动力节点王鹤SpringBoot3学习笔记——第四章 访问数据库
目录
第四章 访问数据库
4.1 DataSource
4.2 轻量的JdbcTemplate
4.2.1 准备环境
4.2.1.1 准备数据库和表脚本
4.2.1.2 创建Spring Boot工程
4.2.2 JdbcTemplate访问MySQL
4.2.3 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
4.2.4 多表查询
4.3 MyBatis
4.3.1 单表CRUD
4.3.2 ResultMap
4.3.3 SQL提供者
4.3.4 @One一对一查询
4.3.5 @Many一对多查询
4.3.6 常用配置参数
4.3.7 MybatisAutoConfiguration
4.4 适合的连接池
4.5 声明式事务
4.5.1.1 准备事务演示环境
4.5.1.2 添加事务注解
4.5.1.3 无效事务1
4.5.1.4 无效事务2
4.5.1.5 事务回滚规则
视频:动力节点SpringBoot3从入门到项目实战
第四章 访问数据库
Spring Boot框架为SQL数据库提供了广泛的支持,既有用JdbcTemplate直接访问JDBC,同时支持“object relational mapping”技术(如Hibernate,MyBatis)。Spring Data独立的项目提供对多种关系型和非关系型数据库的访问支持。比如 MySQL, Oracle , MongoDB , Redis, R2DBC,Apache Solr,Elasticsearch...
Spring Boot也支持嵌入式数据库比如H2, HSQL, and Derby。这些数据库只需要提供jar包就能在内存中维护数据。我们这章访问关系型数据库。
4.1 DataSource
通常项目中使用MySQL,Oracle,PostgreSQL等大型关系数据库。Java中的jdbc技术支持了多种关系型数据库的访问。在代码中访问数据库,我们需要知道数据库程序所在的ip,端口,访问数据库的用户名和密码以及数据库的类型信息。以上信息用来初始化数据源,数据源也就是DataSource。数据源表示数据的来源,从某个ip上的数据库能够获取数据。javax.sql.DataSource接口表示数据源,提供了标准的方法获取与数据库绑定的连接对象(Connection)。
javax.sql.Connection是连接对象,在Connection上能够从程序代码发送查询命令,更新数据的语句给数据库;同时从Connection获取命令的执行结果。Connection很重要,像一个电话线把应用程序和数据库连接起来。
DataSource在application配置文件中以spring.datasource.*作为配置项。类似下面的代码:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/mydb
spring.datasource.username=dbuser
spring.datasource.password=dbpass
DataSourceProperties.java是数据源的配置类,更多配置参考这个类的属性。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {
}
Spring Boot能够从spring.datasource.url推断所使用的数据驱动类,如果需要特殊指定请设置spring.datasource.driver-class-name为驱动类的全限定名称。
Spring Boot支持多种数据库连接池,优先使用 HikariCP,其次是Tomcat pooling,再次是 Commons DBCP2,如果以上都没有,最后会使用Oracle UCP连接池。当项目中starter依赖了spring-boot-starter-jdbc 或者spring-boot-starter-data-jpa默认添加HikariCP连接池依赖,也就是默认使用HikariCP连接池。
4.2 轻量的JdbcTemplate
使用JdbcTemplate我们提供自定义SQL, Spring执行这些SQL得到记录结果集。JdbcTemplate和NamedParameterJdbcTemplate类是自动配置的,您可以@Autowire注入到自己的Bean中。开箱即用。
JdbcTemplate执行完整的SQL语句,我们将SQL语句拼接好,交给JdbcTemplate执行,JdbcTemplate底层就是使用JDBC执行SQL语句。是JDBC的封装类而已。
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate可以在SQL语句部分使用“:命名参数”作为占位符, 对参数命名,可读性更好。NamedParameterJdbcTemplate包装了JdbcTemplate对象,“:命名参数”解析后,交给JdbcTemplate执行SQL语句。
JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration自动配置了JdbcTemplate对象,交给JdbcTemplateConfiguration创建了JdbcTemplate对象。并对JdbcTemplate做了简单的初始设置(QueryTimeout,maxRows等)。
4.2.1 准备环境
访问数据库先准备数据库的script。SpringBoot能够自动执行DDL,DML脚本。两个脚本文件名称默认是schema.sql和data.sql。脚本文件在类路径中自动加载。
自动执行脚本还涉及到spring.sql.init.mode配置项:
- always:总是执行数据库初始化脚本
- never:禁用数据库初始化
更进一步
Spring Boot处理特定的数据库类型,为特定的数据库定制script文件。首先设置spring.sql.init.platform=hsqldb、h2、oracle、mysql、postgresql等等,其次准备 schema-${platform}. sql 、 data-${platform}. sql 脚本文件。
4.2.1.1 准备数据库和表脚本
首先创建数据库,安装MySQL8.5。有可用的MySQL数据库就可以,最好是5以上版本。
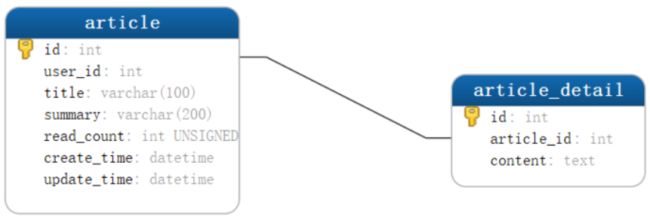
数据库名称Blog , 表目前使用一个 article(文章表),初始两条数据。
schema.sql
CREATE TABLE `article` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键',
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '作者ID',
`title` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT '文章标题',
`summary` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '文章概要',
`read_count` int(11) unsigned zerofill NOT NULL COMMENT '阅读读数',
`create_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`update_time` datetime NOT NULL COMMENT '最后修改时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
data.sql
INSERT INTO `article` VALUES ('1','2101','SpringBoot核心注解',
'核心注解的主要作用','00000008976','2023-01-16 12:11:12','2023-01-16 12:11:19');
INSERT INTO `article` VALUES ('2','356752','JVM调优',
'HotSpot虚拟机详解','00000000026','2023-01-16 12:15:27','2023-01-16 12:15:30');
4.2.1.2 创建Spring Boot工程
新建Spring Boot工程Lession09-JdbcTemplate
构建工具:Maven
包名:com.bjpowernode.jdbc
JDK:19
Starter依赖:Lombok,MySQL Driver, JDBC API
Maven依赖(pom.xml)
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
com.mysql
mysql-connector-j
runtime
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
IDEA Maven Tool查看依赖列表
依赖包含了连接池com.zaxxer:HikariCP:5.0.1 , spring-jdbc 6.0.3 , mysql驱动mysql-connector-j 8.0.31。
4.2.2 JdbcTemplate访问MySQL
项目中依赖了spring-jdbc 6.0.3,JdbcTemplate对象会自动创建好。把JdbcTemplate对象注入给你的Bean,再调用JdbcTemplate的方法执行查询,更新,删除的SQL。
JdbcTemplate上手快,功能非常强大。提供了丰富、实用的方法,归纳起来主要有以下几种类型的方法:
- execute方法:可以用于执行任何SQL语句,常用来执行DDL语句。
- update、batchUpdate方法:用于执行新增、修改与删除等语句。
- query和queryForXXX方法:用于执行查询相关的语句。
- call方法:用于执行数据库存储过程和函数相关的语句。
我们在2.2.1.2已经创建了Spring Boot工程,在工程上继续添加代码,完成对Blog库,article表的CRUD。
step1:将schema.sql , data.sql拷贝到resources目录
step2:修改application.properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
#总是执行数据库脚本,以后设置为never
spring.sql.init.mode=always
step3: 创建实体类 ArticlePO
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
Lomok注解给类的属性生成set,get方法。 默认和所有参数构造方法
step4: 单元测试,注入JdbcTemplate对象
@SpringBootTest
public class TestJdbcTemplate {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
}
测试聚合函数
@Test
void testCount() {
String sql="select count(*) as ct from article";
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Long.class);
System.out.println("文章总数 = " + count);
}
测试“?”占位符
@Test
void testQuery() {
// ?作为占位符
String sql = "select * from article where id= ? ";
//BeanPropertyRowMapper 将查询结果集,列名与属性名称匹配, 名称完全匹配或驼峰
ArticlePO article = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(ArticlePO.class), 1 );
System.out.println("查询到的文章 = " + article);
}
测试自定义RowMapper
@Test
void testQueryRowMapper() {
//只能查询出一个记录,查询不出记录抛出异常
String sql = "select * from article where id= " + 1;
ArticlePO article = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, (rs, rownum) -> {
var id = rs.getInt("id");
var userId = rs.getInt("user_id");
var title = rs.getString("title");
var summary = rs.getString("summary");
var readCount = rs.getInt("read_count");
var createTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("create_time").getTime())
.toLocalDateTime();
var updateTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("update_time").getTime())
.toLocalDateTime();
return new ArticlePO(id, userId, title, summary, readCount,
createTime, updateTime);
});
System.out.println("查询的文章 = " + article);
}
测试List集合
@Test
void testList() {
String sql="select * from article order by id ";
List> listMap = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
listMap.forEach( el->{
el.forEach( (field,value)->{
System.out.println("字段名称:"+field+",列值:"+value);
});
System.out.println("===================================");
});
}
测试更新记录
@Test
void testUpdate() {
String sql="update article set title = ? where id= ? ";
//参数是从左往右 第一个,第二个...
int updated = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "Java核心技术思想", 2);
System.out.println("更新记录:"+updated);
}
4.2.3 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate能够接受命名的参数,通过具名的参数提供代码的可读性,JdbcTemplate使用的是参数索引的方式。
在使用模板的位置注入NamedParameterJdbcTemplate对象,编写SQL语句,在SQL中WHERE部分“:命名参数”。调用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate的诸如query,queryForObject, execute,update等时,将参数封装到Map中。
step1:注入模板对象
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
step2: 使用命名参数
@Test
void testNameQuery() {
// :参数名
String sql="select count(*) as ct from article where user_id=:uid and read_count > :num";
//key是命名参数
Map param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("uid", 2101);
param.put("num", 0);
Long count = nameJdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, param, Long.class);
System.out.println("用户被阅读的文章数量 = " + count);
}
4.2.4 多表查询
多表查询关注是查询结果如何映射为Java Object。常用两种方案:一种是将查询结果转为Map。列名是key,列值是value,这种方式比较通用,适合查询任何表。第二种是根据查询结果中包含的列,创建相对的实体类。属性和查询结果的列对应。将查询结果自定义RowMapper、ResultSetExtractor映射为实体类对象。
现在创建新的表article_detail,存储文章内容,与article表是一对一关系。
article_detail表
CREATE TABLE `article_detail` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '注解',
`article_id` int(11) NOT NULL COMMENT '文章ID',
`content` text NOT NULL COMMENT '文章内容',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`))
ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
需求:查询某个文章的全部属性,包括文章内容
step1:创建新的实体类ArticleMainPO, 将ArticlePO作为成员变量
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ArticleMainPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
private ArticleDetailPO articleDetail;
}
step2: 查询一对一文章
@Test
void testArticleContent() {
String sql= """
select m.*,d.id as detail_id, d.article_id,d.content
from article m join article_detail d
on m.id = d.article_id
where m.id=:id
""";
Map param = new HashMap<>();
param.put("id", 1);
List list = nameJdbcTemplate.query(sql, param, (rs, rowNum) -> {
var id = rs.getInt("id");
var userId = rs.getInt("user_id");
var title = rs.getString("title");
var summary = rs.getString("summary");
var readCount = rs.getInt("read_count");
var createTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("create_time").getTime())
.toLocalDateTime();
var updateTime = new Timestamp(rs.getTimestamp("update_time").getTime())
.toLocalDateTime();
//文章详情
var detailId = rs.getInt("detail_id");
var content = rs.getString("content");
var articleId = rs.getInt("article_id");
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setId(detailId);
detail.setArticleId(articleId);
detail.setContent(content);
return new ArticleMainPO(id, userId, title, summary, readCount,
createTime, updateTime, detail);
});
list.forEach(m -> {
System.out.println("m.getId() = " + m.getId());
System.out.println("m.getArticleDetail() = " + m.getArticleDetail());
});
}
总结:
JdbcTemplate的优点简单,灵活,上手快,访问多种数据库。对数据的处理控制能力比较强,RowMapper, ResultSetExtractor能够提供按需要灵活定制记录集与实体类的关系。
缺点:对SQL要求高,适合对SQL比较了解,自定义查询结果比较多,调优需求的。 JdbcTemplate对象的调整参数,比较少。可设置spring.jdbc.template.开头的配置项目,比如设置超时为10秒,spring.jdbc.template.query-timeout=10。
4.3 MyBatis
数据库访问MyBatis,MyBatis-Plus国内很常用,掌握了MyBatis,MyBatis-Plus就会了大部分了。MyBatis-Plus附加的功能需要单独学习。我们以MyBatis来自介绍Spring Boot集成ORM框架。
MyBatis使用最多的是mapper xml文件编写SQL语句。本章使用MyBatis的注解,JDK新特性文本块,以及Record完成java对象和表数据的处理。
4.3.1 单表CRUD
首先向blog数据库的article表添加新的文章,以及修改,查询文章。在新工程Lession10-MyBatis集成MyBatis框架。项目包名com.bjpowernode.orm。依赖需要mysql驱动、mybatis依赖,Lombok。
step1: Maven依赖
org.mybatis.spring.boot
mybatis-spring-boot-starter
3.0.0
com.mysql
mysql-connector-j
runtime
org.projectlombok
lombok
true
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
test
step2:创建实体类
//PO:Persistent Object
@Data
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
step3: 创建Mapper接口
public interface ArticleMapper {
String field_list="id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time";
@Insert("""
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time) \
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO article);
@Update("""
update article set read_count=#{num} where id=#{id}
""")
int updateReadCount(Integer id,Integer num);
@Delete("""
delete from article where id=#{id}
""")
int deleteById(Integer id);
@Select("select " + field_list + " from article where id=#{articleId}")
@Results({
@Result(id = true,column = "id",property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id",property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count",property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time",property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time",property = "updateTime"),
})
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId") Integer id);
}
@Results部分为结果映射(XML中的
application.properties
#驼峰,下划线命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
step4: 启动类加入扫描注解
@MapperScan({"com.bjpowernode.orm.repository"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Lession10MyBatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Lession10MyBatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
@MapperScan是扫描注解,参数是Mapper接口所在的包名。参数是数组,可以指定多个包位置。
step5: 配置数据源
application.properties或yml都可以
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
#驼峰,下划线命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
step6:单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class Lession10MyBatisApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Test
void testInsert() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("什么时候用微服务");
article.setSummary("微服务优缺点");
article.setUserId(219);
article.setReadCount(560);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
}
@Test void testUpdate() {
int rows = articleMapper.updateReadCount(1, 230);
System.out.println("修改的记录数量:" + rows);
}
@Test
void testDelete(){
int rows = articleMapper.deleteById(11);
System.out.println("删除记录的数量 " + rows);
}
@Test
void testSelect(){
ArticlePO articlePO = articleMapper.selectById(3);
System.out.println("查询到的文章:" + articlePO);
}
}
4.3.2 ResultMap
查询操作得到包含多个列的集合,将列值转为对象属性使用结果映射的功能,注解@Results,@ResultMap能够帮助我们完成此功能。
@Results用于定义结果映射,每个列和Java对象属性的一一对应。
@ResultMap 指定使用哪个结果映射,两种方式可以使用@Results,另一种XML文件。
需求:执行多个select语句,使用结果映射转换数据库记录为Java Object。
step1:创建新的Mapper对象。
public interface ArticleDao {
//定义mapper, id表示唯一名称
@Select("")
@Results(id = "BaseMapper", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
})
ArticlePO articleMapper();
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where user_id=${userId}
""")
@ResultMap("BaseMapper")
List selectList(Integer userId);
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{articleId}
""")
@ResultMap("BaseMapper")
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId") Integer id);
}
@Results的id定义当前结果映射的唯一名称, 后面内容是列和属性的一一映射说明。
其他的查询方法@ResultMap引用@Results的id。使用BaseMapper的映射规则处理查询结果。
step2: 单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class ArticleDaoTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleDao articleDao;
@Test
void testSelectList() {
List poList = articleDao.selectList(219);
poList.forEach(po -> {
System.out.println("po = " + po);
});
}
@Test
void testSelect(){
ArticlePO articlePO = articleDao.selectById(1);
System.out.println("查询到的文章:" + articlePO);
}
}
另一种方法在xml中定义
ArticleMapper.xml 代码清单:
step2:修改application.properties配置mapper文件的路径
mybatis.mapper-locations:自定义mapper xml 文件保存路径。
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&autoReconnect=true&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
#驼峰命名
#mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mappers/**/*.xml
step3:修改ArticleDao的查询方法上面的@ResultMap。
@Select("""
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{articleId}
""")
//@ResultMap("BaseMapper")
@ResultMap("ArticleMapper")
ArticlePO selectById(@Param("articleId") Integer id);
在重复执行单元测试代码。
4.3.3 SQL提供者
我们能在方法上面直接编写SQL语句。使用Text Block编写长的语句。方法上编写SQL显的不够简洁。MyBatis提供了SQL提供者的功能。将SQL以方法的形式定义在单独的类中。 Mapper接口通过引用SQL提供者中的方法名称,表示要执行的SQL。
SQL提供者有四类@SelectProvider,@InsertProvider,@UpdateProvider,@DeleteProvider。
SQL提供者首先创建提供者类,自定义的。类中声明静态方法,方法体是SQL语句并返回SQL。例如:
public static String selectById() {
return "SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = #{id}";
}
其次Mapper接口的方法上面,应用@SelectProvider(type = 提供者类.class, method = "方法名称")
step1: 创建SQL提供者
public class SqlProvider {
public static String selectArticle(){
return """
select id,user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time
from article where id=#{articleId}
""";
}
public static String updateTime(){
return """
update article set update_time=#{newTime} where id=#{id}
""";
}
}
step2: 创建mapper接口
public interface ArticleRepository {
@Select("")
@Results(id = "BaseMapper", value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
})
ArticlePO articleMapper();
//查询
@ResultMap("BaseMapper")
@SelectProvider(type = SqlProvider.class,method = "selectArticle")
ArticlePO selectById(Integer id);
//更新
@UpdateProvider(type = SqlProvider.class,method = "updateTime")
int updateTime(Integer id, LocalDateTime newTime);
}
其他注解@InsertProvider,@DeleteProvider类似的使用方式
step3:单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class ArticleRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleRepository articleRepository;
@Test
void testSelect() {
Integer id = 2;
ArticlePO article = articleRepository.selectById(id);
System.out.println("article = " + article);
}
@Test
void testUpdate() {
int rows = articleRepository.updateTime(3, LocalDateTime.now());
System.out.println("更新的记录数量 = " + rows);
}
}
我们可以分别创建 Insert的提供者, Update提供者,Delete提供者,Select查询者。 每个查询者只提供一种操作。Select提供者的方法只提供Select语句。
4.3.4 @One一对一查询
MyBatis支持一对一,一对多,多对多查询。 XML文件和注解都能实现关系的操作。我们使用注解表示article和article_detail的一对一关系。 MyBatis维护这个关系, 开发人员自己也可以维护这种关系。
@One: 一对一
@Many: 一对多
关系表一个article有一个article_detail 文章内容。
step1: 创建两个表的实体
@Data
public class Article {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
private ArticleDetail articleDetail;
}
@Datapublic class ArticleDetail {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
Article 声明了ArticleDetail 对象。表示文章内容。
step2:创建Mapper查询接口
public interface ArticleOneToOneMapper {
@Select("""
select id,article_id,content from article_detail
where article_id = #{articleId}
""")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "article_id", property = "articleId"),
@Result(column = "content", property = "content")
})
ArticleDetail queryContent(Integer articleId);
@Select("""
select id,
user_id,
title,
summary,
read_count,
create_time,
update_time
from article
where id = #{id}
""")
@Results({
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
@Result(column = "id", property = "articleDetail",
one = @One(select =
"com.bjpowernode.orm.repository.ArticleOneToOneMapper.queryContent",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
Article queryAllArticle(Integer id);
}
step3:单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class OneToOneTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleOneToOneMapper articleOneToOneMapper;
@Test
void testOne() {
Article article = articleOneToOneMapper.queryAllArticle(1);
System.out.println("article = " + article);
}
}
4.3.5 @Many一对多查询
一对多查询使用@Many注解,步骤与一对一基本相同。
准备环境,新建comment评论表。article与comment存在一对多关系。一篇文章多个评论。
step1:创建CommentPO实体
@Data
public class CommentPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
step2:创建新的文章聚合实体
@Data
public class ArticleEntity {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
private List comments; //评论的集合
}
step3:新建Mapper接口
public interface ArticleOneToManyMapper {
@Select("""
select id,article_id,content from comment
where article_id = #{articleId}
""")
@Results(id="CommentMapper",value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "article_id", property = "articleId"),
@Result(column = "content", property = "content")
})
List queryComments(Integer articleId);
@Select("""
select id, user_id,title,summary,
read_count,create_time,update_time
from article
where id = #{id}
""")
@Results(id="ArticleBaseMapper",value={
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "id"),
@Result(column = "user_id", property = "userId"),
@Result(column = "read_count", property = "readCount"),
@Result(column = "create_time", property = "createTime"),
@Result(column = "update_time", property = "updateTime"),
@Result(column = "id", property = "comments",
many = @Many(select = "com.bjpowernode.orm.repository.ArticleOneToManyMapper.queryComments", fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
ArticleEntity queryArticleAndComments(Integer id);
}
step4:单元测试
@SpringBootTest
public class OneToManyTest {
@Autowired
private ArticleOneToManyMapper articleOneToManyMapper;
@Test
void testOnetoMany() {
ArticleEntity article = articleOneToManyMapper.queryArticleAndComments(1);
System.out.println("ArticleEntity = " + article);
}
}
4.3.6 常用配置参数
MyBatis的项设置,在application文件中“mybatis”开头进行设置。
全部设置参考:https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/configuration.html#settings
常用设置:
#驼峰命名
mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
#mapper xml文件位置
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:/mappers/**/*.xml
#启用缓存
mybatis.configuration.cache-enabled=true
#延迟加载mybatis.configuration.lazy-loading-enabled=true
#mybatis主配置文件,按需使用
mybatis.config-location=classpath:/sql-config.xml
上述设置内容比较多时,可以将设置放到MyBatis主配置文件,mybatis.config-location 加载主配置文件。
sql-config.xml
4.3.7 MybatisAutoConfiguration
MyBatis框架的在Spring Boot的自动配置类MybatisAutoConfiguration.class
imports文件中定义了org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.MybatisAutoConfiguration 自动配置类
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class})
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({MybatisProperties.class})
@AutoConfigureAfter({DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class})
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
private static final Logger logger =
LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisAutoConfiguration.class); private final MybatisProperties properties;
.....
}
关注:
MybatisProperties.class
DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class , DataSourceProperties.class
SqlSessionFactory.class
SqlSessionTemplate.class
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
....
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
return executorType != null ? new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType) : new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
SqlSessionTemplate是线程安全的,MyBatis为了与Spring继承。 提供的由Spring管理的Bean。这个SqlSesionTemplate实现了SqlSession接口, 能够由Spring事务管理器使用。提供Spring的事务处理。同时管理SqlSession的创建,销毁。
4.4 适合的连接池
HikariCP连接池
https://github.com/brettwooldridge/HikariCP/wiki
连接池配置:
https://github.com/brettwooldridge/HikariCP/wiki/About-Pool-Sizing
MySQL连接池配置建议
https://github.com/brettwooldridge/HikariCP/wiki/MySQL-Configuration
prepStmtCacheSize
这将设置 MySQL 驱动程序将缓存每个连接的预准备语句数。默认值为保守的 25。我们建议将其设置为 250-500 之间。
prepStmtCacheSqlLimit
这是驱动程序将缓存的准备好的 SQL 语句的最大长度。MySQL 默认值为 256。根据我们的经验,特别是对于像Hibernate这样的ORM框架,这个默认值远低于生成的语句长度的阈值。我们推荐的设置为 2048。
cachePrepStmts
如果缓存实际上被禁用,则上述参数都没有任何影响,因为默认情况下是禁用的。必须将此参数设置为 。true
useServerPrepStmts:较新版本的MySQL支持服务器端准备语句,这可以提供实质性的性能提升。将此属性设置为 。true
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
hikari:
auto-commit: true
# # connections = ((cpu核心数 * 2) + 磁盘数量) 近似值。 默认10
maximum-pool-size: 10
#最小连接数,默认10,不建议设置。默认与maximum-pool-size一样大小。推荐使用固定大小的连接池
minimum-idle: 10
#获取连接时,检测语句
connection-test-query: select 1
###
# 连接超时,默认30秒。
# 控制客户端在获取池中 Connection 的等待时间,
# 如果没有连接可用的情况下超过该时间,则抛出 SQLException 异常,
###
connection-timeout: 20000
#其他属性
data-source-properties:
cachePrepStmts: true
dataSource.cachePrepStmtst: true
dataSource.prepStmtCacheSize: 250
dataSource.prepStmtCacheSqlLimit: 2048
dataSource.useServerPrepStmts: true
4.5 声明式事务
事务分为全局事务与本地事务,本地事务是特定于资源的,例如与JDBC连接关联的事务。本地事务可能更容易使用,但有一个显著的缺点:它们不能跨多个事务资源工作。比如在方法中处理连接多个数据库的事务,本地事务是无效的。
Spring解决了全局和本地事务的缺点。它允许应用程序开发人员在任何环境中使用一致的编程模型。只需编写一次代码,就可以从不同环境中的不同事务管理策略中获益。Spring框架同时提供声明式和编程式事务管理。推荐声明式事务管理。
Spring事务抽象的关键是事务策略的概念,org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager接口定义了事务的策略。
事务控制的属性:
- Propagation : 传播行为。代码可以继续在现有事务中运行(常见情况),也可以暂停现有事务并创建新事务
- Isolation: 隔离级别。此事务与其他事务的工作隔离的程度。例如,这个事务能看到其他事务未提交的写吗?
- Timeout超时时间:该事务在超时和被底层事务基础结构自动回滚之前运行的时间。
- Read-only只读状态:当代码读取但不修改数据时,可以使用只读事务。在某些情况下,例如使用Hibernate时,只读事务可能是一种有用的优化。
AOP:
Spring Framework的声明式事务管理是通过Spring面向方面编程(AOP)实现的。事务方面的代码以样板的方式使用,及时不了解AOP概念,仍然可以有效地使用这些代码。事务使用AOP的环绕通知(TransactionInterceptor)。
声明式事务的方式:
- XML配置文件:全局配置
- @Transactional注解驱动 :和代码一起提供,比较直观。和代码的耦合比较高。【Spring团队建议您只使用@Transactional注释具体类(以及具体类的方法),而不是注释接口。当然,可以将@Transactional注解放在接口(或接口方法)上,但这只有在使用基于接口的代理时才能正常工作】
方法的可见性:
公共(public)方法应用@Transactional主机。如果使用@Transactional注释了受保护的、私有的或包可见的方法,则不会引发错误,但注释的方法不会显示配置的事务设置,事务不生效。如果需要受保护的、私有的方法具有事务考虑使用AspectJ。而不是基于代理的机制。
4.5.1.1 准备事务演示环境
在新的Spring Boot项目演示事务处理。新项目Lession011-Trans 。 添加MyBatis, MySQL, Lombok依赖。使用之前blog库的article , article_detail 表。
需求:某个作者发布了新的文章,article,article_detail两个表同时添加记录。需要事务控制两个表的insert操作。 step1: 创建实体类
@Data
public class ArticlePO {
private Integer id;
private Integer userId;
private String title;
private String summary;
private Integer readCount;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
//PO:Persistent Object
@Data
public class ArticleDetailPO {
private Integer id;
private Integer articleId;
private String content;
}
step2:创建Mapper接口,创建两个方法,添加文章属性,文章内容
public interface ArticleMapper {
@Insert("""
insert into article(user_id,title,summary,read_count,create_time,update_time) \
values(#{userId},#{title},#{summary},#{readCount},#{createTime},#{updateTime})
""")
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true,keyColumn = "id",keyProperty = "id")
int insertArticle(ArticlePO article);
@Insert("""
insert into article_detail(article_id,content)
values(#{articleId},#{content})
""")
int insertArticleContent(ArticleDetailPO detail);
}
step3:创建Service接口,声明发布文章的方法
public interface ArticleService {
boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article,String content);
}
@Service
public class ArticleServiceImpl implements ArticleService {
@Autowired
private ArticleMapper articleMapper;
@Override
public boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
//新增文章
articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
//新增文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
articleMapper.insertArticleContent(detail);
return true;
}
}
step4:启动类
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.bjpowernode.trans.repository")
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class Lession11TransApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Lession11TransApplication.class, args);
}
}
step5:编写配置文件
spring:
datasource:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blog?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: 123456
hikari:
auto-commit: true
# # connections = ((cpu核心数 * 2) + 磁盘数量) 近似值。 默认10
maximum-pool-size: 10
#获取连接时,检测语句
connection-test-query: select 1
mybatis:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
step6:单元测试
@SpringBootTest
class Lession11TransApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ArticleService articleService;
@Test
void testAddArticle() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring事务管理");
article.setSummary("Spring事务属性,事务实现");
article.setUserId(2001);
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
boolean add = articleService.postNewArticle(article, "Spring 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务");
System.out.println("add = " + add);
}
}
现在业务方法正常执行,添加数据到两个表,但是事务没有Spring参与。 postNewArticle()方法没有事务管理。
4.5.1.2 添加事务注解
step1:修改postNewArticle()方法添加@Transactional
@Transactional
@Overridepublic boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
//新增文章
articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
if( article.getReadCount() < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("已读数量不能 < 1 ");
}
//新增文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
articleMapper.insertArticleContent(detail);
return true;
}
@Transactional可在类上,接口,方法上声明。 表示方法需要事务管理。 Spring对public方法添加事务处理。
step2:启动类
@EnableTransactionManagement
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.bjpowernode.trans.repository")
@SpringBootApplication
public class Lession11TransApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Lession11TransApplication.class, args);
}
}
step3:单元测试
@Test
void testAddArticle() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring事务管理111");
article.setSummary("Spring事务属性,事务实现111");
article.setUserId(2202);
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
boolean add = articleService.postNewArticle(article, "Spring 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务111");
System.out.println("add = " + add);
}
添加数据失败, 在事务中抛出运行时异常。Spring默认回滚事务。
4.5.1.3 无效事务1
Spring事务处理是AOP的环绕通知,只有通过代理对象调用具有事务的方法才能生效。类中有A方法,调用带有事务的B方法。 调用A方法事务无效。当然protected, private方法默认是没有事务功能的。
step1: 接口中增加方法managerArticles
接口中增加方法
boolean managerArticle(String action,ArticlePO article,String content);
实现类方法:
@Override
public boolean managerArticle(String action, ArticlePO article, String content) {
return postNewArticle(article,content);
}
step2:单元测试,readCount为0
@Test
void testAddArticle2() {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring事务管理222");
article.setSummary("Spring事务属性,事务实现222");
article.setUserId(2202);
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
boolean add = articleService.managerArticle("add",article, "222 Spring 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务");
System.out.println("add = " + add);
}
测试发现,事务不起作用。aritcleService是代理对象,managerArticle方法不是事务方法。事务无效。
4.5.1.4 无效事务2
方法在线程中运行的,在同一线程中方法具有事务功能, 新的线程中的代码事务无效。
step1:修改接口方法的实现
@Transactional
@Override
public boolean postNewArticle(ArticlePO article, String content) {
System.out.println("Start 父线程:" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println("子线程:" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());
//新增文章
articleMapper.insertArticle(article);
if (article.getReadCount() < 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("===已读数量不能 < 1 ");
}
//新增文章内容
ArticleDetailPO detail = new ArticleDetailPO();
detail.setArticleId(article.getId());
detail.setContent(content);
articleMapper.insertArticleContent(detail);
});
//线程启动
thread.start();
try{
//等他thread执行完成,在继续后面的代码
thread.join();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("End 父线程:" + Thread.currentThread().threadId());
return true;
}
step2: 单元测试
@Test
void testAddArticle() throws InterruptedException {
ArticlePO article = new ArticlePO();
article.setTitle("Spring事务管理555");
article.setSummary("Spring事务属性,事务实现555");
article.setUserId(2203);
article.setReadCount(0);
article.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
article.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
boolean add = articleService.postNewArticle(article, "Spring 统一事务管理。事务管理器管理本地事务");
System.out.println("add = " + add);
}
4.5.1.5 事务回滚规则
- RuntimeException的实例或子类时回滚事务
- Error会导致回滚
- 已检查异常不会回滚。默认提交事务
@Transactional注解的属性控制回滚
- rollbackFor
- noRollbackFor
- rollbackForClassName
- noRollbackForClassName