Spring源码初探 -在AbstractApplicationContext中的refresh简单理解
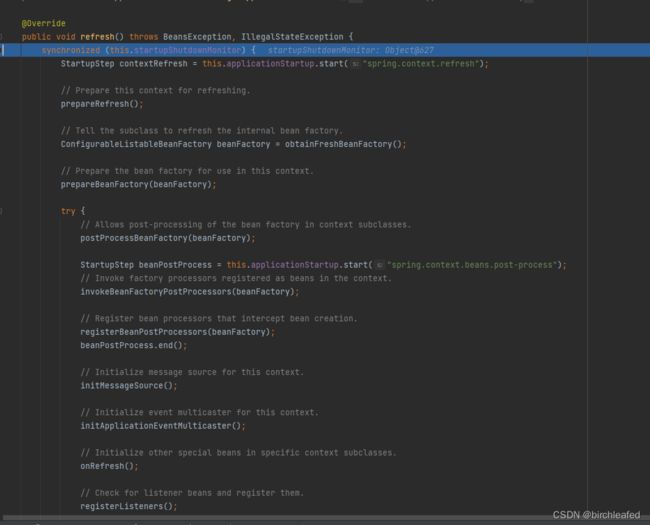
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 这步比较关键,这步完成后,配置文件就会解析成一个个 Bean 定义,注册到 BeanFactory 中,
// 当然,这里说的 Bean 还没有初始化,只是配置信息都提取出来了,
// 注册也只是将这些信息都保存到了注册中心(说到底核心是一个 beanName-> beanDefinition 的 map)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}一共十三个方法
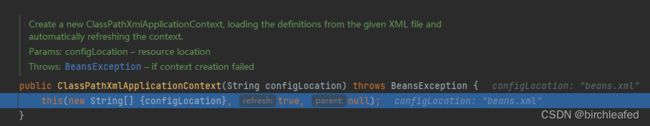
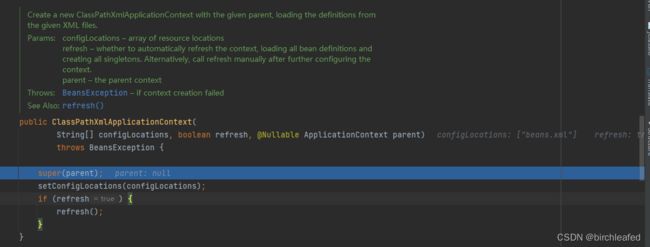
这步我们使用debug来查看new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext来进一步理解
1
2
3
4
在进行初始化之后就开始进行我们的refresh方法
refersh的组件
1prepareRefresh
准备刷新 其中就只是创建了启动时间,设置容器的活跃,初始化资源,获得环境对象并验证,还有创建了一系列的Set集合,并没有创建BeanFactory
/**
* Prepare this context for refreshing, setting its startup date and
* active flag as well as performing any initialization of property sources.
*/
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();//设置启动时间
this.closed.set(false);//设置容器关闭为false
this.active.set(true);//设置容器活跃为true
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
}
else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
initPropertySources();//初始化属性资源 留给子类实现
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();//获取环境对象并且验证属性值
// 里面有createEnviroment--> new StandardEnvironment
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
//创建一系列的set集合
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
}
else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}2obtainFreshBeanFactory 获得新鲜的BeanFactory
该方法还是在AbstractApplicationContext中
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
return getBeanFactory();
}
然后进入到refreshBeanFactory()
/**
* This implementation performs an actual refresh of this context's underlying
* bean factory, shutting down the previous bean factory (if any) and
* initializing a fresh bean factory for the next phase of the context's lifecycle.
*/
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
//判断有没有Bean工厂 有的话就销毁
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//在判断没有bean工厂后 createBeanFactory 创建出 DefaultListableBeanFactory
// return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());//序列化id值
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);//
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}其中的customizeBeanFactory 设置属性值
/**
* Customize the internal bean factory used by this context.
* Called for each {@link #refresh()} attempt.
* The default implementation applies this context's
* {@linkplain #setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding "allowBeanDefinitionOverriding"}
* and {@linkplain #setAllowCircularReferences "allowCircularReferences"} settings,
* if specified. Can be overridden in subclasses to customize any of
* {@link DefaultListableBeanFactory}'s settings.
* @param beanFactory the newly created bean factory for this context
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowCircularReferences
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping
* @see DefaultListableBeanFactory#setAllowEagerClassLoading
*/
protected void customizeBeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding != null) {
// 是否允许 Bean 定义覆盖
beanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.allowCircularReferences != null) {
// 是否允许 Bean 间的循环依赖
beanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
}
}
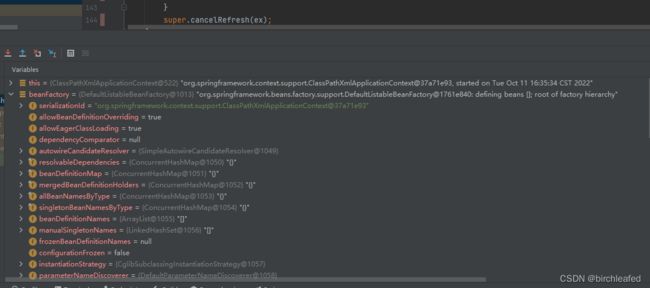
在执行完序列化setSerialization和设置属性值之后beanFactory所含有的值,特别注意beanDefinitionMap与beanDefinitionName
在loadBeanDefinition之后Bean信息加载到容器中
/**
* Loads the bean definitions via an XmlBeanDefinitionReader.
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #initBeanDefinitionReader
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions
*/
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}3prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
/**
* Configure the factory's standard context characteristics,
* such as the context's ClassLoader and post-processors.
* @param beanFactory the BeanFactory to configure
*/
protected void prepareBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,我们知道 BeanFactory 需要加载类,也就需要类加载器,
// 这里设置为加载当前 ApplicationContext 类的类加载器
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(getClassLoader());
// 设置 BeanExpressionResolver
beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver(new StandardBeanExpressionResolver(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
//
beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar(new ResourceEditorRegistrar(this, getEnvironment()));
// 添加一个 BeanPostProcessor,这个 processor 比较简单:
// 实现了 Aware 接口的 beans 在初始化的时候,这个 processor 负责回调,
// 这个我们很常用,如我们会为了获取 ApplicationContext 而 implement ApplicationContextAware
// 注意:它不仅仅回调 ApplicationContextAware,
// 还会负责回调 EnvironmentAware、ResourceLoaderAware 等,看下源码就清楚了
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationContextAwareProcessor(this));
// 下面几行的意思就是,如果某个 bean 依赖于以下几个接口的实现类,在自动装配的时候忽略它们,
// Spring 会通过其他方式来处理这些依赖。
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EnvironmentAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(EmbeddedValueResolverAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ResourceLoaderAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationEventPublisherAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(MessageSourceAware.class);
beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface(ApplicationContextAware.class);
/**
* 下面几行就是为特殊的几个 bean 赋值,如果有 bean 依赖了以下几个,会注入这边相应的值,
* 之前我们说过,"当前 ApplicationContext 持有一个 BeanFactory",这里解释了第一行。
* ApplicationContext 还继承了 ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisher、MessageSource
* 所以对于这几个依赖,可以赋值为 this,注意 this 是一个 ApplicationContext
* 那这里怎么没看到为 MessageSource 赋值呢?那是因为 MessageSource 被注册成为了一个普通的 bean
*/
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(BeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ResourceLoader.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationEventPublisher.class, this);
beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency(ApplicationContext.class, this);
// 这个 BeanPostProcessor 也很简单,在 bean 实例化后,如果是 ApplicationListener 的子类,
// 那么将其添加到 listener 列表中,可以理解成:注册 事件监听器
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(this));
// 这里涉及到特殊的 bean,名为:loadTimeWeaver,这不是我们的重点,忽略它
// tips: ltw 是 AspectJ 的概念,指的是在运行期进行织入,这个和 Spring AOP 不一样,
// 感兴趣的读者请参考我写的关于 AspectJ 的另一篇文章 https://www.javadoop.com/post/aspectj
if (beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
// Set a temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
/**
* 从下面几行代码我们可以知道,Spring 往往很 "智能" 就是因为它会帮我们默认注册一些有用的 bean,
* 我们也可以选择覆盖
*/
// 如果没有定义 "environment" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment());
}
// 如果没有定义 "systemProperties" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemProperties());
}
// 如果没有定义 "systemEnvironment" 这个 bean,那么 Spring 会 "手动" 注册一个
if (!beanFactory.containsLocalBean(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_BEAN_NAME, getEnvironment().getSystemEnvironment());
}
}