Android框架 使用DataBinding绑定View
Google Codelab 学习 databinding
https://developer.android.com/codelabs/android-databinding#0
一、 什么是 dataBinding
数据绑定库是一个 Android Jetpack 库,它允许您使用声明性格式而不是通过编程方式将XML布局中的UI组件绑定到应用程序中的数据源,从而减少了样板代码。dataBinding 可以很好的和 View Model 配合使用。这里就简单学习一下 dataBinding 防止碰到的时候看不懂。
二、dataBinding 的常见使用
1. Gradle 配置
android {
buildFeatures {
dataBinding = true
}
}
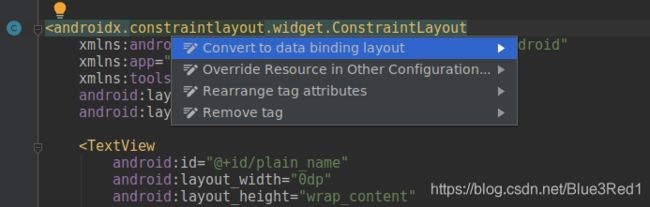
2. Layout 文件改写
<layout >
//原来的layout
layout>
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="24dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
...
LinearLayout>
layout>
3. Activity 文件改写
- 类名根据 xml 文件的名字生成
- xxxBinding
- 生成规则:activity_main.xml -> ActivityMainBinding
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ActivityMainBinding binding
= DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main);
}
}
4. 替换 fingViewById
- 规则:控件id first_Name -> firstName
- binding.xxxView
- 使用:binding.firstName == (TextView) findViewById(R.id.first_Name)
<TextView
android:id="@+id/first_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/last_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
binding.firstName.setText(student.getFirstName());
binding.lastName.setText(student.getLastName());
5. 数据绑定
xml 声明变量
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<variable
name="student"
type="com.test.databingding.Student" />
data>
<LinearLayout>
...
数据绑定
android:text="@{student.firstName}
<TextView
android:id="@+id/first_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{student.firstName}"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/last_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{student.lastName}"/>
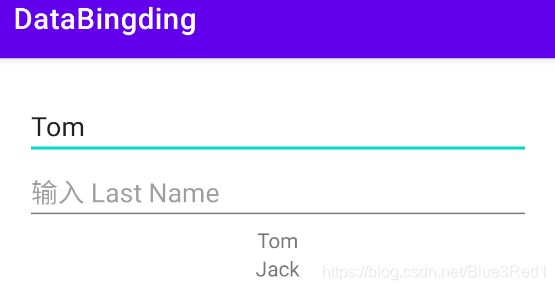
在代码中使用 setStudent 或者 setVariable 传入数据
binding.setStudent(student);
binding.setVariable(BR.student, student);
运行效果与上图相同
6. 事件绑定
处理点击事件1
使用 TextView 实时显示输入内容
- 创建内部类 Presenter 处理事件
public class Presenter {
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
student.setFirstName(s.toString());
binding.setStudent(student);
}
}
- xml
标签中中声明新的变量
<variable
name="presenter"
type="com.test.databingding.MainActivity.Presenter" />
- 调用 Java 代码中的事件方法
android:onTextChanged="@{presenter.onTextChanged}"
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onTextChanged="@{presenter.onTextChanged}"
android:hint="输入 First Name" />
- 向 dataBingding 中传入类
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
binding.setPresenter(new Presenter());
}
android:onClick="@{presenter.onClick}"
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="@{presenter.onClick}"
android:hint="输入 Last Name" />
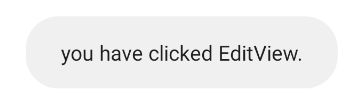
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
"you have clicked EditView.", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
android:onClick="@{() -> presenter.showToast(student)}"
这样使用可以传参数到 Java 代码中。
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:onClick="@{() -> presenter.showToast(student)}"
android:text="show name" />
public void showToast(Student student) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,
student.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
7. 表达式
- 一些运算符的例子
android:text="@{String.valueOf(index + 1)}"
android:visibility="@{age < 13 ? View.GONE : View.VISIBLE}"
android:transitionName='@{"image_" + id}' - 调用成员变量
android:text="@{viewmodel.name}" - 调用方法
android:visibility="@{viewmodel.nameVisible}" - 调用带参数的方法
android:onClick="@{() -> viewmodel.onLike(param)}"
-取非空表达式
android:onClick="@{user.name ?? user.newName)}"
8. 空指针检测
查看 dataBinding 的源码可以发现,它会自动帮我们进行空指针检查。
ActivityMainBindingImpl 类中的 executeBindings() 方法可以查看。
...
if ((dirtyFlags & 0x6L) != 0) {
if (student != null) {
// read student.lastName
studentLastName = student.getLastName();
// read student.firstName
studentFirstName = student.getFirstName();
}
}
...
但注意但的是 xml 中如果引用的数组越界了是会产生异常的。
9. include
创建一个 include_demo.xml
<layout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools">
<data>
<variable
name="student"
type="com.test.databingding.Student" />
data>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="24dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/first_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{student.firstName}" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/last_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@{student.lastName}" />
LinearLayout>
layout>
在 activity_main.xml 中使用 include
<include
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
layout="@layout/include_demo"
app:student="@{student}"/>
app:student=“@{student}” 可以传入变量 include_demo.xml 中的 student
10. viewstub
创建一个 viewstub_demo.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/>
LinearLayout>
在 activity_main.xml 中使用 ViewStub
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/view_stub"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout="@layout/viewstub_demo"/>
在 MainActivity.java infate ViewStub
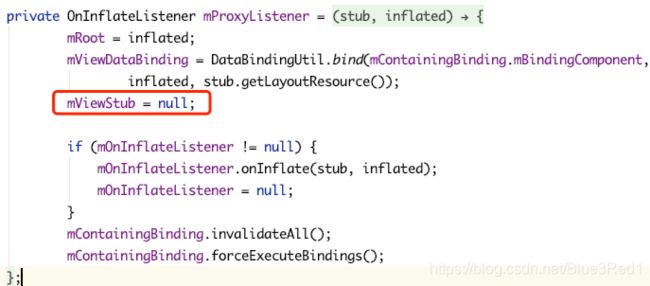
binding.viewStub.getViewStub().inflate();
这里要注意 viewstub 在 inflate 后会变为真正的 view,原来的 viewstub 会变为 null 所以不能重复 inflate。
11. observable
简单来说就是我的数据更新了,需要你刷新绑定该数据的控件。
使用 BaseObservab
使用 BaseObservab 的三个步骤
- 数据对象继承 BaseObservab 类
- 使用 @Bindable
- 调用方法 notifyPropertyChange()
在
public class Student extends BaseObservable {
...
@Bindable
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
//刷新指定的UI
notifyPropertyChanged(BR.firstName);
//刷新相关的全部UI
//notifyChange();
}
...
}
在 MainActivity.java 中修改之前的内部类
public class Presenter {
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
student.setFirstName(s.toString());
//binding.setStudent(student);
}
最后运行代码,可以发现现在数据变更就可以自动刷新变更的UI了,不需要再使用 binding.set。
Observable Collection
在不确定 Observable 里有多少数据时使用。
这里使用 ObservableArrayMap 来举例,ObservableArrayList 使用方法相同。
在 Student.java 中创建一个ObservableArrayMap
public class Student extends BaseObservable {
...
public ObservableArrayMap<String, String> user = new ObservableArrayMap<>();
public Student(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
user.put("Jack", "Rain");
}
...
}
在 xml 文件中引用变量
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text='@{student.user["Jack"]}' />
12. BR 文件
BR 是编译阶段生成的一个类,功能与 R.java 类似,用 @Bindable 标记过 getter 方法会在 BR 中生成一个 entry, 当数据发生变化时需要手动发出通知。 通过调用notifyPropertyChanged(BR.firstName)来通知系统 BR.firstName 这个 entry 的数据已经发生变化,需要更新 UI。