平稳分布向量,满足![]() ,
,![]() 即是P特征值为 1 时对应的特征向量
即是P特征值为 1 时对应的特征向量
灰色马尔可夫模型(Grey Markov model)
y0 是原始序列,y1是累加生成序列,y11是拟合后的累加生成序列,y01是对原时间步的预测
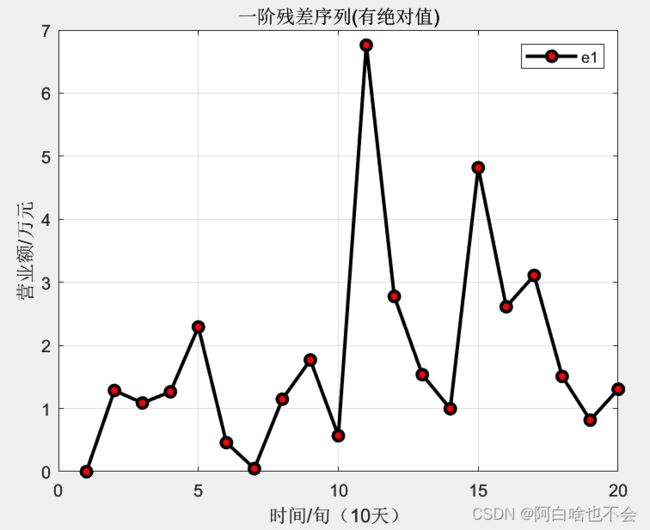
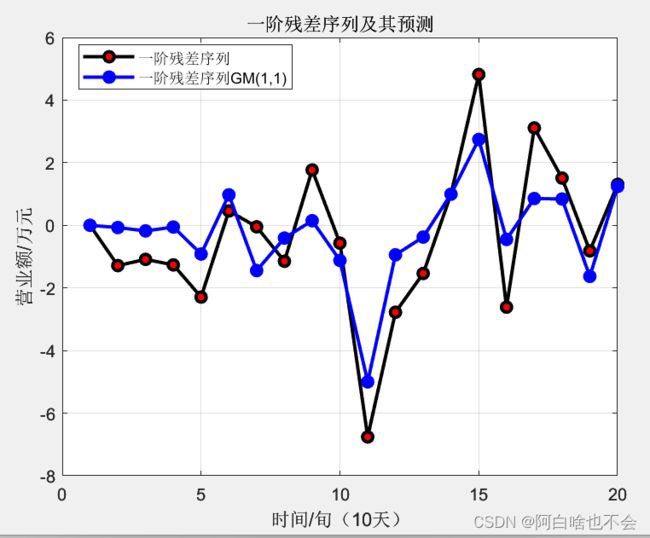
e1是一阶残差序列e1=(y0-y1)
①对y0建立GM(1,1)得到e1
Ⅰ、Grade ratio test
%级比检验 Grade ratio test
y0=d;
[m,n]=size(y0);
k=0;
for i=2:n;
a=y0(i-1)/y0(i);
if exp(-2/(n+1))Ⅱ、Accumulative generation sequence
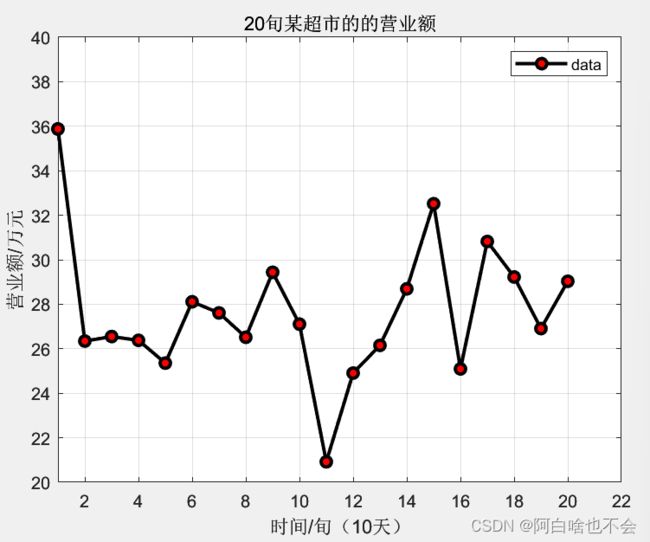
%GM(1,1)
x=1:20;
plot(x,y0,'-ok','markerfacecolor','r','linewidth',2);
axis([1,22,20,40]);
title('20旬某超市的的营业额');grid on;legend('data');
xlabel('时间/旬(10天)');ylabel('营业额/万元')
%累加生成数列
y1=zeros(size(y0));
for i=1:size(y0,2);
y1(i)=sum(y0(1:i));
end
figure,plot(x,y1,'-ok','markerfacecolor','r','linewidth',2);
axis([1,22,0,600]);
grid on;legend('Accumulative generation sequence','location','northwest');
xlabel('时间/旬(10天)');ylabel('营业额/万元')Ⅱ、Regression analysis&Residual test
fit1=polyfit(y1,y0,1);
a1=fit1(1);u1=fit1(2);
%prediction
y11=zeros([1,1+n]);%n=size(y(0),2)
%y11是拟合后的累加生成序列
%y01用来储存时间步的预测值,y01(k+1)=y11(k+1)-y11(k)
y01=[y0(1),zeros([1,n])];
for k=0:n
y11(k+1)=(y0(1)+u1/a1)*exp(a1*k)-u1/a1;
if k~=0
y01(k+1)=y11(k+1)-y11(k);
end
end
figure,plot(x,y0,'b*-');hold on
plot([x,21],y01,'ro--');axis([1,22,20,40]);grid on
legend('actual','Uncorrected GM(1,1)');title('Accumulative generation sequence')
%Residual test
e1=y0-y01(1,1:n)
e2=abs(e1)./y0;
r1=length(e2(find(e2<0.1)));
r2=length(e2(find(e2<0.2)));
if r1==n
disp('The fitting effect of the model is very good')
elseif r2==n
disp('The fitting effect of the model is not bad' )
else
disp('GM(1,1) is not suitable to solve this problem')
end
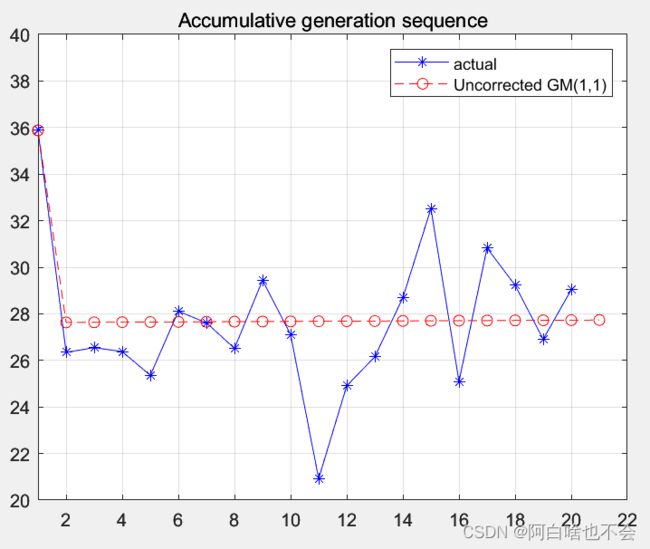 运行后的结果显示:The fitting effect of the model is not bad,但从预测图来看效果是非常差的,因此需要某种方法对GM(1,1)模型做出修正
运行后的结果显示:The fitting effect of the model is not bad,但从预测图来看效果是非常差的,因此需要某种方法对GM(1,1)模型做出修正
②对abs(e1)建立GM(1,1)
代码与上面是基本一致的,只给出各步骤对应结果
Ⅰ、Grade ratio test
grey modle is vailable
Ⅱ、Accumulative generation sequence
Ⅱ、Regression analysis&Residual test
pred即为残差修正值,用e01储存GM(1,1)对e0的预测结果;y00为修正(corrected)的结果;![]() ,其中
,其中![]() ,
,![]()
③修正(revise)
Ⅰ、转移概率矩阵
状态划分为正![]() ,负
,负![]() ,计算后知
,计算后知![]()
Ⅱ、初始分布与预测
以最后一个残差为初始分布![]() ,若大于0,则
,若大于0,则![]() ,否则
,否则![]() ,预测之后 t 个时间步,则对应的状态分布为
,预测之后 t 个时间步,则对应的状态分布为![]() ,若
,若![]() ,则取
,则取![]() ,否则
,否则![]() 。
。
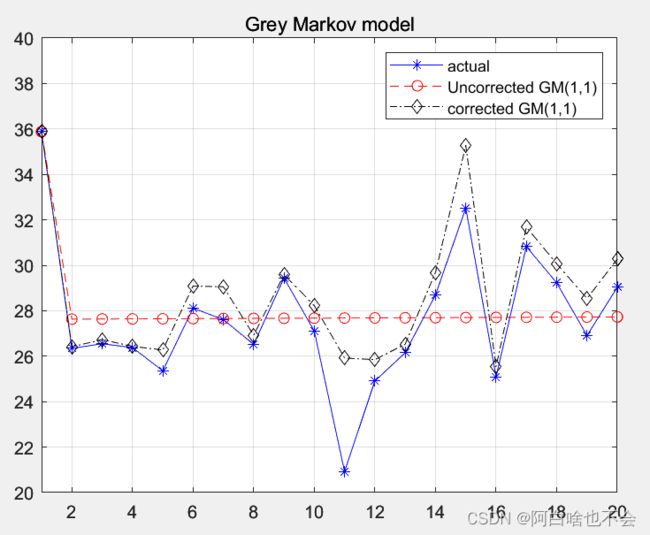
Ⅲ、修正效果
④总结(summary)
通过引入残差的GM(1,1)来修正误差,并采用Markov chain 预测残差和原data下一个时间步的值,通过状态分布向量预估正负号,再对数据进行修正。Grey Markov model 弥补了传统GM(1,1)对波动性和趋势性数据预测精度低的不足
参考文章(Reference articles)
灰色预测模型GM(1,1) 与例题分析
灰色-马尔可夫模型
简述马尔可夫链【通俗易懂】
马尔可夫链 (Markov Chains)