SpringBoot——安全管理(一)
SpringBoot——安全管理
-
-
- 一、简介
- 二、Spring Security
-
一、简介
安全可以说是公司的红线了,一般项目都有严格的认证和授权操作,在Java开发领域常见的安全框架有Shiro和Spring Security。Shiro是一个轻量级的安全管理框架,提供了认证、授权、会话管理、密码管理、缓存管理等功能,Spring Security是一个相对复杂的安全管理框架,功能比Shiro更加强大,权限控制细粒度更高,对OAuth2的支持也更好,又因为Spring Security源自Spring家族,因此可以和Spring框架无缝整合,特别是SpringBoot中提供的自动化配置方案,可以让Spring Security的使用更加便捷。
二、Spring Security
- Spring Secuirty的基本配置
Spring Boot针对Spring Security提供了自动化配置方案,因此可以使Spring Security非常容易地整合进Spring Boot项目中,这也是在Spring Boot项目中使用Spring Security的优势。 - 基本用法
基本整合步骤如下:
- 创建项目,添加依赖
常见一个Spring Boot Web项目,然后添加spring-boot-starter-security依赖即可,代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 添加hello接口
接下来在项目中添加一个简单的/hello接口,内容如下:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello";
}
}
默认的用户名是user,默认的登录密码则在每次启动项目时随机生成,查看项目启动日志,如下图

- 配置用户名和密码
如果开发者对默认的用户名和密码不满意,可以在application.properties中配置默认的用户名、密码以及用户角色,配置方式如下:
spring.security.user.name=song
spring.security.user.password=123
spring.security.user.roles=admin
再次启动项目,项目启动日志就不会打印出随机生成的密码了,用户可以直接使用配置好的用户名和密码登录,登录成功后,用户还具有一个角色——admin。
- 基于内存的认证
可以自定义类继承自WebSecurityConfigurerAdaptor,进而实现对Spring Security更多的自定义配置,例如基于内存的认证,配置方式如下:
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
public class MyWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
//配置用户admin 密码123 具备admin、user角色
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
//配置用户song 密码123 具备user角色
.withUser("song").password("123").roles("USER");
}
}
注意:
- Spring Security 5.* 中引入了多种密码加密方式。必须指定一种。
- 基于内存的用户配置在配置角色时不需要添加“ROLE_”前缀。
- HttpSecurity
虽然可以实现认证功能,但是受保护的资源都是默认的,而且也不能根据实际情况进行角色管理,如果要实现这些功能,就需要重写WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter中的另一个方法,代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("root").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "DBA")
.and()
//配置用户admin 密码123 具备admin、user角色
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
//配置用户song 密码123 具备user角色
.withUser("song").password("123").roles("USER");
}
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN', 'USER')")
.antMatchers("/db/**")
.access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
//除了前面定义的URL模式之外,用户访问其他的URL必须认证后访问(登录后访问)
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
/**
* 表示开启登录,同时配置了登录接口为“/login”,即可以直接调用“/login”接口,发起一个POST请求
* 进行登录,登录参数中用户必须命名为username,密码命名为password,配置loginProcessingUrl接口主要是方便
* Ajax或者移动端调用登录接口。
* 最后还配置了permitAll,表示和登录相关的接口都不需要认证接口即可访问
*/
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
//表示关闭csrf
.csrf()
.disable();
}
}
- 登录表单详细配置
目前前后端分离正在成为企业级应用开发的主流,在前后端分离的开发方式中,前后端的数据交互通过JSON进行,这时,登录成功后就不是页面跳转了,而是一段JSON提示。要实现这些功能,只需要继续完善上文的配置。代码如下:
@Configuration
public class MyWebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
public void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("root").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "DBA")
.and()
//配置用户admin 密码123 具备admin、user角色
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
//配置用户song 密码123 具备user角色
.withUser("song").password("123").roles("USER");
}
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/admin/**")
.hasRole("ADMIN")
.antMatchers("/user/**")
.access("hasAnyRole('ADMIN', 'USER')")
.antMatchers("/db/**")
.access("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
//除了前面定义的URL模式之外,用户访问其他的URL必须认证后访问(登录后访问)
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
/**
* 表示开启登录,同时配置了登录接口为“/login”,即可以直接调用“/login”接口,发起一个POST请求
* 进行登录,登录参数中用户必须命名为username,密码命名为password,配置loginProcessingUrl接口主要是方便
* Ajax或者移动端调用登录接口。
* 最后还配置了permitAll,表示和登录相关的接口都不需要认证接口即可访问
*/
.formLogin()
//自定义登录页面
.loginPage("/login_page")
//表示登录请求处理接口,无论是自定义登录页面还是移动端登录,都需要使用该接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
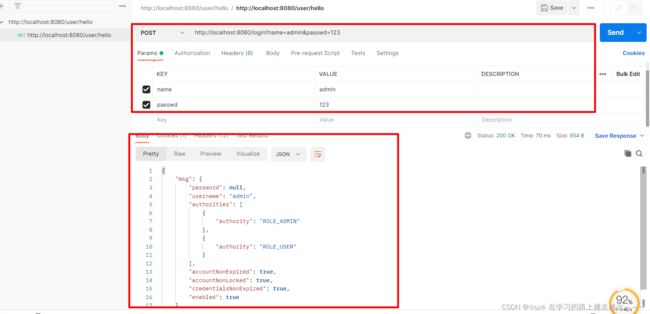
//认证所需的用户名和密码的参数名,默认用户名参数是username,密码参数是passwd,可以在这里自定义
.usernameParameter("name")
.passwordParameter("passwd")
/**
* 定义了登录成功的处理逻辑。用户登录成功后可以跳转到某一个页面,
* 也可以返回一段JSON,这个要看具体的页面逻辑,
* 本案例假设是第二种,用户登录成功后,返回一段登录成功的JSON。
* onAuthenticationSuccess方法的第三个参数一般用来获取当前登录用户的信息
* 在登录成功后,可以获取当前登录用户的信息一起返回给客户端
*
*/
.successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
Object principal = authentication.getPrincipal();
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
response.setStatus(200);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 200);
map.put("msg", principal);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
out.write(om.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
/**
* 定义了登录失败的处理逻辑,和登录成功类似,不同的是
* 登录失败的回调方法里有一个AuthenticationException参数,
* 通过这个异常参数可以获取登录失败的原因,进而给用户一个明确的提示。
*/
.failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
response.setStatus(401);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 401);
if (exception instanceof LockedException) {
map.put("msg", "账户被锁定,登录失败");
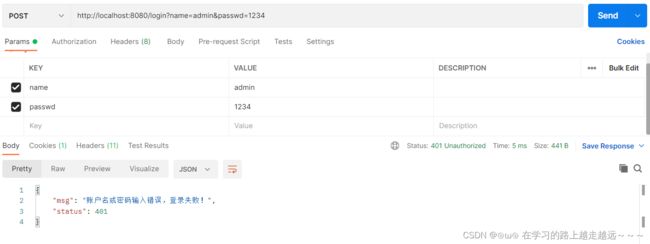
} else if (exception instanceof BadCredentialsException) {
map.put("msg", "账户名或密码输入错误,登录失败!");
} else if (exception instanceof DisabledException) {
map.put("msg", "账户被禁用,登录失败!");
} else if (exception instanceof AccountExpiredException) {
map.put("msg", "账户已过期,登录失败!");
} else if (exception instanceof CredentialsExpiredException) {
map.put("msg", "密码已过期,登录失败!");
} else {
map.put("msg", "登录失败!");
}
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
out.write(om.writeValueAsString(map));
out.flush();
out.close();
}
})
.permitAll()
.and()
//表示关闭csrf
.csrf()
.disable();
}
- 注销登录配置
如果想要注销登录,也只需要提供简单的配置即可。代码如下:
//注销登录,表示开启注销登录的配置
.logout()
//表示配置注销登录请求URL为"/logout",默认为“/logout”
.logoutUrl("/logout")
//表示是否清楚身份认证信息,默认为true,表示清楚
.clearAuthentication(true)
//表示是否使Session失效,默认为true
.invalidateHttpSession(true)
/**
* 配置一个LogoutHandler,开发者可以在LogoutHandler中完成
* 一些数据清楚工作,例如 Cookie的清楚。Spring Security提供了一些常见的实现。
*/
.addLogoutHandler(new LogoutHandler() {
@Override
public void logout(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) {
}
})
/**
* 配置一个LogoutSuccessHandler,开发者可以在这里处理注销成功后的业务逻辑
* 例如 返回一段JSON提示或者跳转到登录页面等。
*/
.logoutSuccessHandler(new LogoutSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("/login_page");
}
})
- 多个HttpSecurity
如果业务比较复杂,开发者也可以配置多个HttpSecurity,实现对WebSecurityConfigurerAdaptor的多次扩展,代码如下:
/**
* 配置多个HttpSecurity时,MultiHttpSecurityConfig不需要继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
* 在MultiHttpSecurityConfig中创建静态内部类继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter即可,
* 静态内部类上添加@Configuration注解和@Order注解,@Order注解表示该配置的优先级
* 数字越小优先级越大,未加@Order注解的配置优先级最小。
*/
@Configuration
public class MultiHttpSecurityConfig {
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Autowired
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin").password("123").roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
.withUser("song").password("123").roles("USER");
}
@Configuration
@Order(1)
public static class AdminSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/admin/**").authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().hasRole("ADMIN");
}
}
@Configuration
public static class OtherSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.formLogin()
.loginProcessingUrl("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.csrf()
.disable();
}
}
}
- 密码加密
- 为什么要加密
数据存储为明文,会造成密码泄露问题会造成很大的安全隐患。 - 加密方案
密码加密一般会用到散列函数、又称散列算法、哈希函数,这是一种从任何数据中创建数字“指纹”的方法。散列函数把消息或数据压缩成摘要,使得数据量变小,将数据的格式固定下来,然后将数据打乱混合,重新创建一个散列值。散列值通常用一个短的随机字母和数字组成的字符串来代表。好的散列函数在输入域中很少出现散列冲突。在散列表和数据处理中,不抑制冲突来区别数据会使得数据库记录更难找到。我们常用的散列函数有MD5消息摘要算法、安全散列算法(Secure Hash Algorithm)。
但是仅仅使用散列函数还不够,为了增加密码的合法性,一般在密码加密过程中还需要加盐,所谓的加盐可以是一个随机数,也可以是用户名,加盐之后,即使密码明文相同的用户生成的密码,密文也不相同,这可以极大地提高密码的安全性。但是传统的加盐方式需要在数据库中有专门的字段来记录盐值,这个字段可能时用户名字段(因为用户名唯一),也可能是一个专门记录盐值的字段,这样的配置比较繁琐。Spring Security提供了多种密码加密方案,官方推荐使用BCryptPasswordEncoder,BCryptPasswordEncoder使用BCrypt强哈希函数,开发者在使用时可以选择提供strength和SecureRandom实例。strength越大,密钥的迭代次数越多,密钥迭代次数为2^strength。strength取值在4~31之间,默认为10。 - 实践
在Spring Boot 中配置密码加密非常容易,只需要修改上下配置的PasswordEncoder这个Bean的实现即可,代码如下:
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
//return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10);
}
创建BCryptPasswordEncoder时传入的参数10就是strength,即密钥的迭代次数(也可以不配置,默认为10)。同时,配置的内存用户的密码也不再是123了,代码如下:
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin")
// .password("123")
.password("$2a$10$PnhbK8g8WlxNktjgmAAvyOl2W6QIfpzudAN.jaiy0wp5.fLLUaH0.")
.roles("ADMIN", "USER")
.and()
.withUser("song")
// .password("123")
.password("$2a$10$jvxbmYE0L/WKMTUNkn7db.LOsItAUm5PUB.iIDREG8sU4kzry7SQq")
.roles("USER");
这里的密码就是使用BCryptPasswordEncoder加密后的密码,虽然admin和song加密后的密码不一样,但是明文都是123。配置完成后,使用admin/123或者song/123就可以实现登录。本案例使用了配置再内存中的用户,一般情况下,用户信息是存储在数据库中的,因此需要在用户注册时对密码进行加密处理,代码如下:
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
//return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10);
String encodepasswd = encoder.encode("123");
System.out.println("encodepasswd--------------->" + encodepasswd);
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(10);
}
- 方法安全
上文介绍的认证与授权都是基于URl的,开发者也可以通过注解来灵活地配置方法安全,要使用相关注解,首先要通过@EnableGlobalMehthodSecurity注解来开启基于注解的安全配置:
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true, securedEnabled = true)
public class MultiHttpSecurityConfig {
解释:
- prePostEnabled = true 会解锁@PreAuthorize和@PostAuthorize两个注解,顾名思义,@PreAuthorize注解会在方法前执行验证,而@PostAuthorize注解在方法执行后进行验证。
- securedEnabled = true会解锁@Secured注解
开启注解安全配置后,接下来创建一个MethodService进行测试,代码如下:
@Service
public class MethodService {
/**
* @Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
* 注解表示访问该方法需要ADMIN角色,注意这里需要在角色前加一个前缀“ROLE_”
* @return
*/
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
public String admin() {
return "hello admin";
}
/**
* @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
* 表示访问该方法既需要ADMIN角色又需要DBA角色
* @return
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN') and hasRole('DBA')")
public String dba() {
return "hello dba";
}
/**
* @PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ADMIN', 'DBA', 'USER')")
* 表示访问该方法既需要ADMIN、DBA或USER角色
* @return
*/
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole('ADMIN', 'DBA', 'USER')")
public String user() {
return "user";
}
}
最后,在Controller中注入Service并调用Service中的方法进行测试。