- 本文未授权 程序员灯塔 网站进行转载,且未注明出处,垃圾网站,偷我文章。
https://www.wangt.cc/2021/11/okhttp缓存篇
文章目录
- OkHttp
-
- Demo代码
- 流程图
- 拦截器 Interceptor
-
-
- RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor
- BridgeInterceptor
- CacheInterceptor
- ConnectInterceptor
- networkInterceptors
- CallServerInterceptor
- `CacheInterceptor`缓存详解
-
-
- Cache.java
- CacheStrategy.java 缓存策略
- okhttp3.Dispatcher 异步请求调度
- Http Header配置知识
-
-
- 查看http请求头的方式
- 常见配置项
- 缓存 Cache-Control
- 协商缓存`Last-Modify/If-Modify-Since`,`If-None-Match/ETag`
- Range和Content-Range
- User-Agent
- SSL加密方式配置
- RealCall类
- http2.0
- Java方法
- 未研究
OkHttp
- 官网文档: https://square.github.io/okhttp/
- 设计模式: 建造者模式、责任链模式
- 对象池,连接池
连接拦截器篇
- https://blog.csdn.net/followYouself/article/details/121086869
Demo代码
addInterceptor:应用层拦截器,在网络请求前拦截。addNetworkInterceptor:网络层拦截器,在发起网络请求后,进行拦截。callTimeout:本次请求的总体超时时间。包括connect、write、read等阶段时间。connectTimeout:连接阶段超时时间,默认10秒。配置tcp层socket参数,java.net.Socket#connect(java.net.SocketAddress, int)。参考Okhttp源码RealConnection#connectSocket。readTimeout:socket read函数超时时间,默认10秒。配置tcp层socket参数,java.net.Socket#setSoTimeout。参考Okhttp源码RealConnection#connectSocket。writeTimeout:连接阶段超时时间,默认10秒。
Interceptor interceptor = chain -> {
Request request = chain.request();
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
Log.i(TAG, String.format("Send request %s on %s%n%s", request.url(), chain.connection(), request.headers()));
Response response = chain.proceed(request);
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
Log.i(TAG, String.format("Received response for %s in %.1fms%n%s",
response.request().url(), (t2 - t1) / 1e6d, response.headers()));
return response;
};
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(interceptor)
.addNetworkInterceptor(interceptor)
.cache(new Cache(new File("/data/data/com.test.http/cache", "http_cache"), 50 * 1024 * 1024))
.callTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.connectTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.readTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.writeTimeout(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.eventListener(new EventListener(){})
.build();
CacheControl cacheControl = new CacheControl.Builder()
.noCache()
.maxAge(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)
.build();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://github.com/square/okhttp")
.cacheControl()
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.i(TAG, "onFailure " + call.request());
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
Log.i(TAG, "onResponse " + call.request() + ", Response Content" + response);
}
});
流程图
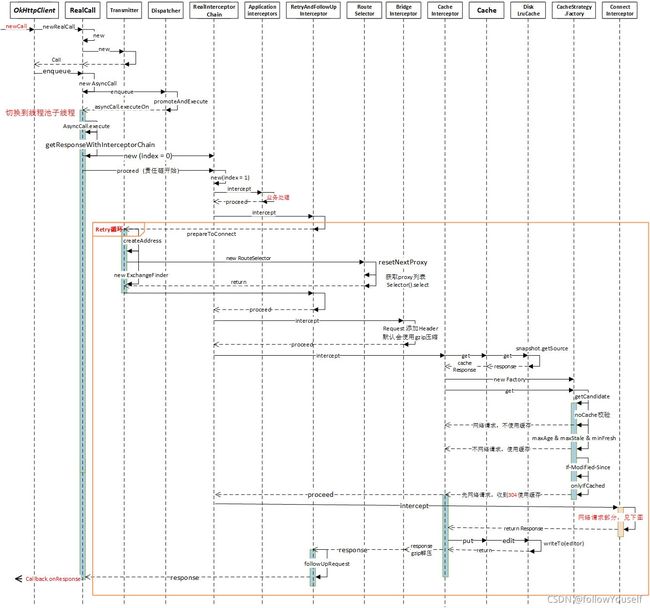
拦截器 Interceptor

- 官网文档: https://square.github.io/okhttp/interceptors/
- 缓存拦截器: https://juejin.cn/post/6845166891476992008
- 无论是异步请求还是同步请求都会通过
RealCall#getResponseWithInterceptorChain这个函数来遍历拦截器,发起网络请求。拦截器是按照添加顺序进行遍历的。
- 拦截器的遍历执行顺序:
client.interceptors()、RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor、BridgeInterceptor、CacheInterceptor、ConnectInterceptor、client.networkInterceptors()、CallServerInterceptor。
okhttp3.Interceptor.Chain接口的唯一实现类是RealInterceptorChain。通过该类的RealInterceptorChain#proceed(okhttp3.Request)实现遍历拦截器的操作。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(new RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client));
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, transmitter, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
boolean calledNoMoreExchanges = false;
try {
Response response = chain.proceed(originalRequest);
if (transmitter.isCanceled()) {
closeQuietly(response);
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
return response;
} catch (IOException e) {
calledNoMoreExchanges = true;
throw transmitter.noMoreExchanges(e);
} finally {
if (!calledNoMoreExchanges) {
transmitter.noMoreExchanges(null);
}
}
}
- 通过
index的累加,实现对interceptors的遍历。设计模式的责任链模式。
public Response proceed(Request request, Transmitter transmitter, @Nullable Exchange exchange)
throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, transmitter, exchange,
index + 1, request, call, connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
return response;
}
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor
- 默认情况下是会进行重试。默认的配置参数是
OkHttpClient.Builder#retryOnConnectionFailure(boolean)
- 重试、重定向拦截器
- 重定向函数
RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor#followUpRequest。做多重定向 20次
BridgeInterceptor
- 相对还比较简单,主要是想Http Header里面添加了一些字段配置。
- 最主要的是自动添加了
gzip压缩配置。同时对收到的数据解压缩
- 配置了
Connection:Keep-Alive代表需要长连接\
if (userRequest.header("Connection") == null) {
requestBuilder.header("Connection", "Keep-Alive");
}
boolean transparentGzip = false;
if (userRequest.header("Accept-Encoding") == null && userRequest.header("Range") == null) {
transparentGzip = true;
requestBuilder.header("Accept-Encoding", "gzip");
}
CacheInterceptor
- 参考
CacheInterceptor缓存详解章节。
ConnectInterceptor
- 参考
连接拦截器篇:https://blog.csdn.net/followYouself/article/details/121086869
networkInterceptors
- 自定义的网络解析拦截器。
- 在和服务器建立连接之后,在真正的发起网络请求之前进行拦截。
CallServerInterceptor
- 实际使用
Okio向服务器进行交互,进行request请求,接收response。
Http2相关的请求类 Http2Stream.java, Http2Reader,Http2Writer。
CacheInterceptor缓存详解
- 默认情况下,不开启任何缓存。开启缓存需要通过
OkHttpClient.Builder#cache(@Nullable Cache cache)方法进行配置,指定缓存File文件路径。
- okhttp只会对get请求进行缓存。
- url作为缓存的key信息。
CacheControl一些关键配置no-cache、no-store、max-age、only-if-cached、max-stale。参考下文Http header章节- 如果服务端不支持缓存配置,也可以source端实现缓存。可以通过
addNetworkInterceptor,在Response中增加cache-control,配置max-age(优先级高),Last-Modify(优先级低)等参数。参考源码CacheStrategy.Factory#computeFreshnessLifetime。
- 官网: https://square.github.io/okhttp/caching/
- 参考资料:https://juejin.cn/post/6850418120729985038。这个wiki有个问题,混淆了
noCache和noStore
Cache.java
get、put、remove、update分别对应缓存的读、写、删除、更新操作。DiskLruCache封装了缓存读写的能力,利用了Okio的读写能力。参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/zwlove5280/article/details/79916662- 缓存的键值是request的url。参考
okhttp3.Cache#key方法。
- Response的
Header信息存储在.0文件,body信息存储在.1文件,所有操作的日志记录在journal文件。
- 如何读写的细节以及
DiskLruCache细节没有研究。
CacheStrategy.java 缓存策略
- 根据request请求和缓存中的Response决定后续的网络请求步骤。关键方法是
CacheStrategy.Factory#get()、CacheStrategy.Factory#getCandidate()
- 这个类有两个成员变量
networkRequest 不为空,表示需要发起网络请求。null,则表示不需要网络请求。cacheResponse不为null,该缓存需要验证或者直接作为结果。为null,表示不使用缓存。
- 需要特别注意的是,如果
networkRequest不为空,同时request也配置了only-if-cached,那么会报504错误, Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)。
CacheStrategy#isCacheable,首先判断Response的状态码是否支持缓存,然后在检查Response和Request的header,如果配置了no-store,那么不支持缓存。- 缓存策略 之
CacheStrategy.Factory#getCandidate函数。代码中的注释 1,2,3分别与下面对应
- 如果在cache中没有找到
cacheResponse,那么需要网络请求。
- 如果是https请求,但是
cacheResponse中没有handshake,那么需要网络请求。
isCacheable判断cacheResponse中的状态码是否支持缓存,同时判断request请求是否配置了noStore。如果配置了noStore,那么禁止使用缓存。- 如果请求配置了
noCache或者配置了If-Modified-Since或者配置了If-None-Match,那么直接发起网络请求。根据CacheInterceptor.java代码,网络请求完成后,如果cacheResponse不为空,并且收到304状态码,那么使用cacheResponse作为请求结果。
- 根据
request的maxage、min-fresh、maxStale,以及根据cacheResponse的sentRequestAtMillis、receivedResponseAtMillis、servedDate、must-revalidate等配置,计算cacheResponse是否过期,是否满足本次的request的要求。如果满足,那么直接使用缓存作为网络请求的结果,不发起实际的网络请求。具体的计算细节没研究…
- 此处根据时间计算,判断是否使用缓存。
ageMillis:cacheResponse从生成到现在的耗时; minFreshMillis:最小新鲜度,距离最终过期的最短时间,request中配置;freshMillis:cacheResponse和request配置的max-age中的较小值;maxStaleMillis在超过max-age后,仍然可以接受的时间,request中配置。
- 在上述条件均没有满足,缓存也过期的情况下,依次 判断
cacheResponse是否携带了ETag、Last-Modified、Date等字段,转换为If-None-Match和If-Modified-Since字段,添加到request header中。
- 如果
networkRequest不为空,同时request也配置了only-if-cached,根据CacheInterceptor.java代码,会上报504错误, Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)。

public CacheStrategy get() {
CacheStrategy candidate = getCandidate();
if (candidate.networkRequest != null && request.cacheControl().onlyIfCached()) {
return new CacheStrategy(null, null);
}
return candidate;
}
private CacheStrategy getCandidate() {
if (cacheResponse == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
if (request.isHttps() && cacheResponse.handshake() == null) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
if (!isCacheable(cacheResponse, request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
CacheControl requestCaching = request.cacheControl();
if (requestCaching.noCache() || hasConditions(request)) {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
CacheControl responseCaching = cacheResponse.cacheControl();
long ageMillis = cacheResponseAge();
long freshMillis = computeFreshnessLifetime();
if (requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds() != -1) {
freshMillis = Math.min(freshMillis, SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxAgeSeconds()));
}
long minFreshMillis = 0;
if (requestCaching.minFreshSeconds() != -1) {
minFreshMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.minFreshSeconds());
}
long maxStaleMillis = 0;
if (!responseCaching.mustRevalidate() && requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds() != -1) {
maxStaleMillis = SECONDS.toMillis(requestCaching.maxStaleSeconds());
}
if (!responseCaching.noCache() && ageMillis + minFreshMillis < freshMillis + maxStaleMillis) {
Response.Builder builder = cacheResponse.newBuilder();
if (ageMillis + minFreshMillis >= freshMillis) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "110 HttpURLConnection \"Response is stale\"");
}
long oneDayMillis = 24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L;
if (ageMillis > oneDayMillis && isFreshnessLifetimeHeuristic()) {
builder.addHeader("Warning", "113 HttpURLConnection \"Heuristic expiration\"");
}
return new CacheStrategy(null, builder.build());
}
String conditionName;
String conditionValue;
if (etag != null) {
conditionName = "If-None-Match";
conditionValue = etag;
} else if (lastModified != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = lastModifiedString;
} else if (servedDate != null) {
conditionName = "If-Modified-Since";
conditionValue = servedDateString;
} else {
return new CacheStrategy(request, null);
}
Headers.Builder conditionalRequestHeaders = request.headers().newBuilder();
Internal.instance.addLenient(conditionalRequestHeaders, conditionName, conditionValue);
Request conditionalRequest = request.newBuilder()
.headers(conditionalRequestHeaders.build())
.build();
return new CacheStrategy(conditionalRequest, cacheResponse);
}
okhttp3.Dispatcher 异步请求调度
maxRequests最大并发请求数量,默认64。maxRequestsPerHost 每个主机host支持的最大并发请求数量,默认5。可配置。- 包含一个线程池
executorService,用于异步的网络请求调度。默认的配置为核心线程为0,最大线程数不限制,存活时间60秒。
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
Http Header配置知识
查看http请求头的方式
- 浏览器内,F12
- F5 刷新网页
- NetWork选项卡,Doc选项卡,在Name中选择一次请求
- 选择Headers选项卡。(和Header选项卡并列的有Preview、Response、Cookies)
常见配置项
Accept-Encoding:gzip 代表压缩编码数据Connection:Keep-Alive代表需要长连接
缓存 Cache-Control
no-cache:资源是可以被客户端缓存的,代理服务器不缓存。但是每次请求都需要先到服务端验证资源是否有效。相关配置参考Last-Modify / If-Modify-Sinceno-store:禁止任何形式的缓存。客户端和服务端均可进行配置生效。max-age:资源可以被缓存的时间,单位秒。max-age会覆盖掉expires。超期后,访问服务器校验有效性。s-maxage:设置代理服务器缓存的最大的有效时间,单位秒。s-maxage会覆盖掉max-age。public:表示当前的请求是一种通用的业务数据,客户端、代理服务器、中间节点服务器都可以缓存这些数据。private:默认值。表示当前的操作是和具体用户强相关的特殊行为,不应该在代理类服务器、中间节点服务器等进行缓存。因为缓存并没有很大的意义。only-if-cached:不进行网络请求,完全只使用缓存.如果缓存不命中,返回504错误。并且此处的优先级要高于no-cache,肯定不会发起网络请求了。must-revalidate: 资源一旦过期,则必须向服务器发起请求确认资源有效性。如果无法访问服务器,则上报 504 Gateway Timeout。优先级高于max-stale,设置之后max-stale变为无效。max-stale:客户端要求缓存代理该时间内(默认不限时间)的资源无论缓存有没有过期都返回给客户端。这个参数表示业务可以接受的响应的过期时间。no-transform:缓存代理不可更改媒体类型,这样可以防止压缩图片、压缩资源的操作min-fresh:距离缓存Response过期(max-age、max-stale之和)剩余的最小时间,保证取到缓存不会在短时间(min-fresh)内超期无效。比如max-age=100, max-stale=500,min-fresh=200。那么Response的max-age + max-stale和是600,由于配置了min-fresh,那么要求在使用缓存是,必须保证距离600这个最终过期时间点,保留200的新鲜度。600 - 200 = 400,那么也就是缓存的Response从缓存开始到现在nowTime最多度过了400的时间长度,才可以使用。- 参考资料 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000022336086
协商缓存Last-Modify/If-Modify-Since,If-None-Match/ETag
etag的校验优先级高于Last-Modify。Last-Modify:在服务器的Response中携带,表示业务数据上次被修改的时间If-Modify-Since:当缓存过期时,在客户端request请求时携带,服务器上检查request的请求时间,并校验服务器资源是否被修改。如果被修改,那么返回最新数据,并返回HTTP 200 OK。如果资源没有修改,那么仅仅返回状态码HTTP 304etag:服务器Response携带的资源tag。资源的任何修改都会导致tag的改变,如果tag不变,是可以表示资源数据没有变化的。If-None-Match:当缓存过期时,客户端request的请求中携带,携带的是缓存中Response的tag值。同样是根据tag判断资源数据是否被修改,相应客户端请求。
Range和Content-Range
- 范围参数,可以制定要从服务器获取文件的范围。
- 设计目的:用于断点续传。比如下载大文件时,网络突然中断,恢复网络时,可以继续下载内容。
User-Agent
- 代表用户行为的程序软件。比如,网页浏览器就是一个“帮助用户获取、渲染网页内容并与之交互”的用户代理;电子邮件阅读器也可以称作邮件代理。
- 举例
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/94.0.4606.61 Safari/537.36
SSL加密方式配置
- 配置函数
OkHttpClient#sslSocketFactory, 默认配置函数OkHttpClient#newSslSocketFactory。
- 分为Android平台和java平台,Android平台的配置函数是
AndroidPlatform#getSSLContext,源码如下
@Override
public SSLContext getSSLContext() {
boolean tryTls12;
try {
tryTls12 = (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 16 && Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < 22);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
tryTls12 = true;
}
if (tryTls12) {
try {
return SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.2");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
}
}
try {
return SSLContext.getInstance("TLS");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No TLS provider", e);
}
}
- CLEARTEXT是用于不安全配置的http://网址。
RealCall类

http2.0
- http2.0 和http1.0 的区别:http2.0支持多路复用,支持多个请求并发传输。http1.0是顺序执行的。发送一个请求之后,等到响应之后,才能发起下一个请求。
- http2.0中重要的概念是
帧(frame)和流(stream)。每一个流都是有一个独一无二的编号。
- HTTP2.0 消息头的压缩算法采用 HPACK。
- http2.0:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016975064
- http2.0:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903935648497678
Java方法
- java.lang.Thread#holdsLock 判断当前线程是否持有某个锁
未研究
- 各个版本的
http协议区别,协议的细节。
Okio开源库作为基础读写库,没有阅读源码。Okio的实现原理不了解,segment机制。DiskLruCache.java 文件缓存方案,没有阅读源码Http2Connection.java http2协议的连接,数据收发,stream使用相关信息



