企业级自动化运维工具---puppet详解
本文收录在Linux运维企业架构实战系列
1、认识puppet
1.1 引入
puppet是什么,咱们先不用专业的名词解释它,咱们先描述一些工作场景,看明白这些工作场景,自然会知道puppet是什么。
(1)场景一:
管理员想要在100台服务器上同时创建一个名叫"along"的用户,怎么办,当然,我们可以"手动解决",登录每一台服务器,然后一台一台的创建用户,如果你真的这样干,那么我只能说,算你狠!!!但是,既然我们这篇文章是介绍puppet的,我们肯定会推荐你使用puppet解决这个问题。
(2)场景二:
公司新买了一堆云服务器,这些服务器最终可能要提供相同的服务,现在需要管理员在这一堆服务器上安装一些相同的应用,而且安装完成后,还需要这些服务器上的应用自动启动,怎么办,当然,手动解决算你狠,兄弟我服了,你说你写脚本解决,嗯,这是个办法,在我没有认识puppet之前我可能也会写个脚本,但是我们是介绍puppet的,我们会推荐你使用puppet解决这个问题。
(3)场景三:
在一些服务器中,执行大批量的重复操作,我们可以使用puppet。
看完上述三个场景,你应该已经大概猜出puppet是干吗的了,没错,说的糙一点,你可以把它理解成批量处理工具,但是你又不能完全把它理解成批量处理工具,因为除了批量处理,他还有一些别的功能和特性,我们暂且先这么认为,以便我们入门。
1.2 介绍
(1)我自己对puppet的了解
像puppet这种工具有几个专业的名词可以用来称呼它们:"配置管理工具"、"自动化运维管理工具"。
Linux中,常见的配置管理工具有puppet、saltstack、ansible(博主之前讲解过)、chef等,它们的功能类似,puppet算是这个领域里面的老大哥,时间久(我说的是创始时间久,不要想歪了····),成熟,被广泛的应用,google、twitter、redhat,cisco等大公司都用到了它,功能强大,puppet是使用ruby研发的,saltstack和ansible都属于python系的, ansible和saltstack与puppet相比,属于后起之秀,我们以后也可能会对它们进行总结,但是现在,我们只聊puppet。
(2)专业术语介绍
- ① puppet是一种Linux/Unix平台下的集中配置管理系统,使用自有的puppet描述语言,可管理配置文件、用户、cron任务、软件包、系统服务等。puppet把这些系统实体称之为资源,puppet的设计目标是简化对这些资源的管理以及妥善处理资源间的依赖关系。
- ② Puppet是开源的基于Ruby的系统配置管理工具,puppet是一个C/S结构。所有的puppet客户端同一个服务器端的puppet通讯,每个puppet客户端每半小时(可以设置)连接一次服务器端,下载最新的配置文件,并且严格按照配置文件来配置服务器。 配置完成以后,puppet客户端可以反馈给服务器端一个消息, 如果出错,也会给服务器端反馈一个消息。
- ③ Puppet是用于大规模集群管理的神器。其本身使用Ruby语言开发,基于C/S架构。在每台机器上部署的客户端每隔一个指定的时间会连接到Master检查资源变化情况,若资源发生变化,将按配置动作进行相应的操作。
- ④ Puppet将所有可操作对象抽象为资源,目前涵盖了40多种,如:File、User、Group、Host、Package、Service、Cron、Exec等,下面我会一一讲述。
- ⑤ Puppet 通过抽象资源的方式,使得每台机器能够“清楚”其本身“应该”是什么“状态”,而客户端根据当前是否达到这个状态决定采取指定的动作。这使得Puppet 不仅可用于传统的应用部署,而且通过合理的手段,也能够将比应用部署更频繁的配置管理一并解决。甚至可以在Master端外接自己开发的平台,通过集中配 置方式管理各项“资源”,实现高度灵活的自动化管理体系。
1.3 puppet 名词解释
- 资源:是puppet的核心,通过资源申报,定义在资源清单中。相当于ansible中的模块,只是抽象的更加彻底。
- 类:一组资源清单。
- 模块:包含多个类。相当于ansible中的角色。
- 站点清单:以主机为核心,应用哪些模块。
本篇文章主要讲解资源;类、模块、站点清单都在下篇进行详解。
1.4 puppet常用资源类型
| group | 组 |
| user | 用户 |
| packge | 程序包 |
| service | 服务 |
| file | 文件 |
| exec | 执行自定义命令 |
| cron | 周期性任务计划 |
| notify | 通知 |
| yumrepo | 源 |
| host | /etc/hosts中主机解析 |
1.5 puppet命令使用
(1)查询资源类型和帮助信息
| 1 |
|
- -l:列出所有资源类型;
- -s:显示指定类型的简要帮助信息;也就是基本选项
- -m:显示指定类型的元参数,一般与-s 一同使用;这些选项只是来描述这个类型的
(2)执行资源清单命令
| 1 |
|
- -d:打开调试信息,会显示很多信息
- -v:显示详细信息
- -e:直接执行给定的命令
- -l:执行结果保存到指定日志的文件中,否则执行结果会输出到标准输出
- --noop:dry run 干跑,只是测试的跑一边,不真正的执行
- --catalog:应用JSON目录
1.6 puppet的优缺点
这类垂直管理系统的使用及活跃,极大减轻了运维人员在重复性、批量化操作方面的负担,能够非常有效地在各自领域完成既定的运维子目标。但其缺陷在于只能针对某一垂直领域的特定问题进行高效处理,对于它们之间的关联性很难应对。因为运维的本质是保证服务的可用性,而自动化运维则是在完全保证这一前提下,尽可能将需要人干涉的部分处理掉,所以判断其优劣的标准则是——与人工处理比,对服务的保证有没有提高。如果仅是解决报警、部署这些单一动作,后续仍然需要人去处理、去关注、去判断的话,就离这个目标还有距离,谈不上真正的自动化,只能算是工具化。
puppet是一个开源的软件自动化配置和部署工具,它使用简单且功能强大,正得到了越来越多地关注,现在很多大型IT公司均在使用puppet对集群中的软件进行管理和部署,如google利用puppet管理超过6000台地mac桌面电脑(2007年数据)。
puppet设计架构是基于c/s架构的。服务器端保存着所有对客户端服务器的配置代码,在puppet里面叫做manifest. 客户端下载manifest之后,可以根据manifest对服务器进行配置,例如软件包管理,用户管理和文件管理等等。
2、puppet的使用模型及工作流程
puppet的使用模型分为 单机使用模型 和 master/agent模型;本文主要讲解单机使用模型,便于入门。
2.1 master/agent模型
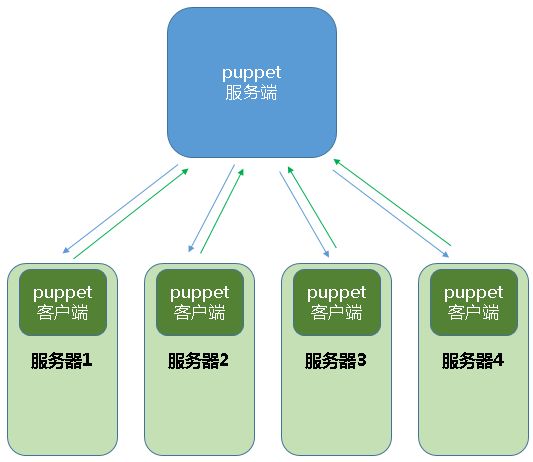
从上述专业的解释中,我们可以得知puppet是C/S架构的,也就是说,它有服务端,也有客户端,管理员可以通过puppet服务端(master),管理每一台被管理的服务器,但是需要puppet客户端作为中介,也就是说,puppet客户端作为代理(agent),接收来自puppet服务端的配置信息,按照服务端(master)发送过来的配置信息,对被管理服务器进行配置,真正执行配置操作的是puppet客户端,puppet服务端只负责将配置信息准备好,发送给puppet客户端,以便客户端执行具体操作,puppet客户端还有另一个作用,就是向puppet服务端发送报告,当客户端按照配置信息执行完成相关配置以后,会将执行信息发送到服务端,比如执行成功与否,执行结果等,默认情况下,每30分钟,puppet客户端会向puppet服务端发起一次请求,请求受管理服务器的配置信息, puppet服务端将配置信息发送给客户端,客户端根据反回的信息进行判断,判断被管理服务器是否符合管理员定义的配置,puppet的这种工作模式就是C/S架构的,也可以理解为master/agent的工作模式,用文字描述显得太无力,我们画个图来看看。
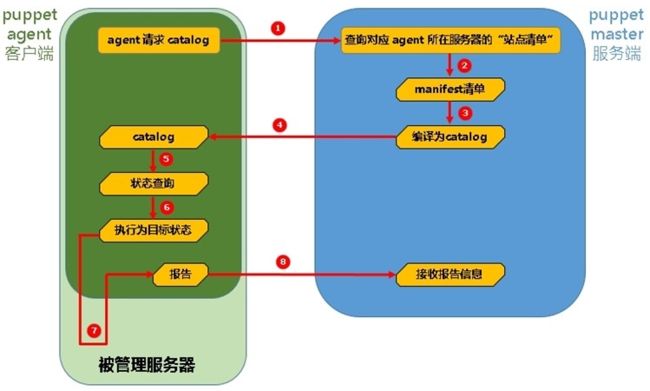
那么,我们把上图中的两台服务器拿出来,详细说说它们之间的具体工作流程,但是此处我们需要说明,在master/agent模型下工作的puppet的工作流程比我们总结的要复杂一点,但是为了入门方便,我们只取出其中的一部分核心的流程进行总结,在后面的实际应用中,我们会不断的丰富这些流程,此处先给出一个简化过的流程图,如下图所示。
过程分析:
① 客户端puppet agent请求catalog,我们已经说过,catalog其实就是被管理服务器对应的配置文件(经过处理过的配置文件),服务端master收到agent的请求,然后找到对应被管理服务器的"站点清单",或者被称为"主机清单",因为一台"被管理服务器"可能同时担任多个"角色",每个角色可能都会对应一个"manifest"(也就是清单),所以,我们可以为每一台被管理服务器配置一个"站点清单",站点清单也可以理解成为一种"清单",只是它是针对一台服务器而存在的一种清单。
② 服务端master找到被管理服务器的站点清单后,根据站点清单,找到对应服务器需要哪些"清单",因为一台服务器可能会需要多张"清单",上图中为了示例,只画出了一个清单,但是这不代表必定只有一个。
③ master将找到的所有"清单"进行处理,处理为catalog。
④ master将处理过的catalog发送到agent端。
⑤ agent收到master发送过来的catalog,然后,agent会查询"被管理服务器的当前状态",看看服务器的当前状态是否符合catalog中定义的目标状态。
⑥ 如果"被管理服务器的当前状态"与"catalog中定义的目标状态"一致,那么资源对应的操作将不会执行,如果"被管理服务器的当前状态"与"catalog中定义的目标状态"不一致,那么资源对应的操作将会执行,以便让"被管理服务器"达到管理员指定的"目标状态"。
⑦ 经过上一步的"状态判断",执行对应操作,不管执行是否成功,都会生成对应的报告信息。
⑧ agent将生成的报告信息发送给master端。
上述过程,就是puppet在master/agent模式下的工作流程,我们说过,默认情况下,客户端每隔30分钟向服务端请求一次配置信息,然后根据服务端返回的配置信息,判断当前服务器是否处于管理员定义的目标状态,如果被管理的服务器不处于管理员定义的目标状态,则需要执行对应的操作,使得被管理主机最终处于管理员定义的目标状态,我们也可以不必每次都等待30分钟,我们可以从master端推送catalog到agent端,主动告诉agent端,配置已经发生了改变,请执行对应的操作。这是后话,我们以后再聊。
2.2 单机使用模型
当然,puppet也可以不在master/agent模式下工作,我们可以在受管理服务器上只安装puppet客户端,使用客户端手动执行对应配置文件,相当于配置文件中的信息并不是通过puppet服务端发送过来,而是通过本地的配置文件获取,也是可以的,我们暂且称这种不需要puppet服务端的工作模式为单机模式,我们在学习puppet时,可以使用单机的模式进行练习,但是在生产环境中,一般都使用master/agent的方式使用puppet。
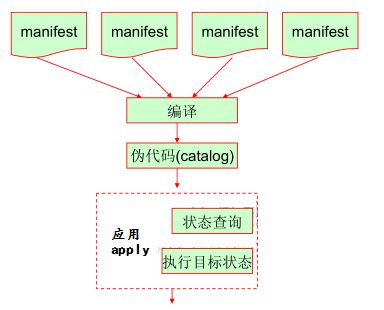
实现定义多个manifests --> complier --> catalog --> apply
3、puppet资源详解
3.1 puppet资源介绍
3.1.1 程序安装及环境
首先,我们还是来安装一下puppet,puppet的安装可以使用源码安装,也可以使用rpm(官方提供)、epel源、官方提供的yum仓库来安装(通过下载官方提供的rpm包可以指定官方的yum仓库)。
在这里,我们就是用 yum 安装的方式。
| 1 |
|
3.1.2 puppet资源简介
(1)资源抽象
puppet 从以下三个维度来对资源完成抽象:
- 相似的资源被抽象成同一种资源“类型”,如程序包资源、用户资源及服务资源等;
- 将资源属性或状态的描述与其实现方式剥离开来,如仅说明安装一个程序包而不用关心其具体是通过yum、pkgadd、ports或是其它方式实现;
- 仅描述资源的目标状态,也即期望其实现的结果,而不是其具体过程,如“确定nginx 运行起来” 而不是具体描述为“运行nginx命令将其启动起来”;
这三个也被称作puppet 的资源抽象层(RAL)
RAL 由type( 类型) 和provider( 提供者,即不同OS 上的特定实现)组成。
(2)资源定义
① 资源定义通过向资源类型的属性赋值来实现,可称为资源类型实例化;
② 定义了资源实例的文件即清单,manifest;
③ 定义资源的语法如下:
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
|
注意:type必须使用小写字符;title是一个字符串,在同一类型中必须惟一;每一个属性之间需要用“,”隔开,最后一个“,”可省略。
例如,可以同时有名为nginx 的“service”资源和“package”资源,但在“package” 类型的资源中只能有一个名为“nginx”的资源。
(3)资源属性中的三个特殊属性:
- Namevar:可简称为name;
- ensure:资源的目标状态;
- Provider:指明资源的管理接口;
3.2 group:Manage groups
3.2.1 类型属性选项
(1)属性 Parameters:
- name:组名;
- gid:GID;
- system:是否为系统组,true OR false;
- ensure:目标状态,present(创建)/absent(删除);
- members:成员用户;
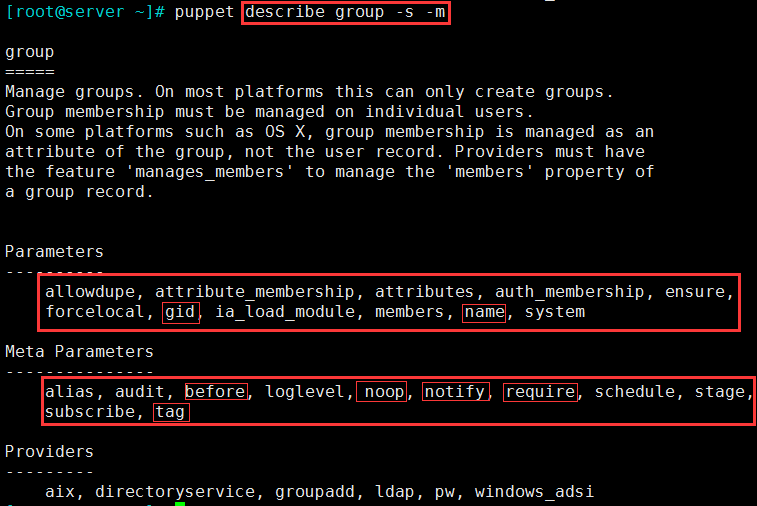
(2)puppet describe group -s -m 使用之前,可以查询这个类型的选项
3.2.2 演示
① 编辑manifest( 清单)
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
② 执行并验证 manifest
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
|
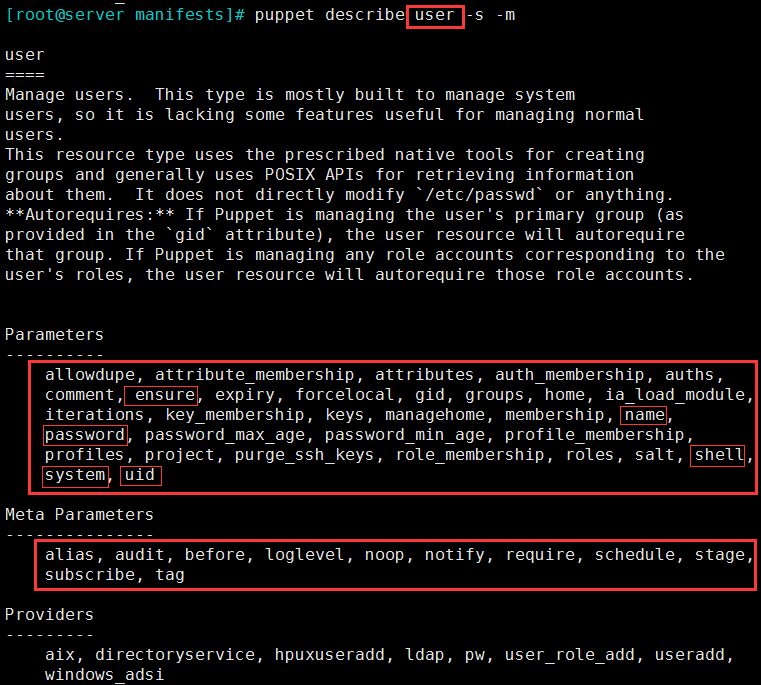
3.3 user:Manage users
3.3.1 类型属性选项
(1)属性 Parameters:
- name:用户名;
- uid: UID;
- gid:基本组ID;
- groups:附加组,不能包含基本组;
- comment:注释;
- expiry:过期时间 ;
- home:家目录;
- shell:默认shell类型;
- system:是否为系统用户 ;
- ensure:present/absent 存在/不存在;
- password:加密后的密码串;
(2)puppet describe user -s -m 使用之前,可以查询这个类型的选项
3.3.2 演示
① 编辑manifest( 清单)
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
② 执行manifest
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
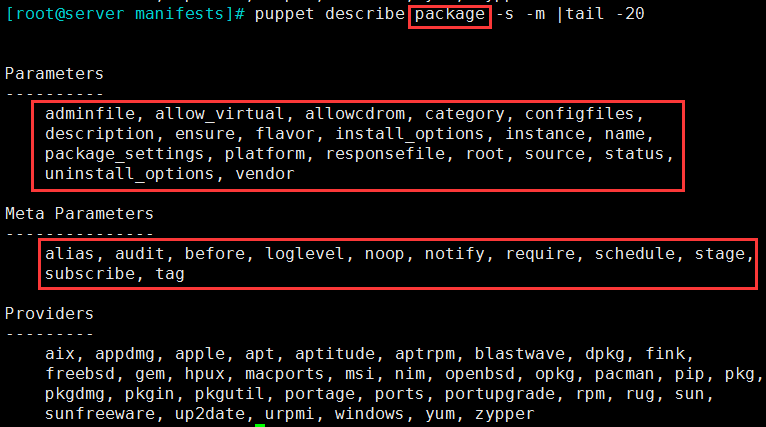
3.4 package:Manage packages
3.4.1 类型属性选项
① 属性:
- ensure:installed, present, latest, absent, any version string (implies present)
- name:包名;
- ource:程序包来源,仅对不会自动下载相关程序包的provider有用,例如rpm或dpkg;
- provider:指明安装方式;rpm/yum/...
② puppet describe package -s -m 可以查询这个类型的选项
3.4.2 演示
① 创建manifest
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
|
② 执行manifest
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
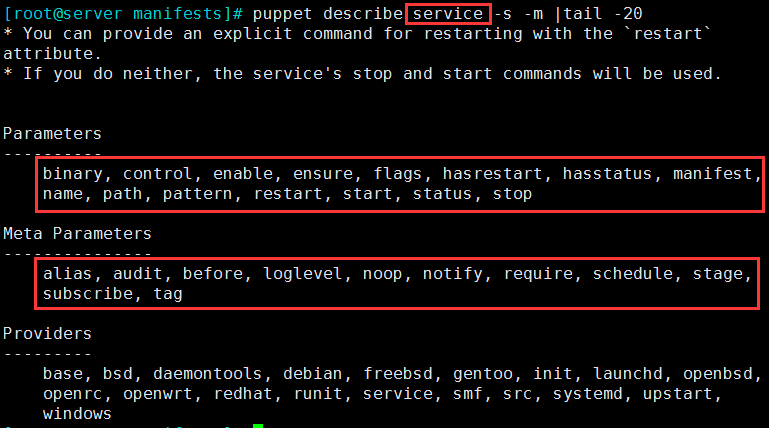
3.5 service:Manage running services
3.5.1 类型属性选项
① 属性:
- ensure:running\true(开启) 或 stopped/false(停止)
- enable:是否开机自启:true(开机自启)、false(不自启)、manual(手动)
- name:服务名
- binary:若服务不是systemctl/service 启动,则需规定启动命令;如nginx -s start
- path:如果不是systemctl/service 这样启动服务,而是通过脚本启动,指明path路径。多个值应该由冒号分隔,或者作为数组提供。脚本的搜索路径,默认为/etc/init.d/;
- hasrestart:是否支持restart 这个参数重启;true/fault ;true 表示支持
- hasstatus:是否支持status 这个参数查看状态;true/false
- start:手动定义启动命令;
- stop:手动定义关闭命令;
- status:若hasstatus 为fals 手动定义查看信息命令;
- restart:若hasrestart 为false 手动定义reload操作
② puppet describe service -s -m 可以查询这个类型的选项
3.5.2 演示1:开启redis 服务
① 编写manifest 资源清单
| 1 2 3 4 5 |
|
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
3.5.2 演示1:下载memcached 包,且开启服务
① 编写manifest 资源清单
[root@along manifest]# vim srv2.pp
package {'memcached':
ensure => installed,
}
service{'memcached':
ensure => running,
enable => false,
require => Package['memcached']
}
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
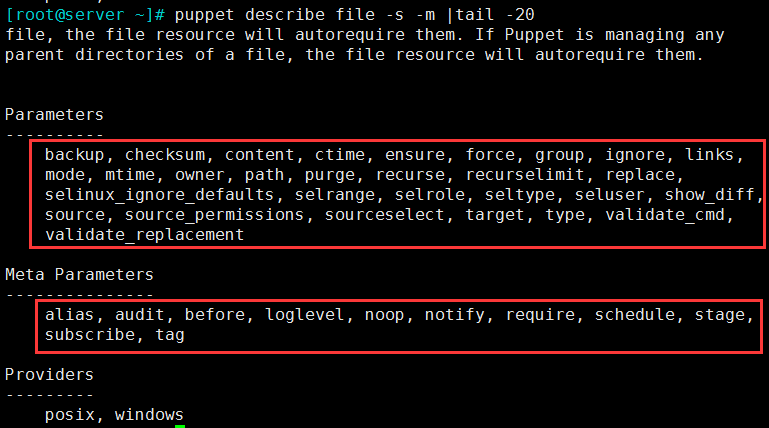
3.6 file:管理文件,包括它们的内容、所有权和权限
3.6.1 类型属性选项
(1)类型的属性、选项
① 属性
- ensure:`present`创建, `absent`删除, `file`创建普通文件, `directory`创建目录, link`创建软链接.
- file:类型为普通文件,其内容由content属性生成或复制由source属性指向的文件路径来创建;
- link:类型为符号链接文件,必须由target属性指明其链接的目标文件;
- directory:类型为目录,可通过source指向的路径复制生成,recurse属性指明是否递归复制;
- path:文件路径;
- source:源文件;当复制文件内容时需要指定
- content:文件内容;直接编写文件内容
- target:符号链接的目标文件;
- owner:属主
- group:属组
- mode:权限;
- atime/ctime/mtime:时间戳;
- access time:访问时间,atime,读取文件内容
- modify time: 修改时间, mtime,改变文件内容(数据)
- change time: 改变时间, ctime,元数据发生改变
② puppet describe file -s -m |tail -20
3.6.2 演示1:创建test.txt,且直接写内容
创建test.txt,且直接写内容
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim file1.pp
file{'/mnt/test.txt':
ensure => file,
content => "How are you?\nHow old are you?\n",
owner => 'along1',
group => 'mygrp',
mode => '0400'
}
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
3.6.3 演示2:创建一个文件,且复制另一个文件的内容;再对这个文件创建一个软链接文件
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim file2.pp
file{'redis.conf':
path => '/mnt/redis.conf',
ensure => file,
source => '/root/manifest/files/redis.conf'
}
file{'symlink.conf':
ensure => link,
path => '/mnt/symlink.conf',
target => '/mnt/redis.conf',
require => File['redis.conf']
}
提示:若要指定source ,最好先把源文件复制到此目录中,因为在master-agent 模式中,不能确保agent 机器上的路径下,一定有要复制的文件;本次操作需要在/root/manifests/files/准备好redis.con文件。
| 1 2 |
|
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
3.6.4 演示3:创建目录,且递归复制另一个目录
创建目录,且递归复制另一个目录
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim file3.pp
file{'test.dir':
ensure => directory,
path => '/app/test.dir',
source => '/etc/httpd',
recurse => true #递归复制
}
注意:
目录复制目录,是将目录下的所有文件递归复制;
不要用path 为目录,source为文件,不会将此文件复制到目录中;只能是目录复制目录
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
|
3.6.5 演示4:下载redis 包,复制配置文件,启动redis 服务
下载redis 包,复制配置文件,启动redis 服务
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim srv3.pp
package{'redis':
ensure => installed,
}
file{'/etc/redis.conf':
ensure => file,
source => '/root/manifest/files/redis.conf',
owner => 'redis',
group => 'root',
mode => '0640'
}
service{'redis':
ensure => running,
enable => false
}
Package['redis'] -> File['/etc/redis.conf'] -> Service['redis']
注意:我事先将/root/manifest/files/redis.conf配置文件的端口修改为了6300
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
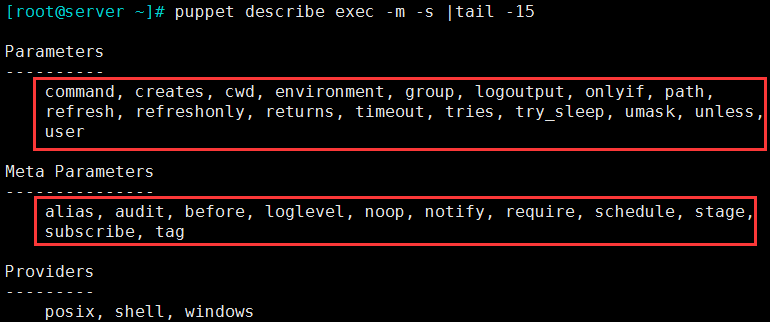
3.7 exec:执行外部命令
注意:exec资源中的任何命令都必须能够多次运行而不会造成损害——也就是说,它必须具有幂等性。
3.7.1 类型属性选项
- command:要运行的命令;
- cwd:用于运行该命令的目录
- creates:文件路径,仅此路径表示的文件不存在时,command方才执行;
- user/group:运行命令的用户身份;
- path:用于执行命令的搜索路径。如果没有指定路径,则命令必须完全限定。
- onlyif:此属性指定一个命令,此命令正常(退出码为0)运行时,当前command才会运行;
- unless:此属性指定一个命令,此命令非正常(退出码为非0)运行时,当前command才会运行;
- refresh:重新执行当前command的替代命令;
- refreshonly:仅接收到订阅的资源的通知时方才运行;
3.7.2 演示1:创建一个目录
创建一个目录
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim cmd1.pp
exec{'cmd':
command => '[ -e /mnt/testdir ] || mkdir /mnt/testdir',
path => ['/bin','sbin','/usr/bin','/usr/sbin'],
# creates => '/mnt/testdir' 判断目录是否存在
}
分析:先判断目录是否存在,不存在再创建目录,使命令具有幂等性;就算是目录已存在,也不会有报错
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
3.7.3 演示2:创建一个用户
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
3.7.4 演示3:下载,开启redis
① 编写manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim cmd3.pp
package{'redis':
ensure => installed,
}
file{'/etc/redis.conf':
ensure => file,
source => '/root/manifest/files/redis.conf',
owner => 'redis',
group => 'root',
mode => '0640'
}
exec{'redis':
command => '/usr/bin/systemctl start redis',
refresh => "/usr/bin/systemctl restart redis",
user => 'redis',
group => 'redis',
}
Package['redis'] -> File['/etc/redis.conf'] ~> Exec['redis']
注意:当配置文件修改,触发动作,会执行refresh 命令替代command
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
|
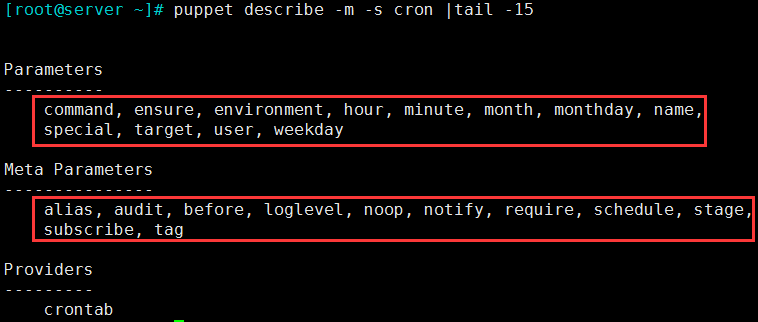
3.8 cron:安装和管理cron作业
由Puppet创建的每个cron资源都需要一个命令和至少一个周期属性(小时、分钟、月、月、工作日、或特殊)
3.8.1 类型属性选项
- command:要执行的任务;
- ensure:present/absent;
- hour:
- minute:
- monthday:
- month:
- weekday:
- user:以哪个用户的身份运行命令
- target:添加为哪个用户的任务
- name:cron job的名称;
3.8.2 演示
① 编写manifest 清单
下载ntpdate包,并制定计划任务,每隔5分钟同步一次时间
[root@along manifest]# vim cron.pp
package{'ntpdate':
ensure => installed,
}
cron{'mysync':
command => '/usr/sbin/ntpdate 192.168.10.1 &> /dec/null',
ensure => present,
minute => "*/5",
target => 'root'
}
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
|
3.9 notify:向代理运行时日志发送一个任意的消息
3.9.1 类型属性选项
- message:信息内容
- name:信息名称;
3.9.2 演示
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
|
3.10 非核心类型的常用资源:yumrepo, host
(1)yumrepo:yum源
(2)host:定义/etc/hosts 中名字解析
4、资源的特殊属性
4.1 资源间依赖和通知关系
4.1.1 依赖关系元参数:before/require
(1)格式:3中实现方法
① A before B: B依赖于A,定义在A资源中;
{
...
before => Type['B'],
...
}
② B require A: B依赖于A,定义在B资源中;
{
...
require => Type['A'],
...
}
③ A -> B,B依赖于A
(2)注意:
① before、 require 和 -> 三者用其一即可
② 资源引用:Type['title']
类型的首字母必须大写
(3)演示:创建一个用户,需要依赖一个组
① 创建manifest
[root@along manifest]# vim user2.pp
[root@along manifest]# cat user2.pp
group{'redhat':
ensure => present,
# before => User['ilinux'], #方案1
}
user{'ilinux':
ensure => present,
comment => "ilinux.io",
groups => 'redhat',
require => Group['redhat'], #方案2
}
#Group['redhat'] -> User['ilinux'] #方案3
② 执行,先创建了组redhat,再创建了用户ilinux
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
|
4.1.2 通知关系:通知相关的其它资源进行“刷新”操作
(1)格式:notify/subscribe
① notify:A notify B:B依赖于A,且A发生改变后会通知B;
{
...
notify => Type['B'],
...
}
② subscribe:B subscribe A:B依赖于A,且B监控A资源的变化产生的事件;
{
...
subscribe => Type['A'],
...
}
③ A ~ B ,B依赖于A缩写版
(2)实例:下载redis 包,复制配置文件,启动redis 服务
① 修改srv3.pp manifest 清单
[root@along manifest]# vim srv3.pp
package{'redis':
ensure => installed,
}
file{'/etc/redis.conf':
ensure => file,
source => '/root/manifest/files/redis.conf',
owner => 'redis',
group => 'root',
mode => '0640',
# notify => Service['redis']
}
service{'redis':
ensure => running,
enable => false,
hasrestart => true,
# subscribe => File['/etc/redis.conf']
}
Package['redis'] -> File['/etc/redis.conf'] ~> Service['redis']
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
③ 修改 /root/manifest/files/redis.conf 把端口改为6000
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 |
|
4.2 tag 标签
如同 anssible 一样,puppet 也可以定义“标签”——tag,打了标签以后,我们在运行资源的时候就可以只运行某个打过标签的部分,而非全部。这样就更方便于我们的操作。
一个资源中,可以有一个tag也可以有多个。
(1)格式:
资源定义:
type{'title':
...
tag => 'TAG1',
}
type{'title':
...
tag => ['TAG1','TAG2',...],
}
手动调用:
| 1 |
|
(2)实例:
① 创建manifest
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 |
|
② 执行
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
5、puppet 变量
puppet 变量以“$”开头,赋值操作符为“=”,语法为$variable_name=value。
(1)数据类型:
- 字符型:引号可有可无;但单引号为强引用,双引号为弱引用;支持转义符;
- 数值型:默认均识别为字符串,仅在数值上下文才以数值对待;
- 数组:[]中以逗号分隔元素列表;
- 布尔型值:true, false;不能加引号;
- hash:{}中以逗号分隔k/v数据列表; 键为字符型,值为任意puppet支持的类型;{ ‘mon’ => ‘Monday’, ‘tue’ => ‘Tuesday’, };
- undef:从未被声明的变量的值类型;
(2)正则表达式:
(?: ) (?- : ) OPTIONS: i:忽略字符大小写; m:把.当换行符; x:忽略 中的空白字符;
注意:不能赋值给变量,仅能用在接受=~或!~操作符的位置;
(3)puppet的变量种类
puppet 种类有三种,为facts,内建变量和用户自定义变量。
- facts:
- 由facter提供;top scope;
- 内建变量:
- master端变量:$servername, $serverip, $serverversion
- agent端变量:$clientcert, $clientversion, $environment
- parser变量:$module_name
- 用户自定义变量
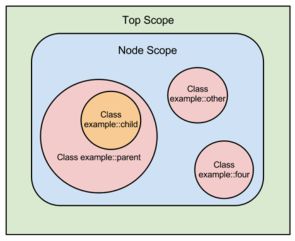
(4)变量的作用域
- 不同的变量也有其不同的作用域。我们称之为Scope。
- 作用域有三种,top scope,node scope,class scope。
- 其生效范围排序为:top scope > node scope > class scope
其优先级排序为:top scope < node scope < class scope