【Spring】常用扩展点及其应用场景
包括各种PostProcessor(后置处理器)和各种Aware(感知,通过回调的方式)
这些扩展点的执行时机可以参考【Spring】IOC容器的创建过程,搜索".postProcessXXX"即可得到每个扩展点的执行时机。
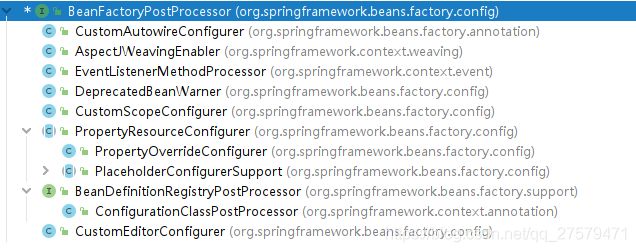
BeanFactoryPostProcessor
//类似于BeanPostProcessor,可对bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理
//即SpringIOC容器允许该类在容器实际实例化任何其他bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它
//可配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,并结合Order接口来控制BeanFactoryPostProcessors的执行次序
//若想改变实际的bean实例,那么最好使用BeanPostProcessor
//BeanFactoryPostProcessor的作用域范围是容器级的,只和当前所使用的容器有关,仅对当前容器中的bean进行后置处理,
//而不会对其他容器中的bean进行处理,即使两个容器处于同一层次上
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean factory after its standard
* initialization. All bean definitions will have been loaded, but no beans
* will have been instantiated yet. This allows for overriding or adding
* properties even to eager-initializing beans.
* 在标准初始化之后,修改应用程序上下文的内部Bean工厂。 所有bean定义都将被加载,但尚未实例化任何bean。 这甚至可以覆盖或添加属性,甚至可以用于初始化bean。
* @param beanFactory the bean factory used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
子接口及实现类:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
/**
* 对标准BeanFactoryPostProcessor SPI的扩展,允许在常规BeanFactoryPostProcessor检测开始之前注册更多的Bean定义。尤其是,
* 那些Bean定义反过来定义了BeanFactoryPostProcessor实例。
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
/**
* Modify the application context's internal bean definition registry after its
* standard initialization. All regular bean definitions will have been loaded,
* but no beans will have been instantiated yet. This allows for adding further
* bean definitions before the next post-processing phase kicks in.
* 在标准初始化之后,修改应用程序上下文的内部bean定义注册表。 所有常规bean定义都将被加载,但尚未实例化任何bean。
* 这允许在下一个后处理阶段开始之前添加更多的bean定义。
* @param registry the bean definition registry used by the application context
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
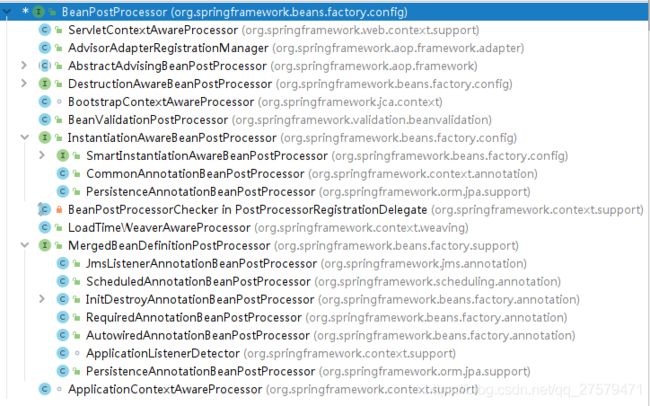
BeanPostProcessor接口
public interface BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance before any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
*/
Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor to the given new bean instance after any bean
* initialization callbacks (like InitializingBean's afterPropertiesSet
* or a custom init-method). The bean will already be populated with property values.
* The returned bean instance may be a wrapper around the original.
* In case of a FactoryBean, this callback will be invoked for both the FactoryBean
* instance and the objects created by the FactoryBean (as of Spring 2.0). The
* post-processor can decide whether to apply to either the FactoryBean or created
* objects or both through corresponding bean instanceof FactoryBean checks.
*
This callback will also be invoked after a short-circuiting triggered by a
* {@link InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation} method,
* in contrast to all other BeanPostProcessor callbacks.
* @param bean the new bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean instance to use, either the original or a wrapped one
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean
*/
Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException;
}
可以在spring容器实例化bean之后,在执行bean的初始化方法前后,添加一些自己的处理逻辑。这里说的初始化方法,指的是下面两种:
1)bean实现了InitializingBean接口,对应的方法为afterPropertiesSet
2)在bean定义的时候,通过init-method设置的方法
子接口及实现类:
CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Resource注解的注入
RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Required注解的注入
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@Autowired注解的注入
PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:支持@PersistenceUnit和@PersistenceContext注解的注入
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor:用来为bean注入ApplicationContext等容器对象
这些注解类的BeanPostProcessor,在spring配置文件中,可以通过这样的配置
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor接口
/**
* 在运行时用于合并的Bean定义的后处理器回调接口。 BeanPostProcessor实现可以实现此子接口,以便对Spring BeanFactory用于创建bean实例的合并bean定义(原始bean定义的已处理副本)进行后处理。
*/
public interface MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Post-process the given merged bean definition for the specified bean.
* @param beanDefinition the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param beanType the actual type of the managed bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @see AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors
*/
void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName);
/**
* A notification that the bean definition for the specified name has been reset,
* and that this post-processor should clear any metadata for the affected bean.
* The default implementation is empty.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @since 5.1
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory#resetBeanDefinition
*/
default void resetBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
}
}
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Apply this BeanPostProcessor before the target bean gets instantiated.
* The returned bean object may be a proxy to use instead of the target bean,
* effectively suppressing default instantiation of the target bean.
* If a non-null object is returned by this method, the bean creation process
* will be short-circuited. The only further processing applied is the
* {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization} callback from the configured
* {@link BeanPostProcessor BeanPostProcessors}.
*
This callback will only be applied to bean definitions with a bean class.
* In particular, it will not be applied to beans with a factory method.
*
Post-processors may implement the extended
* {@link SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor} interface in order
* to predict the type of the bean object that they are going to return here.
*
The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean to be instantiated
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the bean object to expose instead of a default instance of the target bean,
* or {@code null} to proceed with default instantiation
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessAfterInstantiation
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinition#hasBeanClass
*/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Perform operations after the bean has been instantiated, via a constructor or factory method,
* but before Spring property population (from explicit properties or autowiring) occurs.
* This is the ideal callback for performing custom field injection on the given bean
* instance, right before Spring's autowiring kicks in.
*
The default implementation returns {@code true}.
* @param bean the bean instance created, with properties not having been set yet
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return {@code true} if properties should be set on the bean; {@code false}
* if property population should be skipped. Normal implementations should return {@code true}.
* Returning {@code false} will also prevent any subsequent InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
* instances being invoked on this bean instance.
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessBeforeInstantiation
*/
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean, without any need for property descriptors.
* Implementations should return {@code null} (the default) if they provide a custom
* {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} implementation, and {@code pvs} otherwise.
* In a future version of this interface (with {@link #postProcessPropertyValues} removed),
* the default implementation will return the given {@code pvs} as-is directly.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} which proceeds with the existing properties
* but specifically continues with a call to {@link #postProcessPropertyValues}
* (requiring initialized {@code PropertyDescriptor}s for the current bean class)
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @since 5.1
* @see #postProcessPropertyValues
*/
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Post-process the given property values before the factory applies them
* to the given bean. Allows for checking whether all dependencies have been
* satisfied, for example based on a "Required" annotation on bean property setters.
* Also allows for replacing the property values to apply, typically through
* creating a new MutablePropertyValues instance based on the original PropertyValues,
* adding or removing specific values.
*
The default implementation returns the given {@code pvs} as-is.
* @param pvs the property values that the factory is about to apply (never {@code null})
* @param pds the relevant property descriptors for the target bean (with ignored
* dependency types - which the factory handles specifically - already filtered out)
* @param bean the bean instance created, but whose properties have not yet been set
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the actual property values to apply to the given bean (can be the passed-in
* PropertyValues instance), or {@code null} to skip property population
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
* @see #postProcessProperties
* @see org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues
* @deprecated as of 5.1, in favor of {@link #postProcessProperties(PropertyValues, Object, String)}
*/
@Deprecated
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return pvs;
}
}
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
public interface SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
/**
* Predict the type of the bean to be eventually returned from this
* processor's {@link #postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callback.
* The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the raw class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the type of the bean, or {@code null} if not predictable
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
@Nullable
default Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Determine the candidate constructors to use for the given bean.
* The default implementation returns {@code null}.
* @param beanClass the raw class of the bean (never {@code null})
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the candidate constructors, or {@code null} if none specified
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
@Nullable
default Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
/**
* Obtain a reference for early access to the specified bean,
* typically for the purpose of resolving a circular reference.
* This callback gives post-processors a chance to expose a wrapper
* early - that is, before the target bean instance is fully initialized.
* The exposed object should be equivalent to the what
* {@link #postProcessBeforeInitialization} / {@link #postProcessAfterInitialization}
* would expose otherwise. Note that the object returned by this method will
* be used as bean reference unless the post-processor returns a different
* wrapper from said post-process callbacks. In other words: Those post-process
* callbacks may either eventually expose the same reference or alternatively
* return the raw bean instance from those subsequent callbacks (if the wrapper
* for the affected bean has been built for a call to this method already,
* it will be exposes as final bean reference by default).
*
The default implementation returns the given {@code bean} as-is.
* @param bean the raw bean instance
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @return the object to expose as bean reference
* (typically with the passed-in bean instance as default)
* @throws org.springframework.beans.BeansException in case of errors
*/
default Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
ApplicationContextAware
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ApplicationContext that this object runs in.
* Normally this call will be used to initialize the object.
* Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback such
* as {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method. Invoked after {@link ResourceLoaderAware#setResourceLoader},
* {@link ApplicationEventPublisherAware#setApplicationEventPublisher} and
* {@link MessageSourceAware}, if applicable.
* @param applicationContext the ApplicationContext object to be used by this object
* @throws ApplicationContextException in case of context initialization errors
* @throws BeansException if thrown by application context methods
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanInitializationException
*/
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
获取spring 上下文环境的对象,然后通过该上下文对象获取spring容器中的bean对象
BeanFactoryAware
public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware {
/**
* Callback that supplies the owning factory to a bean instance.
* Invoked after the population of normal bean properties
* but before an initialization callback such as
* {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()} or a custom init-method.
* @param beanFactory owning BeanFactory (never {@code null}).
* The bean can immediately call methods on the factory.
* @throws BeansException in case of initialization errors
* @see BeanInitializationException
*/
void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}
Bean获取配置他们的BeanFactory的引用
BeanNameAware
public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the name of the bean in the bean factory that created this bean.
* Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an
* init callback such as {@link InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet()}
* or a custom init-method.
* @param name the name of the bean in the factory.
* Note that this name is the actual bean name used in the factory, which may
* differ from the originally specified name: in particular for inner bean
* names, the actual bean name might have been made unique through appending
* "#..." suffixes. Use the {@link BeanFactoryUtils#originalBeanName(String)}
* method to extract the original bean name (without suffix), if desired.
*/
void setBeanName(String name);
}
获取该bean在BeanFactory配置中的名字
ResourceLoaderAware
public interface ResourceLoaderAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the ResourceLoader that this object runs in.
* This might be a ResourcePatternResolver, which can be checked
* through {@code instanceof ResourcePatternResolver}. See also the
* {@code ResourcePatternUtils.getResourcePatternResolver} method.
*
Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init callback
* like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} or a custom init-method.
* Invoked before ApplicationContextAware's {@code setApplicationContext}.
* @param resourceLoader the ResourceLoader object to be used by this object
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver
* @see org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternUtils#getResourcePatternResolver
*/
void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader);
}
获取ResourceLoader对象,便能够通过它获得各种资源。
ServletContextAware
public interface ServletContextAware extends Aware {
/**
* Set the {@link ServletContext} that this object runs in.
* Invoked after population of normal bean properties but before an init
* callback like InitializingBean's {@code afterPropertiesSet} or a
* custom init-method. Invoked after ApplicationContextAware's
* {@code setApplicationContext}.
* @param servletContext the ServletContext object to be used by this object
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean#afterPropertiesSet
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware#setApplicationContext
*/
void setServletContext(ServletContext servletContext);
}
获取servletContext容器。
其它
Spring中bean的生命周期(最详细)
SpringIOC中Bean的生命周期以及各种PostProcessor后置处理器的执行时机