网络流(一)----最大流Ford-Fulkerson算法
感谢YB大神的总结.

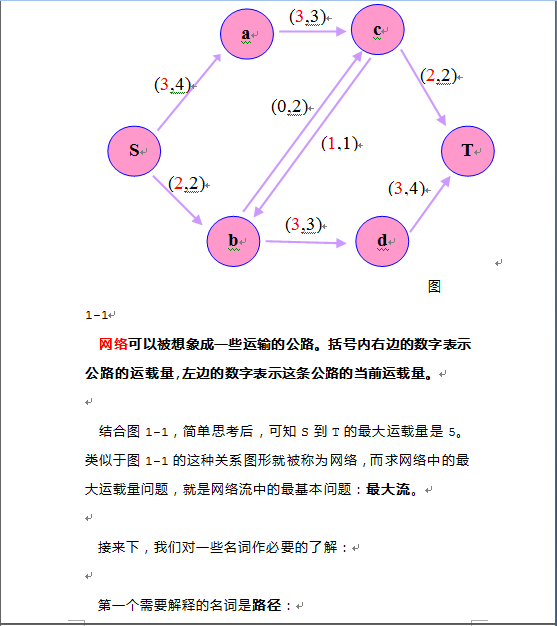



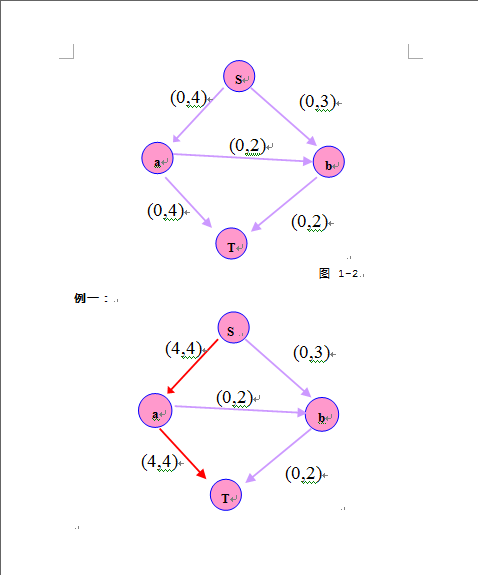
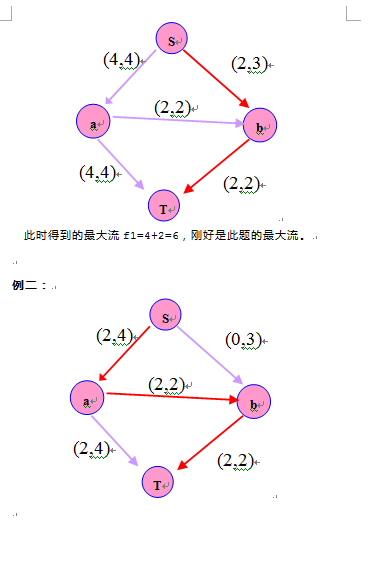
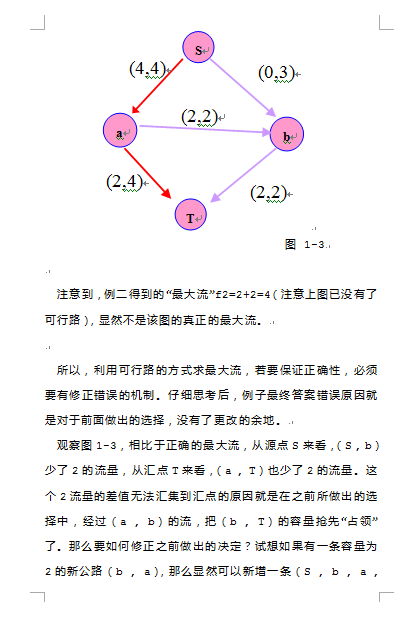


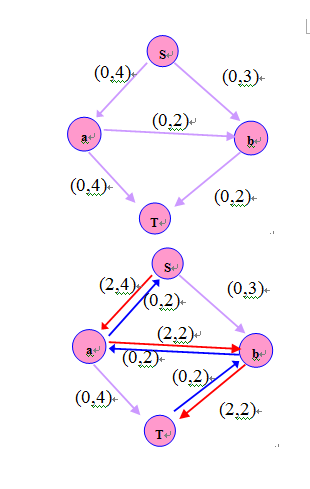
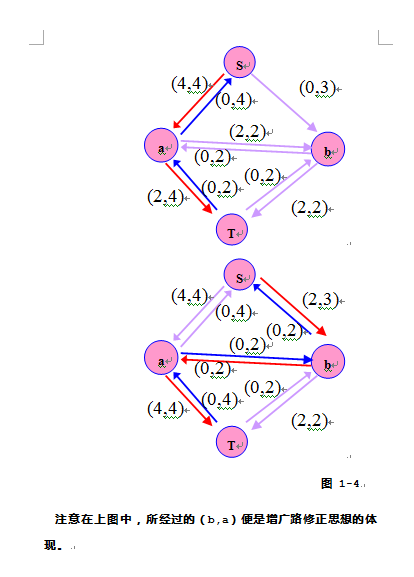

以HDU1532为例的Ford_Fulkerson算法
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1005;
struct Node
{
int to, flow, next;
}edge[maxn * maxn];
int n, m; //顶点数, 边数
int S, T; //源点, 汇点
int tot; //记录邻接表边数
int s[maxn];//DFS保存 结点的 栈
int pre[maxn], rec[maxn], mins[maxn], head[maxn];
void Add_edge(int a, int b, int c)
{
edge[tot].to = b; edge[tot].flow = c; edge[tot].next = head[a];
head[a] = tot++;
edge[tot].to = a; edge[tot].flow = 0; edge[tot].next = head[b];
head[b] = tot++;
}
void Init()
{
tot = 0;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
}
inline int DFS()
{
int top = 1;
memset(pre, -1, sizeof(pre));
s[top] = S;
pre[S] = S;
mins[S] = INF;
while(top)
{
int v = s[top--];
for(int i = head[v]; i != -1; i = edge[i].next)
{
int u = edge[i].to;
if(pre[u] == -1 && edge[i].flow > 0)
{
pre[u] = v;
rec[u] = i;
mins[u] = min(mins[v], edge[i].flow);
s[++top] = u;
}
}
if(pre[T] != -1) //直到找到了汇点
return mins[T];//每次返回增广路径中容量最小的
}
return -1; // 不存在增广路径
}
int Ford_Fulkerson()
{
int add, Maxflow = 0;
while((add = DFS()) != -1)
{//算法知道无法找到增广路径才停止
Maxflow += add;
for(int i = T; i != S; i = pre[i]) //修改残余网络
{
edge[rec[i]].flow -= add; //正向减去流量
edge[rec[i]^1].flow += add;//反向增加流量
}
}
return Maxflow;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d %d", &n, &m))
{
int i, j, k, s, e, c;
Init();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> s >> e >> c;
Add_edge(s, e, c);
}
S = 1; T = m;
cout << Ford_Fulkerson() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
下面是Edmonds-Karp算法代码的实现,bfs使得找到的增广路节点数最少,和上面dfs版本代码的唯一不同就是把保存节点的栈改成了队列:
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cctype>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 0x3f;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn = 1005;
struct Node
{
int to, flow, next;
}edge[maxn * maxn];
int n, m; //顶点数, 边数
int S, T; //源点, 汇点
int tot; //记录邻接表边数
int q[maxn];//DFS保存 结点的 栈
int pre[maxn], rec[maxn], mins[maxn], head[maxn];
void Add_edge(int a, int b, int c)
{
edge[tot].to = b; edge[tot].flow = c; edge[tot].next = head[a];
head[a] = tot++;
edge[tot].to = a; edge[tot].flow = 0; edge[tot].next = head[b];
head[b] = tot++;
}
void Init()
{
tot = 0;
memset(head, -1, sizeof(head));
}
inline int bfs() //bfs寻找增广路
{
int h,t;
h=t=0;
memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre));
q[h]=S;
pre[S]=S;
mins[S]=INF;
while(h<=t)
{
int v=q[h++];
for(int i=head[v];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
{
int u=edge[i].to;
if(pre[u]==-1 && edge[i].flow>0)
{
pre[u]=v;
rec[u]=i;
mins[u]=min(mins[v],edge[i].flow);
q[++t]=u;
}
}
if(pre[T]!=-1) //直到找到了汇点T
return mins[T];//每次返回增广路径中,容量最小的值
}
return -1; // 不存在增广路径
}
int Edmonds_Karp()
{
int add,Maxflow=0;
while((add=bfs())!=-1) //算法直到无法找到增广路径时才停止
{
Maxflow+=add;
for(int i=T;i!=S;i=pre[i]) //修改残留网络
{
edge[rec[i]].flow-=add; //正向减去流量
edge[rec[i]^1].flow+=add;//反向增加流量
}
}
return Maxflow;
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d %d", &n, &m))
{
int i, j, k, s, e, c;
Init();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> s >> e >> c;
Add_edge(s, e, c);
}
S = 1; T = m;
cout << Edmonds_Karp() << endl;
}
return 0;
}