【GPLT】【2022天梯赛真题题解】
L1-1 今天我要赢(5分)
题目描述
2018 年我们曾经出过一题,是输出“2018 我们要赢”。今年是 2022 年,你要输出的句子变成了“我要赢!就在今天!”然后以比赛当天的日期落款。
输入格式:
本题没有输入。
输出格式:
输出分 2 行。在第一行中输出 I’m gonna win! Today!,在第二行中用 年年年年-月月-日日 的格式输出比赛当天的日期。已知比赛的前一天是 2022-04-22。
输入样例:
无
输出样例(第二行的内容要你自己想一想,这里不给出):
I’m gonna win! Today!
这一行的内容我不告诉你…… 你要自己输出正确的日期呀~
代码
#include L1-2 种钻石(5分)
题目描述
2019年10月29日,中央电视台专题报道,中国科学院在培育钻石领域,取得科技突破。科学家们用金刚石的籽晶片作为种子,利用甲烷气体在能量作用下形成碳的等离子体,慢慢地沉积到钻石种子上,一周“种”出了一颗 1 克拉大小的钻石。
本题给出钻石的需求量和人工培育钻石的速度,请你计算出货需要的时间。
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出钻石的需求量 N N N(不超过 1 0 7 10^7 107的正整数,以微克拉为单位)和人工培育钻石的速度 v v v( 1 ≤ v ≤ 200 1≤v≤200 1≤v≤200,以微克拉/天为单位的整数)。
输出格式:
在一行中输出培育 N N N 微克拉钻石需要的整数天数。不到一天的时间不算在内。
输入样例:
102000 130
输出样例:
784
代码
#include L1-3 谁能进图书馆(10分)
题目描述
为了保障安静的阅读环境,有些公共图书馆对儿童入馆做出了限制。例如“12 岁以下儿童禁止入馆,除非有 18 岁以上(包括 18 岁)的成人陪同”。现在有两位小/大朋友跑来问你,他们能不能进去?请你写个程序自动给他们一个回复。
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出 4 个整数:
禁入年龄线 陪同年龄线 询问者1的年龄 询问者2的年龄
这里的禁入年龄线是指严格小于该年龄的儿童禁止入馆;陪同年龄线是指大于等于该年龄的人士可以陪同儿童入馆。默认两个询问者的编号依次分别为 1 和 2;年龄和年龄线都是 [1, 200] 区间内的整数,并且保证 陪同年龄线 严格大于 禁入年龄线。
输出格式:
在一行中输出对两位询问者的回答,如果可以进就输出 年龄-Y,否则输出 年龄-N,中间空 1 格,行首尾不得有多余空格。
在第二行根据两个询问者的情况输出一句话:
- 如果两个人必须一起进,则输出
qing X zhao gu hao Y,其中 X 是陪同人的编号, Y 是小孩子的编号; - 如果两个人都可以进但不是必须一起的,则输出
huan ying ru guan; - 如果两个人都进不去,则输出
zhang da zai lai ba; - 如果一个人能进一个不能,则输出
X: huan ying ru guan,其中 X 是可以入馆的那个人的编号。
输入样例1:
12 18 18 8
输出样例1:
18-Y 8-Y
qing 1 zhao gu hao 2
输入样例 2:
12 18 10 15
输出样例 2:
10-N 15-Y
2: huan ying ru guan
代码
#include L1-4 拯救外星人(10分)
题目描述

你的外星人朋友不认得地球上的加减乘除符号,但是会算阶乘 —— 正整数 N N N 的阶乘记为 “ N ! N! N!”,是从 1 1 1到 N N N 的连乘积。所以当他不知道“ 5 + 7 5+7 5+7”等于多少时,如果你告诉他等于“ 12 ! 12! 12!”,他就写出了“ 479001600 479001600 479001600”这个答案。
本题就请你写程序模仿外星人的行为。
输入格式:
输入在一行中给出两个正整数 A A A和 B B B。
输出格式:
在一行中输出 ( A + B ) (A+B) (A+B)的阶乘。题目保证 ( A + B ) (A+B) (A+B) 的值小于 12 12 12。
输入样例:
3 6
输出样例:
362880
代码
#include L1-5 试试手气(15分)
题目描述

我们知道一个骰子有 6 个面,分别刻了 1 到 6 个点。下面给你 6 个骰子的初始状态,即它们朝上一面的点数,让你一把抓起摇出另一套结果。假设你摇骰子的手段特别精妙,每次摇出的结果都满足以下两个条件:
- 1、每个骰子摇出的点数都跟它之前任何一次出现的点数不同;
- 2、在满足条件 1 的前提下,每次都能让每个骰子得到可能得到的最大点数。
那么你应该可以预知自己第 n n n 次 ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 5 ) (1≤n≤5) (1≤n≤5)摇出的结果。
输入格式:
输入第一行给出 6 6 6 个骰子的初始点数,即 [ 1 , 6 ] [1,6] [1,6] 之间的整数,数字间以空格分隔;第二行给出摇的次数 n n n ( 1 ≤ n ≤ 5 ) (1≤n≤5) (1≤n≤5)。
输出格式:
在一行中顺序列出第 $n $次摇出的每个骰子的点数。数字间必须以 1 个空格分隔,行首位不得有多余空格。
输入样例:
3 6 5 4 1 4
3
输出样例:
4 3 3 3 4 3
分析
可以硬模拟,也可以用数学推一推,但是模拟太好写了就直接无脑模了。
代码
#include L1-6 斯德哥尔摩火车上的题(15分)
题目描述
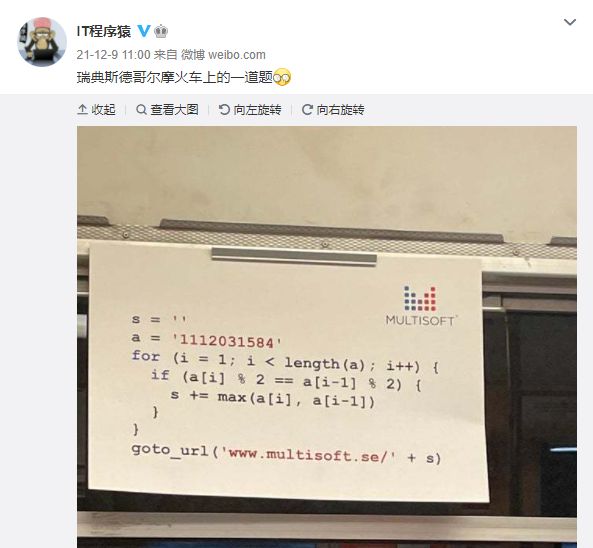
上图是新浪微博上的一则趣闻,是瑞典斯德哥尔摩火车上的一道题,看上去是段伪代码:
s = ‘’
a = ‘1112031584’
for (i = 1; i < length(a); i++) {
if (a[i] % 2 == a[i-1] % 2) {
s += max(a[i], a[i-1])
}
}
goto_url(‘www.multisoft.se/’ + s)
其中字符串的 + 操作是连接两个字符串的意思。所以这道题其实是让大家访问网站 www.multisoft.se/112358(注意:比赛中千万不要访问这个网址!!!)。
当然,能通过上述算法得到 112358 的原始字符串 a 是不唯一的。本题就请你判断,两个给定的原始字符串,能否通过上述算法得到相同的输出?
输入样例 1:
1112031584
011102315849
输出样例 1:
112358
输入样例 2:
111203158412334
12341112031584
输出样例 2:
1123583
112358
分析
字符串处理题,伪代码都给出来了,属于是送分。
代码
#include L1-7 机工士姆斯塔迪奥(20分)
题目描述
在 MMORPG《最终幻想14》的副本“乐欲之所瓯博讷修道院”里,BOSS 机工士姆斯塔迪奥将会接受玩家的挑战。
你需要处理这个副本其中的一个机制: N × M N×M N×M 大小的地图被拆分为了 N × M N×M N×M 个 1 × 1 1×1 1×1 的格子,BOSS 会选择若干行或/及若干列释放技能,玩家不能站在释放技能的方格上,否则就会被击中而失败。
给定 BOSS 所有释放技能的行或列信息,请你计算出最后有多少个格子是安全的。
输入格式:
输入第一行是三个整数 N , M , Q ( 1 ≤ N × M ≤ 1 0 5 , 0 ≤ Q ≤ 1000 ) N,M,Q (1≤N×M≤10^5,0≤Q≤1000) N,M,Q(1≤N×M≤105,0≤Q≤1000),表示地图为 N N N行 M M M列大小以及选择的行/列数量。
接下来 Q Q Q行,每行两个数 T i T_i Ti , C i C _i Ci,其中 T i = 0 T_i=0 Ti=0 表示 BOSS 选择的是一整行, T i = 1 T_i =1 Ti=1 表示选择的是整列, C i C _i Ci为选择的行号/列号。行和列的编号均从 1 1 1 开始。
输出格式:
输出一个数,表示安全格子的数量。
输入样例:
5 5 3
0 2
0 4
1 3
输出样例:
12
分析
很简单的题意,主要坑点就是有可能BOSS技能的位置会有重复输入,重复的数据不处理就好
代码
#include L1-8 静静的推荐(20分)
题目描述
天梯赛结束后,某企业的人力资源部希望组委会能推荐一批优秀的学生,这个整理推荐名单的任务就由静静姐负责。企业接受推荐的流程是这样的:
- 只考虑得分不低于 175 分的学生;
- 一共接受 K K K 批次的推荐名单;
- 同一批推荐名单上的学生的成绩原则上应严格递增;
- 如果有的学生天梯赛成绩虽然与前一个人相同,但其参加过 PAT 考试,且成绩达到了该企业的面试分数线,则也可以接受。
给定全体参赛学生的成绩和他们的 PAT 考试成绩,请你帮静静姐算一算,她最多能向企业推荐多少学生?
输入格式:
输入第一行给出 3 个正整数: N ( ≤ 1 0 5 ) N(≤10^5) N(≤105)为参赛学生人数, K ( ≤ 5 × 1 0 3 ) K(≤5×10^3) K(≤5×103)为企业接受的推荐批次, S ( ≤ 100 ) S(≤100) S(≤100)为该企业的 PAT 面试分数线。
随后 N N N 行,每行给出两个分数,依次为一位学生的天梯赛分数(最高分 290)和 PAT 分数(最高分 100)。
输出格式:
在一行中输出静静姐最多能向企业推荐的学生人数。
输入样例:
10 2 90
203 0
169 91
175 88
175 0
175 90
189 0
189 0
189 95
189 89
256 100
输出样例:
8
样例解释:
第一批可以选择 175、189、203、256 这四个分数的学生各一名,此外 175 分 PAT 分数达到 90 分的学生和 189 分 PAT 分数达到 95 分的学生可以额外进入名单。第二批就只剩下 175、189 两个分数的学生各一名可以进入名单了。最终一共 8 人进入推荐名单。
分析
很有意思的一个题,第一次做这个题很容易纠结在 如果有的学生天梯赛成绩虽然与前一个人相同,但其参加过 PAT 考试,且成绩达到了该企业的面试分数线,则也可以接受。 ”这句话里面的与前一个人相同,可能会不断扫描所有学生,写出一个模拟来判断前一个人的分数。可事实上这个人是哪个人并不重要,问的是人数,又没问推哪个人。
那么其实就可以将175~290的每个分数映射到数组下标,然后从175一直遍历到290。其中有个小细节就是如果天梯赛满足175并且PTA也达到了企业的要求,那么其实这一批人就可以全部跟着上一个分数相同但是PTA不达标的人一起进入同一个推荐名单。
如果样例数据是这样的
175 0
175 90
175 91
175 92
175 93
这批五个175分的学生其实就可以在同一个推荐名单里面
代码
#include L2-1 插松枝(25分)
题目描述
人造松枝加工场的工人需要将各种尺寸的塑料松针插到松枝干上,做成大大小小的松枝。他们的工作流程(并不)是这样的:
- 每人手边有一只小盒子,初始状态为空。
- 每人面前有用不完的松枝干和一个推送器,每次推送一片随机型号的松针片。
- 工人首先捡起一根空的松枝干,从小盒子里摸出最上面的一片松针 —— 如果小盒子是空的,就从推送器上取一片松针。将这片松针插到枝干的最下面。
- 工人在插后面的松针时,需要保证,每一步插到一根非空松枝干上的松针片,不能比前一步插上的松针片大。如果小盒子中最上面的松针满足要求,就取之插好;否则去推送器上取一片。如果推送器上拿到的仍然不满足要求,就把拿到的这片堆放到小盒子里,继续去推送器上取下一片。注意这里假设小盒子里的松针片是按放入的顺序堆叠起来的,工人每次只能取出最上面(即最后放入)的一片。
- 当下列三种情况之一发生时,工人会结束手里的松枝制作,开始做下一个:
(1)小盒子已经满了,但推送器上取到的松针仍然不满足要求。此时将手中的松枝放到成品篮里,推送器上取到的松针压回推送器,开始下一根松枝的制作。
(2)小盒子中最上面的松针不满足要求,但推送器上已经没有松针了。此时将手中的松枝放到成品篮里,开始下一根松枝的制作。
(3)手中的松枝干上已经插满了松针,将之放到成品篮里,开始下一根松枝的制作。
现在给定推送器上顺序传过来的 N N N 片松针的大小,以及小盒子和松枝的容量,请你编写程序自动列出每根成品松枝的信息。
输入格式:
输入在第一行中给出 3 3 3 个正整数: N ( ≤ 1 0 3 ) N(≤10^3) N(≤103),为推送器上松针片的数量; M ( ≤ 20 ) M(≤20) M(≤20)为小盒子能存放的松针片的最大数量; K ( ≤ 5 ) K(≤5) K(≤5)为一根松枝干上能插的松针片的最大数量。
随后一行给出 N N N 个不超过 100 100 100 的正整数,为推送器上顺序推出的松针片的大小。
输出格式:
每支松枝成品的信息占一行,顺序给出自底向上每片松针的大小。数字间以 1 1 1 个空格分隔,行首尾不得有多余空格。
输入样例:
8 3 4
20 25 15 18 20 18 8 5
输出样例:
20 15
20 18 18 8
25 5
分析
开两个容器硬模拟推送器和小盒子,注意一下条件不然可能或出现段错误
代码
#include L2-2 老板的作息表(25分)
题目描述
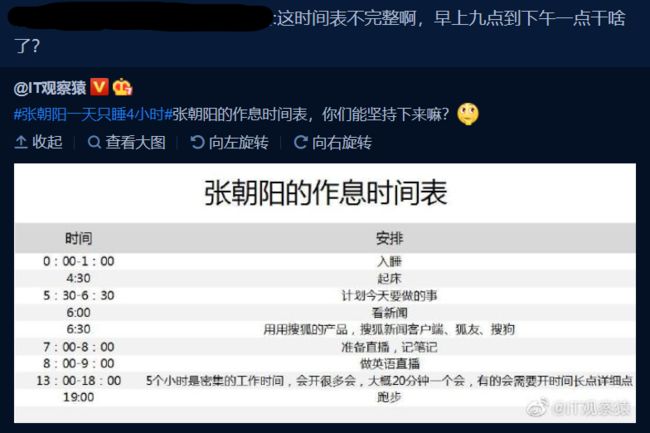
新浪微博上有人发了某老板的作息时间表,表示其每天 4:30 就起床了。但立刻有眼尖的网友问:这时间表不完整啊,早上九点到下午一点干啥了?
本题就请你编写程序,检查任意一张时间表,找出其中没写出来的时间段。
输入格式:
输入第一行给出一个正整数 N N N,为作息表上列出的时间段的个数。随后 N N N 行,每行给出一个时间段,格式为:
hh:mm:ss - hh:mm:ss
其中 hh、mm、ss 分别是两位数表示的小时、分钟、秒。第一个时间是开始时间,第二个是结束时间。题目保证所有时间都在一天之内(即从 00:00:00 到 23:59:59);每个区间间隔至少 1 秒;并且任意两个给出的时间区间最多只在一个端点有重合,没有区间重叠的情况。
输出格式:
按照时间顺序列出时间表中没有出现的区间,每个区间占一行,格式与输入相同。题目保证至少存在一个区间需要输出。
输入样例:
8
13:00:00 - 18:00:00
00:00:00 - 01:00:05
08:00:00 - 09:00:00
07:10:59 - 08:00:00
01:00:05 - 04:30:00
06:30:00 - 07:10:58
05:30:00 - 06:30:00
18:00:00 - 19:00:00
输出样例:
04:30:00 - 05:30:00
07:10:58 - 07:10:59
09:00:00 - 13:00:00
19:00:00 - 23:59:59
分析
考点很简单就是排序(但是我第一反应是一个不需要排序的邪道写法最后还A了 )
将所有的时间存起来然后排序再扫描一遍即可,排序可以手写重载也可以用vector的默认排序,数据量大建议手写,容器自带的排序还是慢了点。
代码
#include 剩下有空了再摸