android输入法架构解析
android输入法架构解析
简介:
前阵子接手维护了一个密码键盘的项目,之前还没有接触过android输入法这块的知识点,所以在熟悉项目的同时将android系统输入法实现框架整理了一遍,记录在此.整个输入法架构可以简单划分为主要三块:
1.android输入法管理服务InputMethodManagerService(IMMS)
2.android输入法管理InputMethodManager(IMM)与当前输入控件(EditText)
3.输入法IME
简要示意图如下:

以下将按照如下流程分别进行介绍:
1.输入法管理服务InputMethodManagerService(IMMS)简介
2.输入法管理InputMethodManager(IMM)简介
3.输入法服务InputMethodService简介
4.从edittext点击到输入法界面显示过程
5.输入法字符传递到edittext过程
1.输入法管理服务InputMethodManagerService简介
IMMS主要管理输入法,通过接收IMM的请求拉起或者隐藏输入法,保持输入法与IMM的连接,系统服务的启动在systemserver中,输入法管理是在startOtherServices中:
if (mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
mSystemServiceManager.startService(InputMethodManagerService.Lifecycle.class);
......
}
进入到InputMethodManagerService中主要进行初始化操作,比如当前安装的输入法列表,设置默认输入法,运行时序图如下:
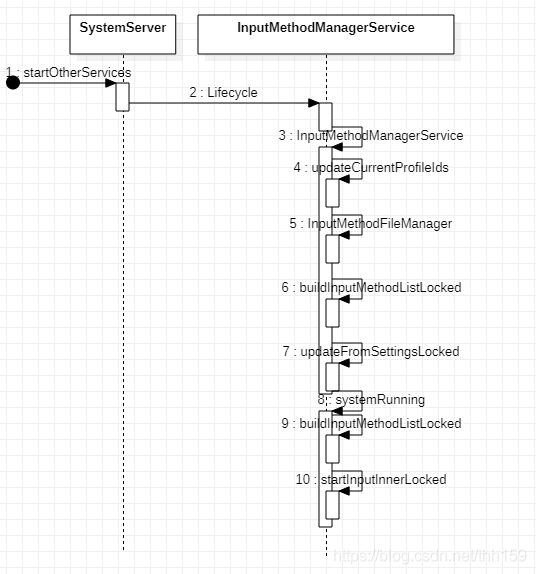
这里获取默认输入法列表和设置默认输入法的操作都在初始化方法中完成:
public InputMethodManagerService(Context context) {
mIPackageManager = AppGlobals.getPackageManager();
mContext = context;
mRes = context.getResources();
mHandler = new Handler(this);
// 这里后续会用来注册几个数据字段的监听
mSettingsObserver = new SettingsObserver(mHandler);
mIWindowManager = IWindowManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE));
mWindowManagerInternal = LocalServices.getService(WindowManagerInternal.class);
mCaller = new HandlerCaller(context, null, new HandlerCaller.Callback() {
@Override
public void executeMessage(Message msg) {
handleMessage(msg);
}
}, true /*asyncHandler*/);
mAppOpsManager = mContext.getSystemService(AppOpsManager.class);
mUserManager = mContext.getSystemService(UserManager.class);
mHardKeyboardListener = new HardKeyboardListener();
mHasFeature = context.getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(
PackageManager.FEATURE_INPUT_METHODS);
//获取默认的系统设置
mSlotIme = mContext.getString(com.android.internal.R.string.status_bar_ime);
mHardKeyboardBehavior = mContext.getResources().getInteger(
com.android.internal.R.integer.config_externalHardKeyboardBehavior);
//初始化通知
Bundle extras = new Bundle();
extras.putBoolean(Notification.EXTRA_ALLOW_DURING_SETUP, true);
mImeSwitcherNotification = new Notification.Builder(mContext)
.setSmallIcon(com.android.internal.R.drawable.ic_notification_ime_default)
.setWhen(0)
.setOngoing(true)
.addExtras(extras)
.setCategory(Notification.CATEGORY_SYSTEM)
.setColor(com.android.internal.R.color.system_notification_accent_color);
Intent intent = new Intent(Settings.ACTION_SHOW_INPUT_METHOD_PICKER);
mImeSwitchPendingIntent = PendingIntent.getBroadcast(mContext, 0, intent, 0);
mShowOngoingImeSwitcherForPhones = false;
//注册用户添加移除,从备份中恢复系统设置广播
final IntentFilter broadcastFilter = new IntentFilter();
broadcastFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_CLOSE_SYSTEM_DIALOGS);
broadcastFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_ADDED);
broadcastFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_USER_REMOVED);
broadcastFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_SETTING_RESTORED);
mContext.registerReceiver(new ImmsBroadcastReceiver(), broadcastFilter);
mNotificationShown = false;
int userId = 0;
try {
userId = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().getCurrentUser().id;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Couldn't get current user ID; guessing it's 0", e);
}
//注册app相关操作广播,包括安装卸载清除数据改变停止等
mMyPackageMonitor.register(mContext, null, UserHandle.ALL, true);
//初始化mSettings,后续用来存放和获取一些InputMethod设置相关内容
mSettings = new InputMethodSettings(
mRes, context.getContentResolver(), mMethodMap, mMethodList, userId, !mSystemReady);
//将从usermanager获取的ProfileIds设置到mSettings中
updateCurrentProfileIds();
//InputMethodFileManager用来缓存用户相关状态
mFileManager = new InputMethodFileManager(mMethodMap, userId);
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
mSwitchingController = InputMethodSubtypeSwitchingController.createInstanceLocked(
mSettings, context);
}
//获取系统默认设置输入法名称
final String defaultImiId = mSettings.getSelectedInputMethod();
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Initial default ime = " + defaultImiId);
}
mImeSelectedOnBoot = !TextUtils.isEmpty(defaultImiId);
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
//解析所有安装的输入法,将其转换为InputMethodInfo添加到列表mMethodList和mMethodMap中,并且处理默认输入法相关,比如设置和重设新的默认输入法
buildInputMethodListLocked(!mImeSelectedOnBoot /* resetDefaultEnabledIme */);
}
//首次启动会将所有的输入法id以":"隔离开组成字符串写入到系统数据库ENABLED_INPUT_METHODS字段中
mSettings.enableAllIMEsIfThereIsNoEnabledIME();
if (!mImeSelectedOnBoot) {
Slog.w(TAG, "No IME selected. Choose the most applicable IME.");
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
//如果还没有设置默认输入法就去设置,将获取到的可用输入法列表的第一个设置为默认输入法
resetDefaultImeLocked(context);
}
}
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
//注册系统数据库中部分跟输入法相关字段改动的监听
mSettingsObserver.registerContentObserverLocked(userId);
//使能当前安装的所有输入法,设置默认输入法,发送输入法变化通知,设置虚拟键盘是否要与实体键盘共存
updateFromSettingsLocked(true);
}
//监听ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED广播以便能够在语言区域发生改变时候能够及时对默认输入法做出调整
final IntentFilter filter = new IntentFilter();
filter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_LOCALE_CHANGED);
mContext.registerReceiver(
new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
synchronized(mMethodMap) {
resetStateIfCurrentLocaleChangedLocked();
}
}
}, filter);
}
这里可以看到,在初始化方法中进行的操作,可以概括为如下几点:
- 一些全局变量初始化,包括mIPackageManager/mIWindowManager/mSettings/mFileManager等。
- 注册广播监听器,监听包括应用安装卸载改变,位置变更在内的广播
- 获取当前系统安装的所有输入法,并且设置默认输入法。
初始化完成后,会调用onBootPhase方法:
@Override
public void onBootPhase(int phase) {
// Called on ActivityManager thread.
// TODO: Dispatch this to a worker thread as needed.
if (phase == SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY) {
StatusBarManagerService statusBarService = (StatusBarManagerService) ServiceManager
.getService(Context.STATUS_BAR_SERVICE);
mService.systemRunning(statusBarService);
}
}
这里详细讲下systemRunning:
public void systemRunning(StatusBarManagerService statusBar) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "--- systemReady");
}
if (!mSystemReady) {
mSystemReady = true;
final int currentUserId = mSettings.getCurrentUserId();
mSettings.switchCurrentUser(currentUserId,
!mUserManager.isUserUnlockingOrUnlocked(currentUserId));
mKeyguardManager = mContext.getSystemService(KeyguardManager.class);
mNotificationManager = mContext.getSystemService(NotificationManager.class);
mStatusBar = statusBar;
if (mStatusBar != null) {
mStatusBar.setIconVisibility(mSlotIme, false);
}
updateSystemUiLocked(mCurToken, mImeWindowVis, mBackDisposition);
mShowOngoingImeSwitcherForPhones = mRes.getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.show_ongoing_ime_switcher);
if (mShowOngoingImeSwitcherForPhones) {
mWindowManagerInternal.setOnHardKeyboardStatusChangeListener(
mHardKeyboardListener);
}
buildInputMethodListLocked(!mImeSelectedOnBoot /* resetDefaultEnabledIme */);
if (!mImeSelectedOnBoot) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Reset the default IME as \"Resource\" is ready here.");
resetStateIfCurrentLocaleChangedLocked();
InputMethodUtils.setNonSelectedSystemImesDisabledUntilUsed(mIPackageManager,
mSettings.getEnabledInputMethodListLocked(),
mSettings.getCurrentUserId(), mContext.getBasePackageName());
}
mLastSystemLocales = mRes.getConfiguration().getLocales();
try {
//连接默认输入法的服务
startInputInnerLocked();
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unexpected exception", e);
}
}
}
}
systemRunning中还会继续进行一遍初始化方法中进行过的,获取当前所有安装的输入法然会设置默认输入法的操作,更重要的是,在这里会与默认输入法的服务进行连接
InputBindResult startInputInnerLocked() {
if (mCurMethodId == null) {
return mNoBinding;
}
if (!mSystemReady) {
// If the system is not yet ready, we shouldn't be running third
// party code.
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurMethodId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
}
InputMethodInfo info = mMethodMap.get(mCurMethodId);
if (info == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown id: " + mCurMethodId);
}
unbindCurrentMethodLocked(true);
mCurIntent = new Intent(InputMethod.SERVICE_INTERFACE);
mCurIntent.setComponent(info.getComponent());
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_LABEL,
com.android.internal.R.string.input_method_binding_label);
mCurIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CLIENT_INTENT, PendingIntent.getActivity(
mContext, 0, new Intent(Settings.ACTION_INPUT_METHOD_SETTINGS), 0));
if (bindCurrentInputMethodService(mCurIntent, this, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE
| Context.BIND_NOT_VISIBLE | Context.BIND_NOT_FOREGROUND
| Context.BIND_SHOWING_UI)) {
mLastBindTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
mHaveConnection = true;
mCurId = info.getId();
mCurToken = new Binder();
try {
if (true || DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Adding window token: " + mCurToken);
//服务连接成功就将该服务添加到窗口管理token列表中
mIWindowManager.addWindowToken(mCurToken,
WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_INPUT_METHOD);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
return new InputBindResult(null, null, mCurId, mCurSeq,
mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
} else {
mCurIntent = null;
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure connecting to input method service: "
+ mCurIntent);
}
return null;
}
输入法管理服务暂时分析到这里,这里还有几个类说明下其承担的功能:
InputMethodInfo/InputMethodSubtype用来描述输入法相关信息
InputMethodUtils$InputMethodSettings包含了所有与输入法相关数据信息的读取和写入
InputMethodFileManager用于从subtypes.xml文件中读取和写入subtype信息
InputBindResult 用于记录和描述一次成功的输入法管理服务到输入法的绑定
ClientState 用于记录一次远程连接到当前输入法的客户端描述
SessionState 用于记录一次连接的会话状态
总结:输入法管理服务主要用于管理输入法,默认输入法的设置,输入法应用的安装卸载监听等,输入法界面的弹出,退出,持有当前输入法和当前输入法服务对象的连接。
2. 输入法管理InputMethodManager(IMM)简介
InputMethodManager存在应用进程中,在activity展示阶段在就初始化了,其主要功能是管理当前焦点view,与IMMS通信完成输入法的展示与隐藏,让EditText与输入法产生交互,之后输入法发送的内容就可以直接通过从IMM传入到输入法的连接通道发送到edittext中。
/**
* This is the root view of the overall window that currently has input
* method focus.
*/
View mCurRootView;
/**
* This is the view that should currently be served by an input method,
* regardless of the state of setting that up.
*/
View mServedView;
/**
* This is then next view that will be served by the input method, when
* we get around to updating things.
*/
View mNextServedView;
IMM中的三个view,mCurRootView是当前activity的decorview,mServedView是当前正在被服务的输入框edittext,mNextServedView是当前焦点处在的view,也就是很有可能成为下一个被服务的view。当view焦点发生改变时候就会通过focusIn与focusOut方法改变mNextServedView的值:
void focusInLocked(View view) {
......对view合法性的检测
mNextServedView = view;
scheduleCheckFocusLocked(view);
}
如果对当前view有进一步的操作,就会将mNextServedView赋值给mServedView
private boolean checkFocusNoStartInput(boolean forceNewFocus) {
......
synchronized (mH) {
......
ic = mServedInputConnectionWrapper;
mServedView = mNextServedView;
mCurrentTextBoxAttribute = null;
mCompletions = null;
mServedConnecting = true;
}
......
return true;
}
checkFocusNoStartInput方法被调用的频次非常高
变量mClien表示当前输入法服务对象,由IMMS持有
final IInputMethodClient.Stub mClient = new IInputMethodClient.Stub() {}
其内部类ControlledInputConnectionWrapper,持有EditableInputConnection通过IMMS最终传递到了IputMethodService中,建立了edittext与输入法之间的连接,输入法中提交的字符通过这个通道的commitText方法展示到了edittext中。
3.输入法服务InputMethodService简介
InputMethodService是每个输入法服务都必须要继承的基类,结构如下:

通过IInputMethodWrapper类包装后,在父类的onbind方法中返回给IMMS,
final public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
if (mInputMethod == null) {
mInputMethod = onCreateInputMethodInterface();
}
return new IInputMethodWrapper(this, mInputMethod);
}
IMMS中绑定服务成功后获得IInputMethodWrapper,
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurIntent != null && name.equals(mCurIntent.getComponent())) {
mCurMethod = IInputMethod.Stub.asInterface(service);
if (mCurToken == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Service connected without a token!");
unbindCurrentMethodLocked(false);
return;
}
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Initiating attach with token: " + mCurToken);
executeOrSendMessage(mCurMethod, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_ATTACH_TOKEN, mCurMethod, mCurToken));
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
requestClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
}
}
}
}
方法中mCurToken非空,在mCurMethod被赋值后,会继续通过requestClientSessionLocked建立会话,会话建立完成后会将InputMethodService的子类InputMethodSessionImpl传递过来保存到ClientState中
void onSessionCreated(IInputMethod method, IInputMethodSession session,
InputChannel channel) {
synchronized (mMethodMap) {
if (mCurMethod != null && method != null
&& mCurMethod.asBinder() == method.asBinder()) {
if (mCurClient != null) {
clearClientSessionLocked(mCurClient);
mCurClient.curSession = new SessionState(mCurClient,
method, session, channel);
InputBindResult res = attachNewInputLocked(true);
if (res.method != null) {
executeOrSendMessage(mCurClient.client, mCaller.obtainMessageOO(
MSG_BIND_CLIENT, mCurClient.client, res));
}
return;
}
}
}
// Session abandoned. Close its associated input channel.
channel.dispose();
}
4.从edittext点击到输入法界面显示过程
该过程分为两步,点击后与输入法的bind与start过程,输入法界面的展示过程。
点击后的bind与start过程如下:

这里重点看下startInputInner与attachNewInputLocked,在这里会生成view的EditableInputConnection,作为参数传入到ControlledInputConnectionWrapper中,ControlledInputConnectionWrapper作为参数传入到IMMS中,最后通过startInput在将IInputMethodWrapper再次包装成一个ControlledInputConnectionWrapper传入到InputMethodService中赋值给mStartedInputConnection。这样输入法与EditText之间的就关联上了。
boolean startInputInner(@InputMethodClient.StartInputReason final int startInputReason,
IBinder windowGainingFocus, int controlFlags, int softInputMode,
int windowFlags) {
.....
//得到view的连接EditableInputConnection
InputConnection ic = view.onCreateInputConnection(tba);
......
servedContext = new ControlledInputConnectionWrapper(
icHandler != null ? icHandler.getLooper() : vh.getLooper(), ic, this);
......
final InputBindResult res = mService.startInputOrWindowGainedFocus(
startInputReason, mClient, windowGainingFocus, controlFlags, softInputMode,
windowFlags, tba, servedContext, missingMethodFlags);
......
}
InputBindResult attachNewInputLocked(boolean initial) {
......
final SessionState session = mCurClient.curSession;
if (initial) {
executeOrSendMessage(session.method, mCaller.obtainMessageIOOO(
MSG_START_INPUT, mCurInputContextMissingMethods, session, mCurInputContext,
mCurAttribute));
} else {
executeOrSendMessage(session.method, mCaller.obtainMessageIOOO(
MSG_RESTART_INPUT, mCurInputContextMissingMethods, session, mCurInputContext,
mCurAttribute));
}
if (mShowRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Slog.v(TAG, "Attach new input asks to show input");
showCurrentInputLocked(getAppShowFlags(), null);
}
return new InputBindResult(session.session,
(session.channel != null ? session.channel.dup() : null),
mCurId, mCurSeq, mCurUserActionNotificationSequenceNumber);
}
进入到InputMethodWrapper中,参数中的inputContext就是IMM中生成的ControlledInputConnectionWrapper
public void startInput(IInputContext inputContext,
@InputConnectionInspector.MissingMethodFlags final int missingMethods,
EditorInfo attribute) {
mCaller.executeOrSendMessage(mCaller.obtainMessageIOO(DO_START_INPUT,
missingMethods, inputContext, attribute));
}
case DO_START_INPUT: {
SomeArgs args = (SomeArgs)msg.obj;
int missingMethods = msg.arg1;
IInputContext inputContext = (IInputContext)args.arg1;
//再次封装一层,这里不明白为何还要再封装一层
InputConnection ic = inputContext != null
? new InputConnectionWrapper(mTarget, inputContext, missingMethods) : null;
EditorInfo info = (EditorInfo)args.arg2;
info.makeCompatible(mTargetSdkVersion);
//ic赋值给了InputMethodService中的mStartedInputConnection
inputMethod.startInput(ic, info);
args.recycle();
return;
}
void doStartInput(InputConnection ic, EditorInfo attribute, boolean restarting) {
if (!restarting) {
doFinishInput();
}
mInputStarted = true;
//连接建立
mStartedInputConnection = ic;
mInputEditorInfo = attribute;
initialize();
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartInput");
onStartInput(attribute, restarting);
if (mWindowVisible) {
if (mShowInputRequested) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartInputView");
mInputViewStarted = true;
onStartInputView(mInputEditorInfo, restarting);
startExtractingText(true);
} else if (mCandidatesVisibility == View.VISIBLE) {
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "CALL: onStartCandidatesView");
mCandidatesViewStarted = true;
onStartCandidatesView(mInputEditorInfo, restarting);
}
}
}
以上流程完成之后输入法与edittext之间的连接建立,输入法也已经绑定,可以展示界面进行输入操作了。输入法界面展示流程如下:

5.输入法字符传递到edittext过程
输入法字符发送到edittext的流程如下,这里以sendKeyChar为开头,看过源码中的拉丁输入法是直接getCurrentInputConnection.commitText发送字符的

在BaseInputConnection中的replaceText方法中
private void replaceText(CharSequence text, int newCursorPosition,
boolean composing) {
final Editable content = getEditable();
......
content.replace(a, b, text);
.....
}
子类EditableInputConnection中的重载方法如下:
public Editable getEditable() {
TextView tv = mTextView;
if (tv != null) {
return tv.getEditableText();
}
return null;
}
所以最终文字的字符从输入法发送到edittext是通过按索引替换来实现的。
