python django运用(4.与MySQL数据库交互)
前言:
1.走到这里大家对django的应用都有一个大概的逻辑了解;
2.MySQL数据库的数据怎样能够随时查看
3.看了查看很多大佬对MySQL数据库数据的交互资料,要么太高端,要么太复杂
4.结合以前的学习把django与MySQL数据库交互简单、实用化
一、MySQL数据库的建立:
1.MySQL数据库服务器的启动:
net start MySQ
2.pyCharmd创建jango文件my_site,子文件app01;
3.把my_site内的子文件my_site内新建一个文件[testdb.py]:
(1).在MySQL数据库中创建自己的数据库和数据表:
import mysql.connector
#链接mysql数据库:
my_db = mysql.connector.connect(
host = 'localhost',
user = 'root',
passwd = '123456',
)
my_cursor = my_db.cursor()
#创建数据库:
my_cursor.execute("CREATE DATABASE my_datas")
#检验数据库创建是否成功:
print(my_db)
输出:<mysql.connector.connection_cext.CMySQLConnection object at 0x000001D63040AFD0> #标明已经创建成功了.
#数据库中创建数据表:
my_cursor.execute('CREATE TABLE table_01 (name VARCHAR(255), url VARCHAR(255))')
也可以直接去MySQL数据库[data]查看:
数据库:
 数据表:
数据表:

(2).创建好后在testdb.py文件中编写:
class UIfo:
def __init__(self):
self.my_db = mysql.connector.connect(
host='localhost',
user='root',
passwd='123456',
database='my_datas' # 创建后加入
)
def pop_data(self, name):
# 删除数据
my_cursor = self.my_db.cursor()
sql = 'DELETE FROM table_01 WHERE name = %s'%name
my_cursor.execute(sql, name)
self.my_db.cursor.commit()
def add_data(self, name, url):
# 添加数据
my_cursor = self.my_db.cursor()
sql = "INSERT INTO table_01 (name,url) VALUES (%s, %s ,%s) "
val = [ (name, url)]
my_cursor.executemany(sql, val)
self.my_db.cursor.commit()
4.在my_site内的子文件my_site内的[settings.py]文件内容 DATABASES 配置项修改成:
ATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', # 数据库引擎
'NAME': 'my_datas',
'HOST' :'localhost',
'PORT': 3306,
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD' : '123456',
}
}
5.在my_site内的templates子文件夹内创建一个空文本(如:index_02.txt)
6.在testdb.py文件继续编写:
import mysql.connector
my_db = mysql.connector.connect(
host = 'localhost',
user = 'root',
passwd = '123456',
database = 'my_datas'#创建后加入
)
my_cursor = my_db.cursor()
#插入数据
sql = "INSERT INTO table_01 (name, url) VALUES (%s, %s)"
val = [
# ("Google", "https://www.google.com"),
# ("Github", "https://www.github.com"),
# ("Taobao", "https://www.taobao.com"),
# ("stackoverflow", "https://www.stackoverflow.com/"),
('jingdong','https://www.jd.com/'),
]
my_cursor.executemany(sql, val)
my_db.commit() # 数据表内容有更新,必须使用到该语句
#查表填入数据详细:
my_cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM table_01")
my_result = my_cursor.fetchall() # fetchall() 获取所有记录
with open('.my_site/templates/index_02.txt','r+') as f:
for x in my_result:
if type(x) != str:
for j in x:
if type(j) == str:
print(j)
x = j
f.write(x + '\n'+'
')
elif type(j) != str:
f.write('\n')
my_result = j
elif type(x) == str:
f.write(x)
f.close()
else:
break
7.在my_site内的app01子文件夹内创建一个空文本文件中views子文件中views.py编写:
from django.shortcuts import render
def index(request):
return render(request,'index_02.txt')
在app01子文件中url.py编写:
from django.urls import path
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path('index/', views.index),
]
8.启动项目:
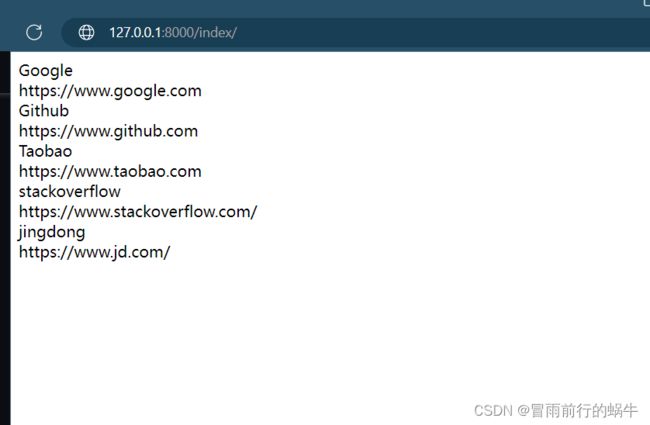
python manage.py runserver IP(自己定义,默认8000)
未完后面补充