基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 (二) —— OpenCV的使用
计算机视觉领域的应用一般都会以OpenCV为基础。产品里我们使用OpenCV来做图像的读写、色彩变化、图像截取和拼接、图像畸变矫正、轮廓分析,另外还有图像矩阵的均值、标准差的计算和图像矩阵加减乘除运算等。
OpenCV在Java项目中的配置
服务端用的SpringBoot,所以需要在SpringBoot项目里使用OpenCV。OpenCV没有Java版本的实现,但提供了JNI来调用 C 编译出的动态库。缺点是引入麻烦,优点是 C语言对于包含大量矩阵计算的图形操作执行速度很快。
Windows
开发环境用的windows10,首先下载安装windows版本的OpenCV,然后在安装目录 opencv\build\java 下找到opencv-xxx.jar 和 opencv_javaxxx.dll (xxx是版本号)两个文件。
jar文件可copy到项目的resource目录中,我放到 src\main\resources\lib.opencv目录下。这个jar里面封装了对底层 C 方法调用接口,在Windows和Linux环境下通用。
另外的 opencv_javaxxx.dll 文件需要复制到 C:\Windows\System32 目录下。要将jar添加到项目依赖的库中,还需要在pom.xml中增加 dependency 配置:
...
org
opencv
4.5.3
system
${pom.basedir}/src/main/resources/lib.opencv/opencv-453.jar
...
...
Docker(Linux)
部署用的Docker,因为没有找到版本合适的Java+OpenCV的Docker Image,所以只能用一个Java Docker Image作为基础,在基础 Image 上再安装OpenCV。
Linux下安装OpenCV需要用cmake对OpenCV的源码做编译,稍微麻烦一些。索性我绕过这个环节找了一个 sh脚本 搞定(这个脚本里可以设置安装版本等参数)。
另外,将SpringBoot项目打包为Docker Image时, 需要在SpringBoot项目的pom.xml配置文件中增加如下设置,让批处理将指定的 jar 文件打包到的项目依赖的 lib 目录下。
...
...
src/main/resources
.
**/*
src/main/resources/lib.opencv
BOOT-INF/lib/
**/*.jar
src/main/resources
BOOT-INF/classes/
**/*.properties
...
加载动态库
OpenCV在Java中是通过JNI调用,在调用之前还要加载对应的动态库(Windows下是dll文件,Linux下是so文件)。 可以在CvService中以静态代码块的方式在初始化类时做JNI加载。
import org.opencv.core.Core;
public class CvService {
static {
System.loadLibrary(
Core.NATIVE_LIBRARY_NAME
);
}
...
}
OpenCV的常用 Java API
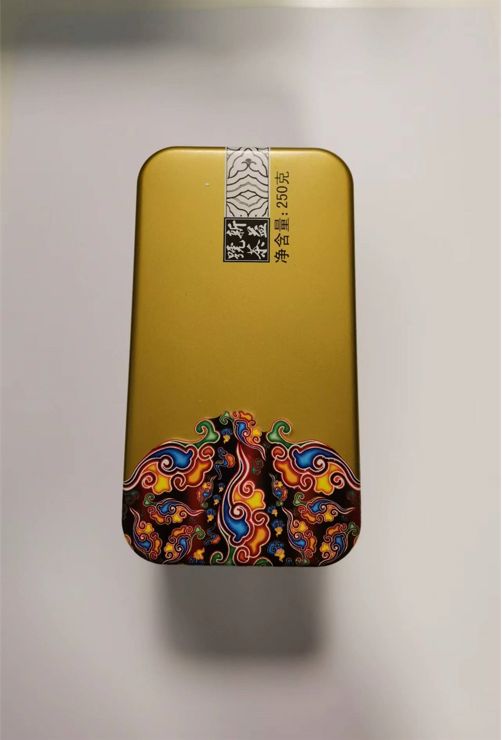
下面简要介绍Java中OpenCV的调用方式。 首先随手拍张照片作为演示图片。
Mat
首先在OpenCV中,图像数据是通过Mat矩阵类来包装的。
用 Imgcodecs 读写图像
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgcodecs;
/**
从文件路径读图像
*/
String path = "D:\\demo.jpg";
Mat img = Imgcodecs.imread(path);
/**
图像写到指定路径
*/
String savePath = "D:\\demo_bak.jpg";
Imgcodecs.imwrite(savePath, img);
用 Imgproc 进行简单图像处理
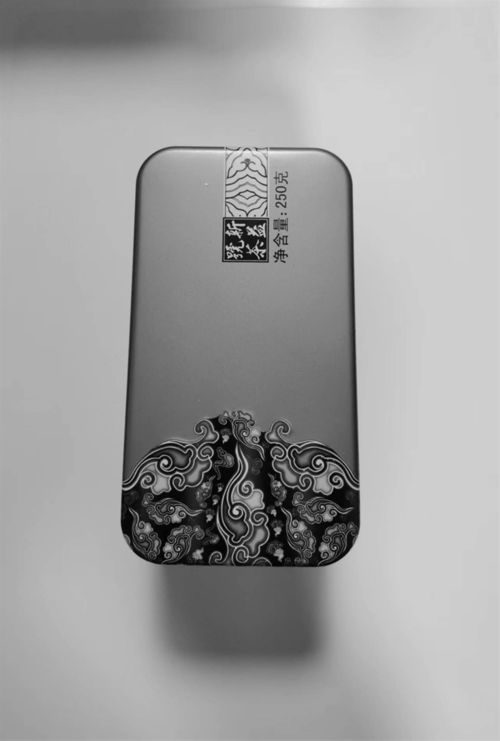
图形灰度化
import org.opencv.imgproc.Imgproc;
/**
* 创建一个空的Mat对象,用来存储图片处理中间结果
*/
Mat grayImg = new Mat();
/**
* 将图像img由BGR转为灰度图,结果保存到tempImg
*/
Imgproc.cvtColor(
img, grayImg, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY
);
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\gray.jpg",
grayImg);
图形二值化
/**
* 高斯滤波降噪
*/
Mat blurImg = new Mat();
Imgproc.GaussianBlur(
grayImg,
blurImg,
new Size(3,3), 2, 2
);
/**
* 使用自适应移动平均阈值法
* 继续对图像进行黑白二值化处理
*/
Mat binaryImg = new Mat();
Imgproc.adaptiveThreshold(
blurImg,
binaryImg,
255,
Imgproc.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,
Imgproc.THRESH_BINARY,
45,
11
);
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\binary.jpg",
binaryImg);
Canny边缘检测
Mat cannyImg = new Mat();
Imgproc.Canny(
binaryImg,
cannyImg,
20,
60,
3,
false);
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\Canny.jpg",
cannyImg);
膨胀增强边缘
Mat dilateImg = new Mat();
Imgproc.dilate(
cannyImg,
dilateImg,
new Mat(),
new Point(-1,-1),
3, 1,
new Scalar(1));
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\dilateImg.jpg",
dilateImg);
轮廓查找
/**
* 从图片中搜索所有轮廓
*/
List contours = new ArrayList();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
Imgproc.findContours(
binaryImg,
contours,
hierarchy,
Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL,
Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE
);
/**
* 从所有轮廓中找到最大的轮廓
*/
int maxIdx = 0;
double maxSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < contours.size(); i++) {
double size = Imgproc.contourArea(
contours.get(i)
);
if(maxSize < size) {
maxIdx = i;
maxSize = size;
}
}
MatOfPoint maxContour = contours.get(maxIdx);
/**
* 将最大的轮廓绘制在原始图片上
*/
Mat imgCopy = img.clone();
Imgproc.drawContours(
imgCopy,
contours,
maxIdx,
new Scalar(0, 0, 255),
4,
LINE_8
);
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\contour.jpg",
imgCopy);
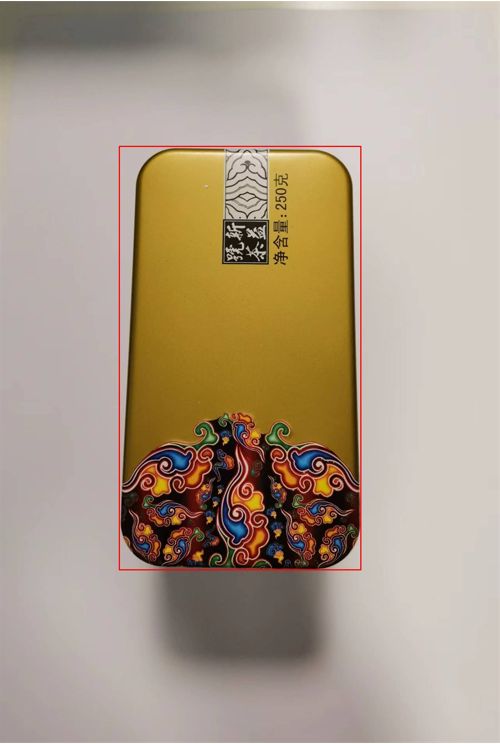
外接矩形
/**
* 找到轮廓的外接矩形
*/
Rect rect = Imgproc.boundingRect(maxContour);
/**
* 在原图上绘制出外接矩形
*/
Mat rectImg = img.clone();
Imgproc.rectangle(
rectImg,
rect,
new Scalar(0, 0, 255),
2,
Imgproc.LINE_8
);
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\rect.jpg",
rectImg);
综合应用(切取图中的轮廓并矫正为矩形)
切图效果
/**
* 计算边框的凸包
*/
MatOfInt hull = new MatOfInt();
Imgproc.convexHull(maxContour, hull);
/**
* 得到凸包对应的轮廓点
*/
Point[] contourPoints = maxContour.toArray();
int[] indices = hull.toArray();
List newPoints = new ArrayList();
for (int index : indices) {
newPoints.add(contourPoints[index]);
}
MatOfPoint2f contourHull = new MatOfPoint2f();
contourHull.fromList(newPoints);
/**
* 使用轮廓周长的1%作为阈值
*/
double thresholdL = Imgproc.arcLength(contourHull, true) * 0.01;
/**
* 用多边形拟合凸包边框,取得拟合多边形的所有顶点
*/
MatOfPoint2f approx = new MatOfPoint2f();
approx.convertTo(approx, CvType.CV_32F);
Imgproc.approxPolyDP(contourHull, approx, thresholdL, true);
List points = approx.toList();
/**
* 找到所有顶点连线中,边长大于 4 * thresholdL的四条边作为四边形物体的四条边
*/
List lines = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < points.size(); i++) {
Point p1 = points.get(i);
Point p2 = points.get((i + 1) % points.size());
if (getSpacePointToPoint(p1, p2) > 4 * thresholdL) {
lines.add(new double[]{p1.x, p1.y, p2.x, p2.y});
}
}
/**
* 计算出这四条边中 相邻两条边的交点,即物体的四个顶点
*/
List corners = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++) {
Point corner = computeIntersect(
lines.get(i),
lines.get((i + 1) % lines.size()));
corners.add(corner);
}
/**
* 对顶点顺时针排序
*/
sortCorners(corners);
/**
* 使用第1、2点距离作为宽,第1、4点间距离作为高
*/
Point p0 = corners.get(0);
Point p1 = corners.get(1);
Point p2 = corners.get(2);
Point p3 = corners.get(3);
double imgWidth = getSpacePointToPoint(p0, p1);
double imgHeight = getSpacePointToPoint(p3, p0);
/**
* 定义存放切图的矩阵
*/
Mat dstMat = Mat.zeros(
(int) imgHeight,
(int) imgWidth,
CvType.CV_8UC3);
/**
* 定义图形矫正源的四个顶点
*/
MatOfPoint2f src = new MatOfPoint2f(p0, p1, p2, p3);
/**
* 定义图形矫正目标的四个顶点
*/
MatOfPoint2f dst = new MatOfPoint2f(
new Point(0, 0),
new Point(imgWidth, 0),
new Point(imgWidth, imgHeight),
new Point(0, imgHeight));
/**
* 定义透视变换矩阵并进行变换操作
*/
Mat trans = Imgproc.getPerspectiveTransform(src, dst);
Imgproc.warpPerspective(img, dstMat, trans, dstMat.size());
Imgcodecs.imwrite(
"D:\\card_test\\process\\cutMat.jpg",
dstMat);
上述过程中用到得一些方法实现
计算点到点的距离
/**
* 点到点的距离
*
* @param p1
* @param p2
* @return
*/
public double getSpacePointToPoint(Point p1,
Point p2) {
if (p1 == null || p2 == null) {
return 0;
}
double a = p1.x - p2.x;
double b = p1.y - p2.y;
return Math.sqrt(a * a + b * b);
}
计算两直线的交点
/**
* 计算两直线的交点
*
* @param a
* @param b
* @return
*/
public Point computeIntersect(double[] a, double[] b) {
if (a.length != 4 || b.length != 4)
throw new ClassFormatError();
double x1 = a[0], y1 = a[1], x2 = a[2], y2 = a[3], x3 = b[0], y3 = b[1], x4 = b[2], y4 = b[3];
double d = ((x1 - x2) * (y3 - y4)) - ((y1 - y2) * (x3 - x4));
if (d != 0) {
Point pt = new Point();
pt.x = ((x1 * y2 - y1 * x2) * (x3 - x4) - (x1 - x2) * (x3 * y4 - y3 * x4)) / d;
pt.y = ((x1 * y2 - y1 * x2) * (y3 - y4) - (y1 - y2) * (x3 * y4 - y3 * x4)) / d;
return pt;
} else {
return new Point(-1, -1);
}
}
对多个点按顺时针排序(右上、左上、左下、右下)
/**
* 对多个点按顺时针排序(右上、左上、左下、右下)
*
* @param corners
*/
public void sortCorners(List corners) {
if (corners.size() == 0) return;
// 首先取得矩形中心点的 x,y值
int centerX = 0, centerY = 0;
for (Point point : corners) {
centerX += point.x;
centerY += point.y;
}
centerX = centerX / 4;
centerY = centerY / 4;
/* 如果位于中心点右上,则index = 0
* 如果位于中心点左上,则index = 1
* 如果位于中心点左下,则index = 2
* 如果位于中心点右下,则index = 3
*/
Point[] result = new Point[4];
for (Point point : corners) {
if (point.x < centerX && point.y < centerY) {
result[3] = point;
} else if (point.x > centerX && point.y < centerY) {
result[2] = point;
} else if (point.x > centerX && point.y > centerY) {
result[1] = point;
} else if (point.x < centerX && point.y > centerY) {
result[0] = point;
}
}
corners.clear();
for (Point point : result) {
corners.add(0, point);
}
}
本期到此为止。《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用》专题将按下列章节展开,欢迎关注我的个人公众号和CSDN。
一、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— 背景》
二、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— OpenCV的使用》
三、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— 搭建基于Docker的深度学习训练环境》
四、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— 准备深度学习训练数据》
五、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— 深度模型的训练调优》
六、《基于AI的计算机视觉识别在Java项目中的使用 —— 深度模型在Java环境中的部署》