Postman & Newman & Jenkins 持续集成自动化测试
介绍
Postman&Newman&Jenkins 持续集成自动化测试的文章主要讲解通过 postman 编写接口测试,结合 Newman 以及 Jenkins 进行自动化测试。postman 本身是不支持命令行执行的,恰好 Newman 填补了 postman 这个缺口,通过部署到 Jenkins 可以完成自动化测试。
postman
介绍略过….
postman 脚本函数介绍
postman 的所有函数是基于 node.js 运行。那么在编写 postman 的脚本都是 JavaScript 代码。
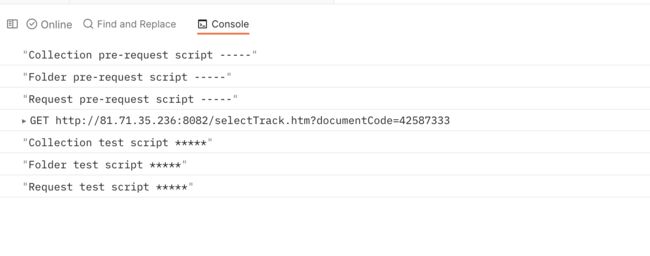
在 postman 中编写代码的地方有:collection,folder,request 里面的 pre-request-script 和 test。
postman 执行顺序
针对单个请求,请求的顺序如下:
在请求前会先执行 pre-request Script 里面的脚本
在请求后会执行 test 里面的脚本
针对整个 collection 里面的请求,那么请求的顺序如下:
先执行 collection 里面的 pre-request Script
再执行 folder 里面的 pre-request Script
最后执行 request 里面的 pre-request Script
请求完成之后,先执行 collection 里面的 test
再执行 folder 里面的 test
最终执行 request 里面的 test
上面主要介绍在 postman 中的脚本的执行顺序,主要针对 pre-request Script 和 Test 的函数在接下来实践。
postman 读取变量优先级
postman 读取变量的优先级:优先级 Global < Collection < Environment < Data < Local
这样设置的一个好处就是,在请求体中只需要设置一个参数,不需要变来变去。在 request 部分会讲到。
更多获取变量的方式:postman JavaScript reference
pre-request script 重点
运行前的脚本,在这里可以编写需要在运行前的脚本。在以下情况可能你会使用到请求前的脚本。
登录验证加密
切换环境变量
异步请求
场景一: 登录验证加密
现在有一个我们项目中,登录接口是通过 user token 登录的。前端页面需要填写 username 以及 password,再通过 js 进行 MD5 加密处理,最后请求接口验证返回登录状态。
api : /api/login
method : post
headers :
token: user_token
Content-Type: application/json生成 user_token 方式: username&psaaword 大写
上面就是接口文档说明的,要通过 md5 方式对 username&password 进行加密。那么在 pre-request script 里面,我们可以这样做。
var username = "[email protected]"
var password = "a123456"
var token= CryptoJS.MD5(username+'&'+password).toString().toUpperCase();//使用MD5()方法对变量 token 的内容加密,然后转成字符串,最后转成大写
pm.environment.set('user_token',token);//加密后的密码字符串赋值给环境变量 user_token点开环境变量会看到已经生成了 user_token 对应的加密 token 了。
场景二: 切换环境变量
下面的例子意思就是运行前根据环境环境变量设置对应的 url
var varbs = new Set()
pm.collectionVariables.values.each(v => {
varbs.add(v.key.toUpperCase())
})
pm.collectionVariables.values.each(v => {
let envVarbKey = [pm.environment.name, v.key].join("_").toUpperCase()
if (varbs.has(envVarbKey)) {
pm.collectionVariables.set(v.key, pm.collectionVariables.get(envVarbKey))
}
});
// console.log(pm.request.headers)
// console.log(pm.environment.name)
console.log(pm.environment.name.toUpperCase()) // 将环境变量名改成大写 ,返回大写变量
console.log(pm.variables.has("TEST_HOST")) // 验证是否含有变量名 True| False
console.log(pm.variables.get("HOST")) // 获取变量名
console.log(pm.variables.set("TEST_HOST","https://www.baidu.com")) //设置变量的值,前提是这个变量得存在。官方:设置具有指定名称和值的局部变量
//返回脚本内动态变量的解析值
const stringWithVars = pm.variables.replaceIn("Hi, my name is {{$randomFirstName}}");
console.log(stringWithVars)
console.log(pm.collectionVariables.get("HOST")) //获取 collection 的变量
console.log(pm.globals.get("token")) //获取 global 的变量
// 优先级 Global < Collection < Environment < Data < Local场景三: 获取另外接口的响应值并进行更新
在请求的时候,需要获取到另外一个接口的响应值,并将响应值作为当前 request 的参数。
在这里,pre-request script 不仅仅能写函数,还能写请求函数。
// Refresh the OAuth token if necessary
var tokenDate = new Date(2022,9,3);
var tokenTimestamp = pm.environment.get("OAuth_Timestamp");
if(tokenTimestamp){
tokenDate = Date.parse(tokenTimestamp);
}
var expiresInTime = pm.environment.get("ExpiresInTime");
if(!expiresInTime){
expiresInTime = 300000; // Set default expiration time to 5 minutes
}
if((new Date() - tokenDate) >= expiresInTime)
{
pm.sendRequest({
url: pm.variables.get("Auth_Url"),
method: 'POST',
header: {
'Accept': 'application/json',
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded',
'Authorization': pm.variables.get("Basic_Auth")
}
}, function (err, res) {
try{
pm.environment.set("OAuth_Token", res.json().access_token);
pm.environment.set("OAuth_Timestamp", new Date());
// Set the ExpiresInTime variable to the time given in the response if it exists
if(res.json().expires_in){
expiresInTime = res.json().expires_in * 1000;
}
pm.environment.set("ExpiresInTime", expiresInTime);
}
catch(e) {
console.log('Unable to load access token from response);
}
});
}
这里面的函数,主要是通过检索 token 是否过期,重新生成 token 的请求方法。比较简单理解。
检查 token 是否过期
如果过期,就生成新的 token
将新的 token 设置到环境变量,然后记录设置的时间
tests 模块应用
test 断言规范
这里说明一下,在过去的版本中,可能还有很多小伙伴使用的断言方式是这样的,例如断言一个响应体里面是否包含 user_id :
tests["Body contains user_id"] = responsebody.has("user_id");在新版本中,postman 官方已经不推荐使用这种方式断言
新的断言方式应该是这样的,在 pm.test 的函数下包含 pm.expect 的断言:
pm.test("Status code is 200", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.code).to.eql(200);
});当然,这是官方不推荐,并不是说官方停止。目前来说,两种方式的断言还是可以用的。
test 断言语法
对于 http/https 请求来说,现在很多公司都是使用 json 作为响应体,postman 不仅仅支持 json 的断言,还有包括 xml,html,csv 都可以进行断言,所有格式都会解析成 postman 认识的 js 内容。
# 响应体为 json
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
# 响应体为 xml
const responseJson = xml2Json(pm.response.text());
# 响应体为 html
const $ = cheerio.load(pm.response.text());
//output the html for testing
console.log($.html());
# 响应体为 csv
const parse = require('csv-parse/lib/sync');
const responseJson = parse(pm.response.text());
断言状态码
pm.test("Status code is 201", () => {
pm.response.to.have.status(200);
});
如果您想测试状态代码是否是一组中的一个,请将它们全部包含在一个数组中并使用oneOf
pm.test("Successful POST request", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.code).to.be.oneOf([201,202]);
});
断言请求体
pm.test("Content-Type header is present", () => {
pm.response.to.have.header("Content-Type");
});
测试具有特定值的响应标头
pm.test("Content-Type header is application/json", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.headers.get('Content-Type')).to.eql('application/json');
});
断言响应体
pm.test("Person is Jane", () => {
const responseJson = pm.response.json();
pm.expect(responseJson.name).to.eql("Jane");
pm.expect(responseJson.age).to.eql(23);
});
断言响应时间
pm.test("Response time is less than 200ms", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.responseTime).to.be.below(200);
});
上面举部分例子说明断言的用法,具体更多断言语法可以查看 Chai 断言库文档
test 常见断言
断言响应值的类型
根据响应体返回的 value 的类型进行断言,检查返回的类型是否符合我们的期待类型。当然这部分需要跟 api 文档描述的一致。
/* response has this structure:
{
"name": "Postman",
"age": 18,
"hobbies": [
"skating",
"painting"
],
"email": null
}
*/
const jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.test("Test data type of the response", () => {
pm.expect(jsonData).to.be.an("object");
pm.expect(jsonData.name).to.be.a("string");
pm.expect(jsonData.age).to.be.a("number");
pm.expect(jsonData.hobbies).to.be.an("array");
pm.expect(jsonData.website).to.be.undefined;
pm.expect(jsonData.email).to.be.null;
});
断言数组属性
检查数组是否为空,以及它是否包含特定值:
/*
response has this structure:
{
"errors": [],
"areas": [ "goods", "services" ],
"settings": [
{
"type": "notification",
"detail": [ "email", "sms" ]
},
{
"type": "visual",
"detail": [ "light", "large" ]
}
]
}
*/
const jsonData = pm.response.json();
pm.test("Test array properties", () => {
//errors array is empty
pm.expect(jsonData.errors).to.be.empty;
//areas includes "goods"
pm.expect(jsonData.areas).to.include("goods");
//get the notification settings object
const notificationSettings = jsonData.settings.find
(m => m.type === "notification");
pm.expect(notificationSettings)
.to.be.an("object", "Could not find the setting");
//detail array must include "sms"
pm.expect(notificationSettings.detail).to.include("sms");
//detail array must include all listed
pm.expect(notificationSettings.detail)
.to.have.members(["email", "sms"]);
});
断言对象属性
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.all.keys('a', 'b');
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.have.any.keys('a', 'b');
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.not.have.any.keys('c', 'd');
pm.expect({a: 1}).to.have.property('a');
pm.expect({a: 1, b: 2}).to.be.an('object')
.that.has.all.keys('a', 'b');
断言一个值在一个集合中
pm.test("Value is in valid list", () => {
pm.expect(pm.response.json().type)
.to.be.oneOf(["Subscriber", "Customer", "User"]);
});
断言包含一个对象
/*
response has the following structure:
{
"id": "d8893057-3e91-4cdd-a36f-a0af460b6373",
"created": true,
"errors": []
}
*/
pm.test("Object is contained", () => {
const expectedObject = {
"created": true,
"errors": []
};
pm.expect(pm.response.json()).to.deep.include(expectedObject);
});
test 验证响应体结构
很多小伙伴应该遇到过一种情况,就是我希望可以验证响应的结构是否符合我期待的结构,而不是响应体里面的值。
postman 提供了两种方式对 json 的结构体进行验证
使用 Tiny Validator V4 (tv4) 执行 JSON 模式验证:
const schema = {
"items": {
"type": "boolean"
}
};
const data1 = [true, false];
const data2 = [true, 123];
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data1, schema)).to.be.true;
pm.expect(tv4.validate(data2, schema)).to.be.true;
});
使用 Ajv JSON 模式验证器验证 JSON 模式:
const schema = {
"properties": {
"alpha": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
};
pm.test('Schema is valid', function() {
pm.response.to.have.jsonSchema(schema);
});
test setNextrequest()
可能在使用 postman 的过程中,有些小伙伴比较疑惑,如果我写了很多 request 了,但是在执行 collection 的时候,执行的顺序并不是我期待的那种,这样应该怎么解决呢?在 postman 中,我们可以在 tests 模块下,编写我们需要执行下一步 request 的方法,告诉 postman 我们下一步应该执行哪一个接口.
postman.setNextRequest("get user credentials");这样在执行完当前的接口时,postman 会执行下一个接口。request_name 指的是我们保存下来的 request 的名称。
test 实践应用
// 读取的 slug 名称
var body = pm.request
var slug = body.url.path[2]
var subcode = 20000
var jsonData = pm.response.json();
var trackings = jsonData.data.trackings[0]
var checkpoints = jsonData.data.trackings[0].checkpoints
//验证返回为 20000
var success_code = slug + " - 验证返回 20000"
pm.test(success_code, function () {
pm.expect(jsonData.data.trackings[0].status.subcode).to.eql(subcode);
});
// 验证 response 返回不包含异常码
var response_code = slug + "返回码不包含以下异常码"
var error_code = [60200, 80100, 42203, 60100, 42901, 70100, 70200, 70300, 80200, 40000, 42201,42202, 40300, 40400, 40800, 42900, 50000, 50200, 50300, 50400, 50401, 50402,50001, 41201, 42204, 42205, 42206]
pm.test(response_code, function () {
pm.expect(jsonData.data.trackings[0].status.subcode).to.not.be.oneOf(error_code);
});
// 验证 message 不包含前端标签
var fronted_tag = ["href","&","not found",""]
// console.log(message)
var list = []
for (var i=0;i < checkpoints.length;i++){
// console.log("list:",checkpoints[i].message);
for (var f = 0; f < fronted_tag.length;f++){
pm.test("验证 meesage 不包含前端标签"+checkpoints[i].message, function () {
pm.expect(checkpoints[i].message).to.not.contain(fronted_tag[f]);
}
)}
}
// 验证 date_time 不为空
var verify_date_time = null
var date_time_list =[]
for (var i=0;i < checkpoints.length;i++){
date_time_list.push(checkpoints[i].date_time)
}
pm.test("验证 date_time 不为空", function () {
pm.expect(date_time_list).to.not.include(verify_date_time);
})
// 如果 scheduled_delivery_date_time 不为空,验证时间为 2022。
// 到了明年需要修改期望值
scheduled_delivery_date_time = trackings.scheduled_delivery_date_time.date
sd_date = scheduled_delivery_date_time.split("-")
if (scheduled_delivery_date_time != null){
pm.test("验证 scheduled_delivery_date_time 为 2022 年", function(){
pm.expect(sd_date[0]).to.eql("2022")
})
}更多相关的断言的语法可以参考:ChaiJS BDD
newman 在命令运行集合
Newman 是 Postman 的命令行 Collection Runner。它使您能够直接从命令行运行和测试 Postman 集合。它在构建时考虑了可扩展性,因此您可以将其与您的持续集成服务器和构建系统集成。
安装 newman
npm install -g newmannewman 执行测试
newman run courier.json -e env.json -r cli,html,json,junit --reporter-html-export report.html更多关于 newman 命令:newman option
Jenkins 持续集成
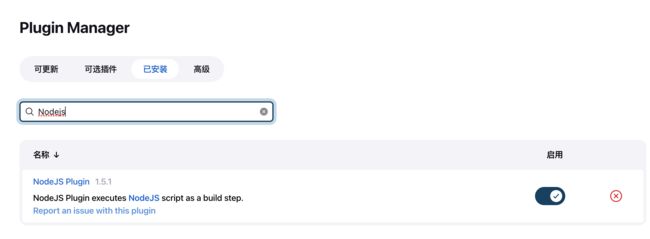
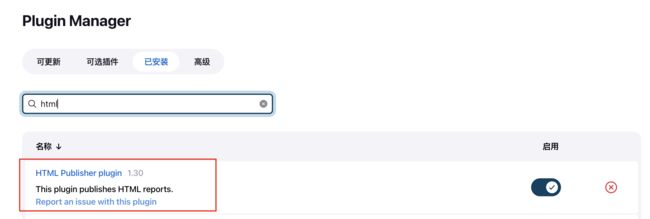
安装插件
Nodejs安装完成之后,还需要配置版本以及安装 Newman
路由到DashBoard —> 系统管理 —> 全局工具配置 ,拉到底部的 NodeJS 配置,安装 npm 包填上 newman,保存
Groovy
HTML Publisher
配置工程
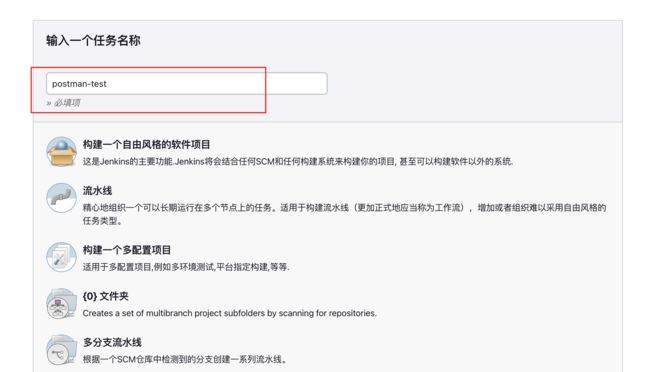
创建工程,输入工程名字,在下面选择构建一个自由风格的软件项目 ,点击确定
2.选择使用自定义的工作空间因为我这里是使用本地执行项目的方式,所以在这里我把我的本地项目地址放进去。/Users/bw.ling/myself/postman-test
3.拉到构建环境 节点,选择 Provide Node & npm bin/ folder to PATH ,如果没有安装 Nodejs 插件就不会有这个选项。
4.拉到Build Steps ,选择执行 shell,直接执行刚才我们写在 shell 里面的脚本即可
5.还是Build Steps,选择 Execute system Groovy script ,把System.setProperty("hudson.model.DirectoryBrowserSupport.CSP", "")贴上去,主要是为了兼容报告的样式,要不然会出现样式混乱的情况
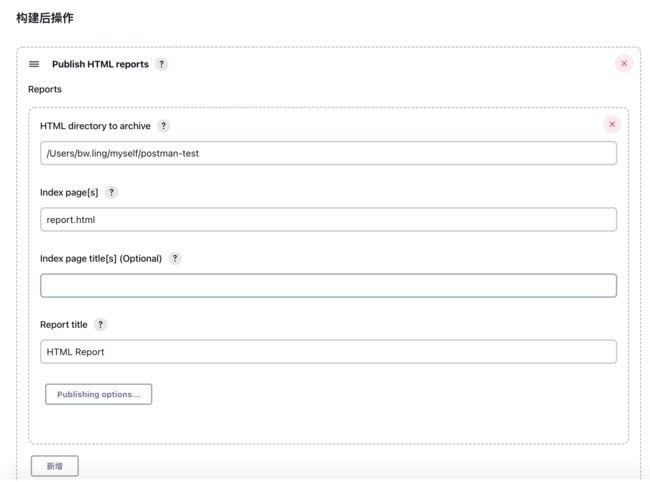
6.拉到构建后操作,选择 Publish HTML Reports,把你的项目存放的报告地址贴上去,把 index.html 更改成你的项目报告名字即可
7.执行构建,查看报告
扩展
postman 加解密方法
MD5加密
CryptoJS.MD5("待加密数据").toString();SHA256加密
CryptoJS.SHA256("待加密数据").toString();HmacSHA256加密
CryptoJS.HmacSHA256("待加密数据", "秘钥")base64加密解密
// 加密 写法1
var utf8Str = CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("待加密字符串")
CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify(utf8Str)
// 加密 写法2
CryptoJS.enc.Utf8.parse("待加密字符串").toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64)
// 解密
CryptoJS.enc.Base64.parse("带解密").toString(CryptoJS.enc.Utf8)
// CryptoJS.enc.Base64.stringify("字符串") 和 "字符串".toString(CryptoJS.enc.Base64) 是相同的含义AES简单加密解密
// 加密
CryptoJS.AES.encrypt('待加密字符串', '秘钥').toString()
// 解密
CryptoJS.AES.decrypt('待解密字符串', '秘钥').toString(CryptoJS.enc.Utf8)