Octree(八叉树)
1. 算法原理
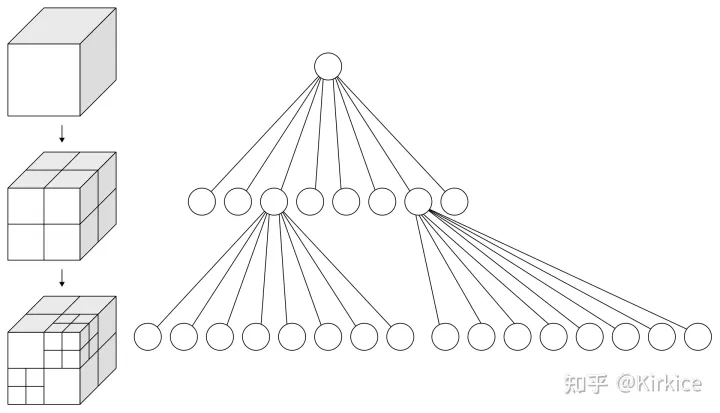
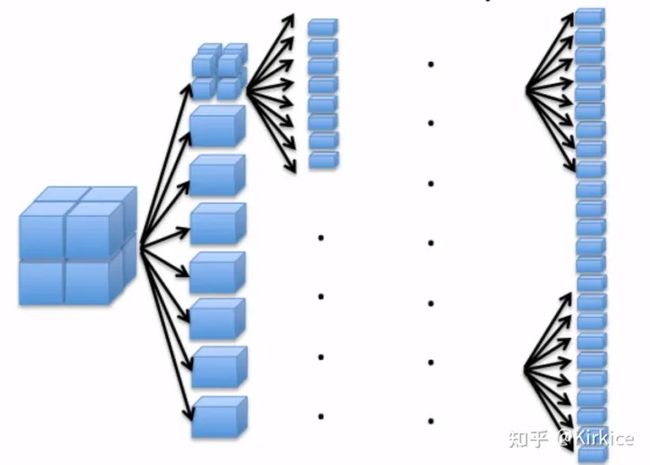
八叉树(Octree)是一种用于描述三维空间的树状数据结构。八叉树的每个节点表示一个正方体的体积元素,每个节点有八个子节点,将八个子节点所表示的体积元素加在一起就等于父节点的体积。八叉树是四叉树在三维空间上的扩展,二维上我们有四个象限,而三维上,我们有8个卦限。八叉树主要用于空间划分和最近邻搜索。
实现Octree的原理
- 将当前的立方体细分为八个子立方体。
- 如果任何一个子立方体内包含多个点,则将其进一步细分为八个子立方体。
- 重复以上操作使得每个子立方体内包含最多一个点。
2. 实现
class OccupancyVoxelTree:
# only root node's parent node is None
def __init__(self, min_voxel_sizes=np.ones(3), parent_node=None, depth=0):
self.min_voxel_sizes = min_voxel_sizes
self.num_points = 0
self.points = np.array([])
self.center = np.zeros(3, float)
self.min_values = np.zeros(3, float)
self.max_values = np.zeros(3, float)
self.parent_node = parent_node
self.depth = depth
self.voxel_indices = np.zeros(3, int)
self.child_nodes = []
self.is_leaf = False
def get_tree_points(self):
if self.is_leaf:
return [self.points]
else:
points = []
for node in self.child_nodes:
if node is not None:
points.extend(node.get_tree_points())
return points
# only root node call this method
def build_tree(self, points):
min_values = np.min(points, axis=0)
max_values = np.max(points, axis=0)
center = (min_values + max_values) * 0.5
num_grids = np.max((max_values - min_values) / self.min_voxel_sizes)
num_grids = 2 ** int(math.ceil(math.log2(num_grids)))
half_sizes = self.min_voxel_sizes * (num_grids * 0.5)
self.min_values = center - half_sizes
self.max_values = center + half_sizes
self.build_child_tree(points)
def empty(self):
return self.num_points == 0
def get_all_leaves(self):
if self.is_leaf:
return [self]
else:
leaves = []
for node in self.child_nodes:
if node is not None:
leaves.extend(node.get_all_leaves())
return leaves
def get_neighbors(self):
indices_from_root = self.get_indices_from_root()
neighbors = []
for i in range(-1, 2):
for j in range(-1, 2):
for k in range(-1, 2):
voxel_indices = self.voxel_indices + np.array([i, j, k])
neighbors.append(self.parent_node.get_voxel(voxel_indices, 1))
return neighbors
def get_voxel(self, indices, depth_from_this_node):
if depth_from_this_node > 1:
half_octave = 2 ** (depth_from_this_node - 1)
octave = half_octave * 2
if np.any(indices < 0) or np.any(indices >= octave):
voxel_indices = self.voxel_indices * 2 + indices
return self.parent_node.get_voxel(voxel_indices, depth_from_this_node + 1)
else:
child_indices = indices // half_octave
indices_from_child = indices - child_indices * half_octave
child_node = self.get_child_node(child_indices)
if child_node is None:
return None
else:
return child_node.get_voxel(indices_from_child, depth_from_this_node - 1)
elif self.is_leaf:
return self
elif np.all(np.abs(indices) < 2): # depth is 1
child_node = self.get_child_node(indices)
if child_node is None:
return None
else:
return child_node
else: # depth is 1
voxel_indices = self.voxel_indices * 2 + indices
return self.parent_node.get_voxel(voxel_indices, depth_from_this_node + 1)
def get_child_node(self, indices):
child_index = indices[0] * 4 + indices[1] * 2 + indices[2]
return self.child_nodes[child_index]
def get_indices_from_root(self):
if self.parent_node is None:
return self.voxel_indices
else:
return self.voxel_indices + 2 * self.parent_node.get_indices_from_root()
def get_child_center_points(self):
if self.is_leaf:
return [self.center]
else:
points = []
for child_node in self.child_nodes:
if child_node is not None:
points.extend(child_node.get_child_center_points())
return points
def get_all_voxels(self):
if self.is_leaf:
return [self.center], [self]
else:
centers, voxels = [], [], []
for child_node in self.child_nodes:
if child_node is not None:
child_centers, child_voxels = child_node.get_all_voxels()
centers.extend(child_centers)
voxels.extend(child_voxels)
return centers, voxels
def visualize(self):
points = self.get_child_center_points()
pcd = o3d.geometry.PointCloud()
pcd.points = o3d.utility.Vector3dVector(np.vstack(points))
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([pcd])
def build_child_tree(self, points):
self.num_points = points.shape[0]
# print("Number of points", self.num_points, self.min_values, self.max_values)
self.center = (self.max_values + self.min_values) * 0.5
half_sizes = (self.max_values - self.min_values) * 0.5
if self.empty():
return False
if np.any(half_sizes < self.min_voxel_sizes):
self.points = points
self.is_leaf = True
return True
else:
points_3d = points
for i in range(2):
for j in range(2):
for k in range(2):
child_node = OccupancyVoxelTree(self.min_voxel_sizes, self, self.depth + 1)
child_node.voxel_indices = np.array([i, j, k])
child_node.min_values = self.min_values + child_node.voxel_indices * half_sizes
child_node.max_values = child_node.min_values + half_sizes
point_indices = np.where(np.all(points_3d >= child_node.min_values, axis=1) &
np.all(points_3d < child_node.max_values, axis=1))[0]
if child_node.build_child_tree(points[point_indices, :]):
self.child_nodes.append(child_node)
else:
self.child_nodes.append(None)
return True3. 开源库
PCL八叉树组件提供了几种八叉树类型。它们的主要区别在于它们的单个叶节点特征。
OctreePointCloudPointVector(等于OctreePointCloud):这个八叉树可以在每个叶节点上保存一个点索引列表。
OctreePointCloudSinglePoint:这个八叉树类在每个叶节点上只有一个单点索引。仅存储分配给叶节点的最近的点索引。
OctreePointCloudOccupancy:这个八叉树在它的叶子节点上不存储任何点信息。它可以用于空间占用检查。
OctreePointCloudDensity:这个八叉树计算每个叶节点体素内的点的数量。它允许空间密度查询。
如果需要高速创建八叉树,请查看八叉树双缓冲实现(Octree2BufBase类)。这个类同时在内存中保存两个并行的八叉树结构。除了搜索操作之外,这还支持空间变化检测。此外,高级内存管理减少了八叉树构建过程中的内存分配和回收操作。双缓冲八叉树实现可以通过模板参数OctreeT赋值给所有的OctreePointCloud类。
所有八叉树都支持八叉树结构和八叉树数据内容的序列化和非序列化。
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int
main ()
{
srand ((unsigned int) time (NULL));
// [1]创建点云指针
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud);
// [2] 构造1000个随机的点云数据
cloud->width = 1000;
cloud->height = 1;
cloud->points.resize (cloud->width * cloud->height);
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < cloud->size (); ++i)
{
(*cloud)[i].x = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
(*cloud)[i].y = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
(*cloud)[i].z = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
}
float resolution = 128.0f;
// [3]八叉树点云搜索实例
pcl::octree::OctreePointCloudSearch octree (resolution);
// [4]将点云设置成八叉树结构
octree.setInputCloud (cloud);
octree.addPointsFromInputCloud ();
// [5]随机定义一个要查找的点
pcl::PointXYZ searchPoint;
searchPoint.x = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
searchPoint.y = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
searchPoint.z = 1024.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
//**************************体素搜索(搜索相同体素内的点)************************
// [6]创建点云索引容器
std::vector pointIdxVec;
// [7]开始进行体素内近邻点搜索
if (octree.voxelSearch (searchPoint, pointIdxVec))
{
// [8] 将查找点所在体素内的邻点全都输出打印到命令窗口
std::cout << "Neighbors within voxel search at (" << searchPoint.x
<< " " << searchPoint.y
<< " " << searchPoint.z << ")"
<< std::endl;
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxVec.size (); ++i)
std::cout << " " << (*cloud)[pointIdxVec[i]].x
<< " " << (*cloud)[pointIdxVec[i]].y
<< " " << (*cloud)[pointIdxVec[i]].z << std::endl;
}
//*************************K近邻搜索(搜索K个最近点)************************
int K = 10;
// 创建点索引容器,用于按距离保存搜索到的点
std::vector pointIdxNKNSearch;
// 创建点距离容器
std::vector pointNKNSquaredDistance;
std::cout << "K nearest neighbor search at (" << searchPoint.x
<< " " << searchPoint.y
<< " " << searchPoint.z
<< ") with K=" << K << std::endl;
// 开始最近K邻搜索
if (octree.nearestKSearch (searchPoint, K, pointIdxNKNSearch, pointNKNSquaredDistance) > 0)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxNKNSearch.size (); ++i)
std::cout << " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].x
<< " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].y
<< " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxNKNSearch[i] ].z
<< " (squared distance: " << pointNKNSquaredDistance[i] << ")" << std::endl;
}
//*************************K近邻搜索(搜索半径范围内的点)************************
// 创建半径范围内点索引的容器
std::vector pointIdxRadiusSearch;
// 创建搜索到的点的距离容器
std::vector pointRadiusSquaredDistance;
float radius = 256.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
std::cout << "Neighbors within radius search at (" << searchPoint.x
<< " " << searchPoint.y
<< " " << searchPoint.z
<< ") with radius=" << radius << std::endl;
// 开始半径搜索
if (octree.radiusSearch (searchPoint, radius, pointIdxRadiusSearch, pointRadiusSquaredDistance) > 0)
{
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxRadiusSearch.size (); ++i)
std::cout << " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].x
<< " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].y
<< " " << (*cloud)[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].z
<< " (squared distance: " << pointRadiusSquaredDistance[i] << ")" << std::endl;
}
}
参考文献
几何体数据结构学习(2)八叉树 - 知乎
【PCL自学:ocTree】八叉树(octree)的原理及应用案例(点云压缩,搜索,空间变化)_斯坦福的兔子的博客-CSDN博客