Spring常用知识点简介
Spring常用知识点简介
- spring概述
- spring与IoC
-
- 依赖注入
- spring容器初始化过程
-
- web容器初始化过程
- Spring AOP
-
- 相关术语
- 配置方式使用AOP
- 注解方式使用AOP
- AOP事务管理
spring概述
spring的官方网址是spring.io(点这里直接进入)。但是在Java中常说的spring一般是指Spring Framework(点这里可以直接进入)。
Spring根据功能的不同,将代码划分为两类:主业务逻辑与系统级服务(交叉业务逻辑)。主业务逻辑间,及主业务逻辑与系统级服务间的耦合度是较高的。Spring对于前述两种较高的耦合度,采用了两种不同的技术进行解耦。使用IoC解耦主业务逻辑间的耦合度,使用AOP解耦主业务逻辑与系统级服务间的耦合度。
spring与IoC
IoC,Inversion of Control,控制反转。将传统上由程序代码直接操控的对象创建权交给容器,通过容器来管理对象的生命周期。控制反转是对对象控制权的转移,从代码本身转移到了容器。
IoC是一种思想,是一个概念,其实现方式有很多。当前比较流行的实现方式有两种:依赖注入与依赖查找。
- 依赖查找:DL,Dependency Lookup,代码中需要给出目标对象的存放路径,系统会根据路径到容器中查找相应的对象。典型的应用是JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface,Java命名与目录接口,这是一个第三方容器,是一个服务器)。
- 依赖注入:DI,Dependency Injection,代码中无需给出目标对象的定位路径,只需给定对象名称或类型,系统就会直接到容器中进行查找。是目前最优秀的解耦方式。典型应用是Spring。
依赖注入
在spring中使用依赖注入之前,我们需要先向spring容器中注册被配置成单例的实例bean,然后就可以注入了。spring依赖注入方式有构造方法注入(了解)和set方法注入(重点)。set方法注入分为手动装配注入和自动装配注入。
- 手动装配注入(XML方式):通过
标签的子标签 标签设置需要注入的属性和属性值。需要在bean对应的类中设置set方法。 - 自动装配方式(注解方式):@Authowired注解(根据注册bean的类型注入)和@Resource注解(根据注册bean的名字注入),使用注解方式需要在配置文件中配置好注解扫描器。
spring容器初始化过程
可参考处地址(点这里)
- web服务器(servlet容器):Tomcat,Jetty和Jboss等。
- web容器:ServletContext(servlet上下文)、Servlet三大域对象(生命周期范围最大的一个)
- spring容器:ApplicationContext(spring上下文,实现了Beanfactory接口)
web容器初始化过程
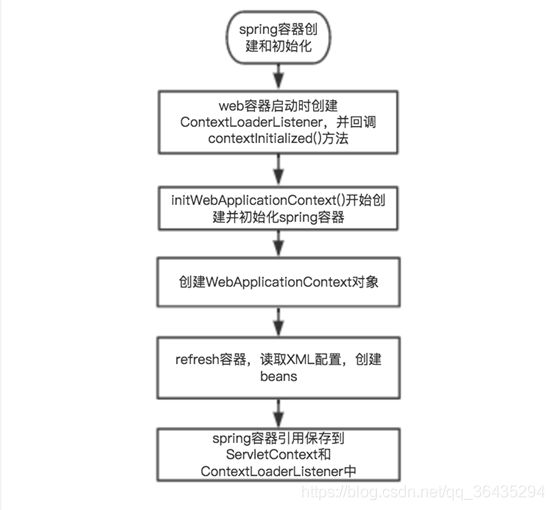
在web应用中,web服务器启动时会加载web.xml配置文件(启动ContextLoaderListener监听器),会创建web容器,spring容器的创建和初始化是在web容器创建的过程中。
- web容器启动时通过ContextLoaderListener这个类中调用contextInitialized()方法。
- 在contextInitialized()方法中调用了initWebApplicationContext()方法。
- initWebApplicationContext()中,先创建了一个WebApplicationContext的对象,再调用了configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法。
- 在configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法中调用了一个非常重要的方法,refresh()方法。
- refresh()方法(位于org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext这个类中)中有十二步,这十二步完成了spring容器的创建和初始化过程。
- 通过servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context)方法,将spring容器的上下文挂载到servletContext 这个web容器的上下文中。

public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 准备更新上下文,设置开始时间,标记活动标志,初始化配置文件中的占位符
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 一、 web工程 AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext
// 将 bean 定义加载到给定的 BeanFactory 中
// 1. createBeanFactory(); 为此上下文创建内部 BeanFactory
// 2. customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory); 定制 BeanFactory,是否允许 BeanDefinition 覆盖、是否允许循环引用
// 3. loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory); 通过 BeanDefinitionReader 解析 xml 文件,解析封装信息到 BeanDefinition,并将其 register 到 BeanFactory 中
// 以 beanName为key将beanDefinition 存到 DefaultListableBeanFactory#beanDefinitionMap 中
// 二、 SpringBoot GenericApplicationContext,实际 register 过程在 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors 中
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 准备 BeanFactory 以便在此上下文中使用。
// 1. 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器
// 2. 添加几个 BeanPostProcessor,
// 3. 实例化几个特殊的 bean
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 在 AbstractApplicationContext#postProcessBeanFactory 为空实现,留给子类做扩展,不同 ApplicationContext 实现不同,不作详细描述
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// Spring 的 SPI
// 先调用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 和 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 的实现类
// 再调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法
// 例如:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 会扫描 Spring AOP
AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程。AOP最早由AOP联盟的组织提出的,制定了一套规范.Spring将AOP思想引入到框架中,必须遵守AOP联盟的规范。通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。
相关术语
- Joinpoint(连接点):是目标对象中可以被拦截的方法,我们可以理解是候选方法。
- Pointcut(切入点):是目标对象中实际被拦截的方法,我们可以理解是被选中的候选方法。
- Advice(增强/通知):是要对被拦截的连接点做处理的代码,增强可以分为,前置增强、后置增强、异常增强、最终增强和环绕增强。
- Introduction(引介):引介是一种特殊的通知在不修改类代码的前提下, Introduction可以在运行期为类动态地添加一些方法或Field。
- Target(目标对象):被代理的目标对象。
- Weaving(织入):将增强和切入点整合生成代理对象的过程。
- Proxy(代理):目标对象被织入后生成的代理对象。
- Aspect(切面):切入点和通知的组合,我们称为切面。
配置方式使用AOP
就是在xml配置文件中配置好匹配的规则。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean class="com.czy.service.UserServiceImpl" />
<bean id="myAdvice" class="com.czy.advice.Myadvice" />
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(void *..*.UserService*.save*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAdvice">
<aop:before method="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
<aop:after method="log2" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
注解方式使用AOP
使用注解方式可以把在xml配置文件中配置的切点匹配规则放到注解类中。
配置文件加载扫描注解,和自动代理
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.czy" />
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy />
beans>
被注解标记的切面类
package com.czy.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// @Aspect注解:标记该类是一个切面类
@Aspect
// 将该类交给spring容器管理
@Component
public class MyAspect {
private static final String pointcut = "execution(* *..*.*ServiceImpl.*(..))";
@Before(value = "fn()")
public void beforeAdvice() {
System.out.println("前置增强...");
}
@After(value = "fn()")
public void afterAdvice() {
System.out.println("后置增强...");
}
// 定义一个通用的切点
@Pointcut(value = pointcut)
public void fn(){}
}
AOP事务管理
spring配置文件(省略数据库账号密码配置文件)
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:database.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${db.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${db.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${db.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${db.password}" />
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.czy.dao.AccountDao" />
<context:component-scan base-package="com.czy.service" />
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager" />
beans>
使用spring的JdbcTemplate访问数据库。
package com.czy.dao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
public class AccountDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public double queryMoney(String from) {
double money= 0;
String sql = "SELECT MONEY FROM ACCOUNT WHERE NAME = ?";
String[] strArray = new String[]{from};
money = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, strArray, Double.class);
return money;
}
public void update(String name, double money) {
Object[] args = { money, name };
// jdbcTemplate.update("UPDATE account SET money = ? WHERE name = ? ", args);
jdbcTemplate.update("UPDATE account SET money = ? WHERE name = ? ", args);
}
}
注解事务测试的业务类
package com.czy.service;
import com.czy.dao.AccountDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
//@Transactional:标记该类的所有方法都已经被事务进行管理了,至于管理属性,不设置的话,都采取默认值
@Transactional
@Service
public class AccountServiceImpl {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(String from, String to, double money) {
// 先查询from账户的钱
double fromMoney = accountDao.queryMoney(from);
// 对from账户进行扣钱操作
accountDao.update(from, fromMoney - money);
//手动制造异常
System.out.println(1/0);
// 先查询from账户的钱
double toMoney = accountDao.queryMoney(to);
// 对to账户进行加钱操作
accountDao.update(to, toMoney + money);
}
}