数据结构—二叉树链式结构的实现
目录
0、前言
1、二叉树链式结构的创建
2、二叉树的遍历
3、 前序、中序以及后序遍历
4、 前序、中序以及后序遍历的实现——双路递归
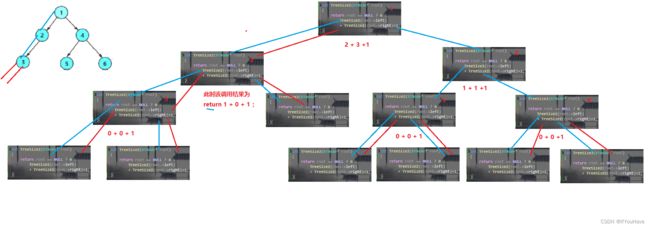
分治思想_ 求叶子节点数量,分治思想:
分治思想_求第k层节点个数:
分治思想_求二叉树的深度:
分治思想_二叉树查找值为x的结点:
5、二叉树基础oj练习
1. 单值二叉树。
2、检查两颗树是否相同。
3. 对称二叉树。
4. 二叉树的前序遍历。
5. 二叉树中序遍历 。
6. 二叉树的后序遍历 。
7. 另一颗树的子树。
0、前言
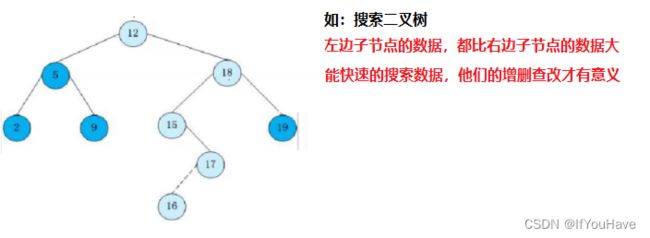
普通二叉树的增删查改没有什么意义,主要学习遍历、结构
而存储数据,不如用顺序表,链表,那么学习他的意义是为了什么?
1.为了后面学习更为复杂的二叉树打基础。(搜索二叉树、ALV树、红黑树、B树、B+树、B*树)
2.有很多二叉树的OJ算法题,都是出在普通二叉树上。
1、二叉树链式结构的创建
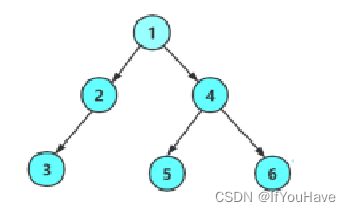
在学习二叉树的基本操作前,需先要创建一棵二叉树,然后才能学习其相关的基本操作。此处手动快速创建一棵简单的二叉树,快速进入二叉树操作学习,等二叉树结构了解的差不多时,反过头再来研究二叉树真正的创建方式。
手搓上图二叉树的链式结构:
typedef int BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
}BTNode;
//手搓二叉树
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
return 0;
}2、二叉树的遍历
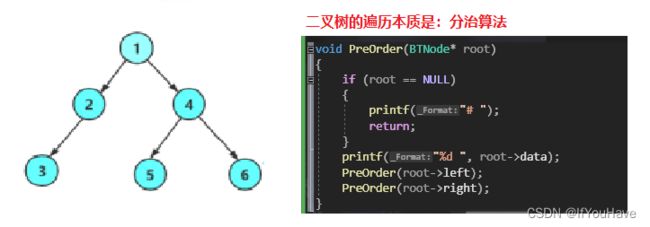
学习二叉树结构,最简单的方式就是遍历。
所谓二叉树遍历(Traversal)是按照某种特定的规则,依次对二叉 树中的节点进行相应的操作,并且每个节点只操作一次。访问结点所做的操作依赖于具体的应用问题。
遍历 是二叉树上最重要的运算之一,也是二叉树上进行其它运算的基础。
3、 前序、中序以及后序遍历
按照规则,二叉树的遍历有:前序/中序/后序的递归结构遍历:
- 前序遍历(Preorder Traversal 亦称先序遍历)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之前。
- 中序遍历(Inorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之中(间)。
- 后序遍历(Postorder Traversal)——访问根结点的操作发生在遍历其左右子树之后。
由于被访问的结点必是某子树的根,所以N(Node)、L(Left subtree)和R(Right subtree)又可解释为 根、根的左子树和根的右子树。NLR、LNR和LRN分别又称为先根遍历、中根遍历和后根遍历。
4、 前序、中序以及后序遍历的实现——双路递归
// 二叉树前序遍历
void PreOrder(BTNode * root);
// 二叉树中序遍历
void InOrder(BTNode* root);
// 二叉树后序遍历
void PostOrder(BTNode* root);
//求树的数据个数
void TreeSize1(BTNode* root);
//解决TreeSize1的问题,分治算法求Size
int TreeSize2(BTNode* root);
#include"BinaryTree.h"
BTNode* BuyNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
assert(node);
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
BTNode* CreatBinaryTree()
{
BTNode* node1 = BuyNode(1);
BTNode* node2 = BuyNode(2);
BTNode* node3 = BuyNode(3);
BTNode* node4 = BuyNode(4);
BTNode* node5 = BuyNode(5);
BTNode* node6 = BuyNode(6);
node1->left = node2;
node1->right = node4;
node2->left = node3;
node4->left = node5;
node4->right = node6;
return node1;
}
void PreOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
printf("%d ", root->data);
PreOrder(root->left);
PreOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%d ", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("# ");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
}
int count = 0;
//不能定义局部变量count,因为每次函数的栈帧,增加的是自己的count
void TreeSize1(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
++count;
TreeSize1(root->left);
TreeSize1(root->right);
}
int TreeSize2(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize2(root->left) + TreeSize2(root->right)+1;
}#include"BinaryTree.h"
extern int count;
int main()
{
BTNode* root = CreatBinaryTree();
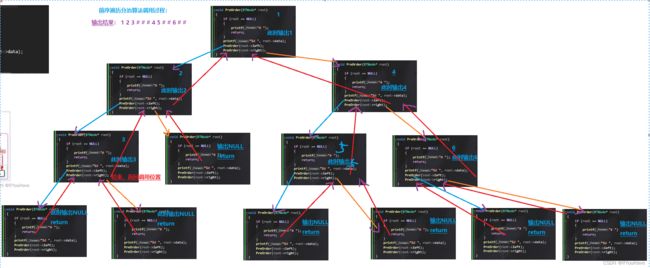
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
PostOrder(root);
printf("\n");
//每次调用前将count结果置为空
count = 0;
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n",count);
count = 0;
TreeSize1(root);
printf("%d\n", count);
printf("%d\n", TreeSize2(root));
printf("%d\n", TreeSize2(root));
return 0;
}TreeSize1 此时定义局部变量,在多线程调用,并行计数,就会失败
TreeSize2 此时运用分治思想,在任何情况,只要调用,便会返回size大小
分治思想_ 求叶子节点数量,分治思想:
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root) { if (root == 0) { return 0; } if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) { return 1; } return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right); }
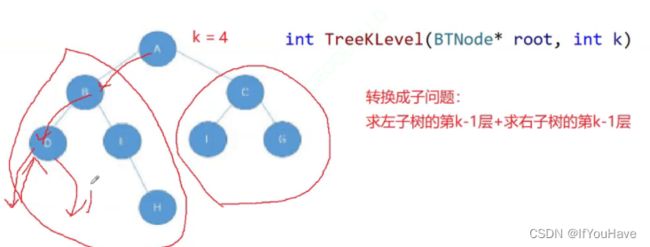
分治思想_求第k层节点个数:
//求第k层节点个数 int TreeKLevel(BTNode* root, int k) { assert(k >= 1); if (root == NULL) { return 0; } if (k == 1); { return 1; } return TreeKLevel(root->left, k - 1) + TreeKLevel(root->right, k - 1); }
分治思想_求二叉树的深度:
//求二叉树的深度
int TreeDepth(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
int ret1 = TreeDepth(root->left) + 1;
int ret2 = TreeDepth(root->right) + 1;
return ret1 > ret2 ? ret1 : ret2;
}分治思想_二叉树查找值为x的结点:
//二叉树查找值为x的结点
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
if (root->data == x)
{
return root;
}
BTNode* ret1 = TreeFind(root->left, x);
if (ret1)
{
return ret1;
}
BTNode* ret2 = TreeFind(root->right, x);
if (ret2)
{
return ret2;
}
return NULL;
}5、二叉树基础oj练习
1. 单值二叉树。
965. 单值二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/univalued-binary-tree/
bool PreOrderCompare(struct TreeNode* root,int val)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->val != val)
{
return false;
}
return PreOrderCompare(root->left,val) && PreOrderCompare(root->right,val);
}
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return PreOrderCompare(root,root->val);
}bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left && root->left->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
if(root->right && root->right->val != root->val)
{
return false;
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
//此时左边为false,右边就不进行运算,减少空间时间消耗
}
2、检查两颗树是否相同。
100. 相同的树 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}3. 对称二叉树。
101. 对称二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left, q->right) && isSameTree(p->right,q->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return isSameTree(root->left,root->right);
}4. 二叉树的前序遍历。
144. 二叉树的前序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/submissions/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/submissions/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
void preOrder(struct TreeNode* root,int* result,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
result[*returnSize] = root->val;
(*returnSize) ++;
preOrder(root->left,result,returnSize);
preOrder(root->right,result,returnSize);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int* result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
*returnSize = 0;
preOrder(root,result,returnSize);
return result;
}5. 二叉树中序遍历 。
Loading Question... - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
void inOrder(struct TreeNode* root,int* result,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
inOrder(root->left,result,returnSize);
result[*returnSize] = root->val;
(*returnSize) ++;
inOrder(root->right,result,returnSize);
}
int* inorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int* result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
*returnSize = 0;
inOrder(root,result,returnSize);
return result;
}6. 二叉树的后序遍历 。
145. 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
void postOrder(struct TreeNode* root,int* result,int* returnSize)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
postOrder(root->left,result,returnSize);
postOrder(root->right,result,returnSize);
result[*returnSize] = root->val;
(*returnSize) ++;
}
int* postorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int* result = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
*returnSize = 0;
postOrder(root,result,returnSize);
return result;
}7. 另一颗树的子树。
力扣 (leetcode.cn)![]() https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right,q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){
if(root==NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot) == true)
{
return true;
}
return isSubtree(root->left,subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right,subRoot);
}