数据结构之(三):队列
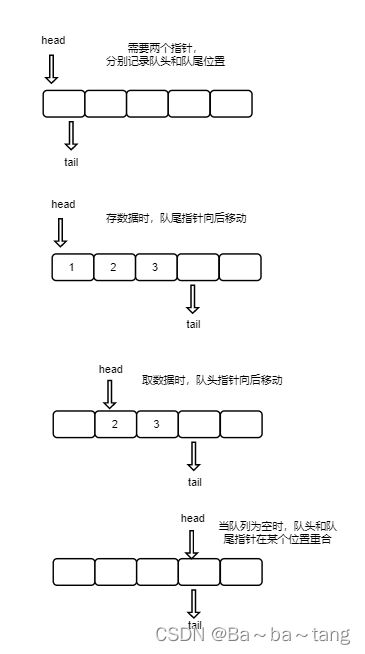
队列初体验之数组实现方式
队列
1 、初识队列
队列,是一种对存取有严格要求的数据结构只能从尾部存入数据,从头部取出数据遵循 “ 先进先出 ” 原则队列的实现有两种方式:顺序队列(基于数组)、链队列(基于链表)
用数组实现队列
public class ArrayQueue {
// 最大容量
int maxCapacity;
// 声明头尾指针
int head;
int tail;
// 存储元素
int[] arr;
public ArrayQueue(int maxCapacity) {
arr = new int[maxCapacity];
maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return tail == maxCapacity;
}
public void add(int n) {
// 先判断队列的容量大小
if (!isFull()) {
arr[tail] = n;
}
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == tail;
}
public int get() {
// 先判断队列是否为空
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
int result = arr[head];
head++;
return result;
}
} LinkedList 的使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 都能添加元素
// queue.add(1);
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
// 两者区别 当队列满的时候 add会抛出异常 offer会返回false 更健壮更友好
// 取出元素 分为两种
// 只获取队头元素 不取出
queue.peek();
queue.element();
// 两者区别 当队列为空时 element会抛出异常 peek会返回null
// 获取队头元素 同时取出
queue.poll();
queue.remove();
// 两者区别 当队列为空时 remove会抛出异常 poll会返回null
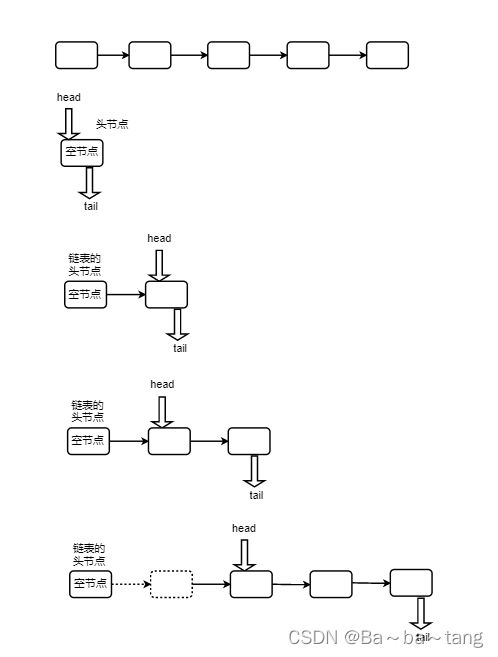
} 链队列原理分析
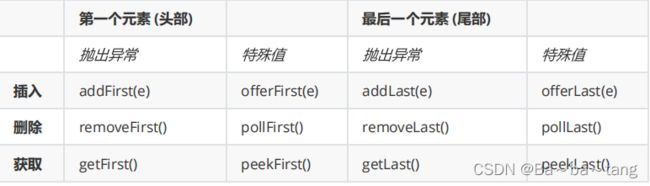
双端队列和各式队列
双端队列双端队列,区别于普通队列两端都可以进行入队和出队deque = "double ended queue"LinkedList 和 ArrayDeque
【特别的队列】
1 ) 优先级队列元素携带了相关的优先级,优先级更高的元素排在头部PriorityQueue ,提供了 Comparable 接口,元素可以实现其方法,改变在队列中的顺序2 )阻塞队列当队列满的时候,等待有空余位置再存数据;当队列空的时候,等待有新数据再读取BlockingQueue , put() 和 take() 提供了存取的阻塞逻辑分为两种情况,一种是无限期的等,一种是指定阻塞时间3 )延迟队列在指定时间内获取队列元素,头部元素是最接近过期时间的。DelayQueue 给定一个接口设置延迟时间 元素会按照时间排序
挑战升级之队列的最大值
队列的最大值
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/dui-lie-de-zui-da-zhi-lcof/
剑指 Offffer 59 - II. 队列的最大值请定义一个队列并实现函数 max_value得到队列里的最大值,要求函数 max_value 、 push_back 和 pop_front 的均摊时间复杂度都是O(1) 。若队列为空, pop_front 和 max_value 需要返回 -1示例 1 :输入 :["MaxQueue","push_back","push_back","max_value","pop_front","max_value"][[],[1],[2],[],[],[]]输出 : [null,null,null,2,1,2]分别对应 方法名、参数 以及 返回结果示例 2 :输入 :["MaxQueue","pop_front","max_value"][[],[],[]]输出 : [null,-1,-1]
分析:队头 队尾[1,2,3,4,3,2,1]在队列发生更改时 记录出最大值[] -1[1] 1[1,2] 2[1,2,3] 3[2,3] 3[2,3,2,1] 3[3,2,1] 3[2,1] 2因为增删操作时 都可能影响最大值的变化如果是新增操作,比较新元素和当前最大值之间,更大的值是新的最大值如果是删除操作,删除的元素如果不是最大值,那么最大值不变,如果是最大值,最大值要更改为剩余元素的最大值使用额外的队列,来记录最大值发生的变化max 队列,队头元素是当前的最大值,而其他元素是未来可能成为最大值的候选值新增元素 ele 时 ele>max 取队列中队尾元素比较,如果满足,进行覆盖并且循环比较直到把所有比它小的值都覆盖为止ele将其存到 max 队列中 原队列 max 队列[1] [1][1,2] [2][1,2,3] [3][2,3] [3][2,3,2] [3,2][2,3,2,1] [3,2,1][3,2,1] [3,2,1][2,1] [2,1][2,1,4] [4]
public class MaxQueue {
// 原始队列
LinkedList queue;
// 最大值的候选值
LinkedList max;
public MaxQueue() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
max = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int max_value() {
if (max.isEmpty()) return -1;
return max.peekFirst();
}
// 新增元素 ele时 ele>max 取队列中队尾元素比较,如果满足,进行覆盖并且循环比较
// 直到把所有比它小的值都覆盖为止
// ele 经典算法思想之滑动窗口
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/hua-dong-chuang-kou-de-zui-da-zhi-lcof/
剑指 Offffer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值给定一个数组 nums 和滑动窗口的大小 k ,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。示例 :输入 : nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], 和 k = 3输出 : [3,3,5,5,6,7]解释 :滑动窗口的位置 最大值[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 31 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 31 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 51 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 51 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 61 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
分析:数组的长度为 n 窗口的大小为 k 可形成的窗口个数 n-k+1通过队列来记录最大值窗口未形成的阶段遍历数组,同时更新队列窗口已形成的阶段每次窗口移动,都是在头部移除元素,尾部增加元素在窗口变化过程中 记录其最大值的变化 ( 让最大值一直出现在第一位 )让队列中已存在的元素 和新添加的元素比较 如果已存在的更小 那么覆盖如果已存在的更大 新添加的元素是候选 缀到队列之后滑动窗口的位置 最大值
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
窗口 max 队列
[1 3 -1] [1] -> [3] -> [3,-1]
[3 -1 -3] [3,-1,-3]
[-1 -3 5] [-1,-3] -> [5]
[-3 5 3] [5,3]
[5 3 6] [6]
[3 6 7] [7]
public static int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
// 记录每个窗口的最大值 n-k+1为形成的窗口个数
int[] result = new int[nums.length - k + 1];
// 使用队列记录最大值的候选值
Deque deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 窗口未形成的阶段
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
print(deque);
// 每次都取 队尾元素和新元素 比较 如果队尾更小 删除
while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < nums[i]){
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(nums[i]);
}
// 此时第一个窗口形成 deque的队头元素就是第一个窗口的最大值
result[0] = deque.peekFirst();
print(deque);
// 窗口已形成的阶段
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
System.out.println("-----第" + (i-k+1) + "次滑动");
// 删了元素 nums[i-k] 添了元素 nums[i]
if(nums[i-k] == deque.peekFirst()){
// 如果删的是最大值 同时从deque移除
deque.pollFirst();
}
// 新增
while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < nums[i]){
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(nums[i]);
result[i-k+1] = deque.peekFirst();
print(deque);
}
return result;
}
public static void print(Deque deque){
for (Integer integer : deque) {
System.out.print(integer + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
} 循环队列的设计和实现
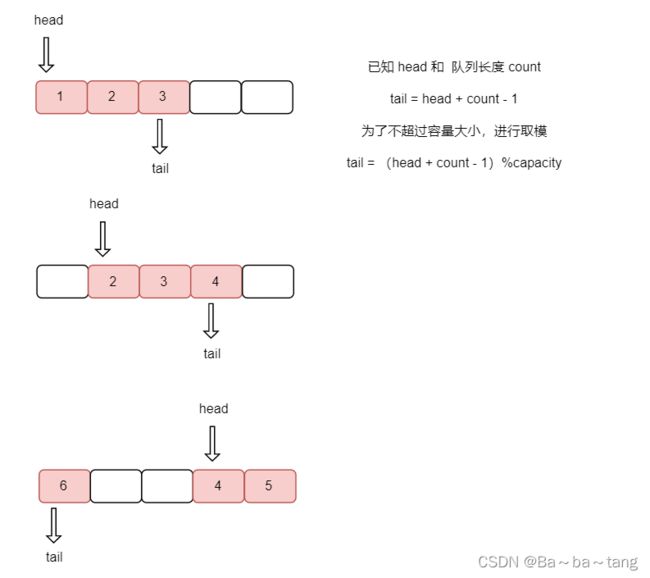
循环队列
循环队列为解决,队列存取数据后,空间无法重复利用的问题,通过构造环形,重复使用
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-circular-queue/
622. 设计循环队列设计你的循环队列实现。 循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO (先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为 “ 环形缓冲器 ” 。循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。你的实现应该支持如下操作:MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为 k 。Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 -1 。enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真。deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真。isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空。isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满。
public class MyCircularQueue {
// 存储元素的数组
int[] queue;
// 最大容量
int capacity;
// 头指针
int head;
// 实际队列长度
int count;
/**
* Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k.
*/
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
capacity = k;
queue = new int[k];
head = 0;
count = 0;
}
/**
* Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation
is successful.
*/
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull()) return false;
int index = (head + count) % capacity;
queue[index] = value;
count++;
return true;
}
/**
* Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation
is successful.
*/
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) return false;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
count--;
return true;
}
/**
* Get the front item from the queue.
*/
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
return queue[head];
}
/**
* Get the last item from the queue.
*/
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty()) return -1;
int tail = (head + count - 1) % capacity;
return queue[tail];
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not.
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return count == 0;
}
/**
* Checks whether the circular queue is full or not.
*/
public boolean isFull() {
return count == capacity;
}
}