数据结构——队列(C语言)
C语言实现队列
- GitHub代码下载
- 一、队列的概念及结构
- 二、队列的实现
-
- 2.1 队列的链式结构存储
- 2.2 初始化队列
- 2.3 队尾入队列
- 2.4 队头出队列
- 2.5 获取队列头部元素
- 2.6 获取队列队尾元素
- 2.7 获取队列中有效元素个数
- 2.8 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
- 2.9 销毁队列
- 三、队列的接口测试
- 四、代码清单
-
- 4.1 Queue.h
- 4.2 Queue.c
- 4.3 test.c
GitHub代码下载
https://github.com/Kyrie-leon/Data_Structures/tree/main/stack_queue
在掌握栈(数据结构——栈(C语言))的实现过程后,队列的实现就会变的非常简单了
一、队列的概念及结构
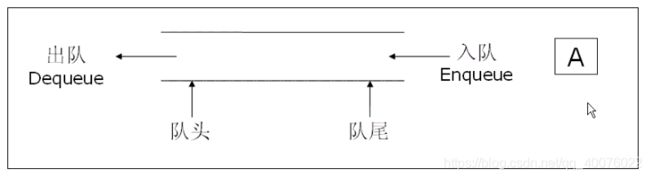
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾 ==
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头==
二、队列的实现
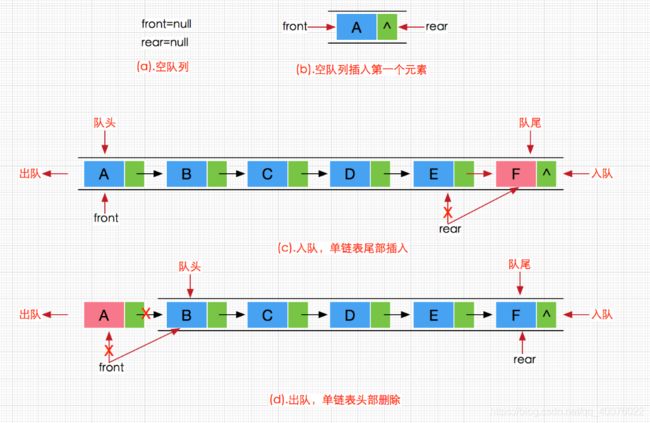
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
2.1 队列的链式结构存储
typedef int QDataType;
//队列的链表
typedef struct QListNode
{
struct QListNode* _next;
QDataType _data;
}QNode;
//队列的结构
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode *_front; //队头
QNode *_rear; //队尾
}Queue;
2.2 初始化队列
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->_front = pq->_rear = NULL; //队头队尾置空即可
}
2.3 队尾入队列
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType data)
{
assert(pq);
QNode * newNode = (QNode *)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); //向内存申请一个结点
//判断是否申请成功
if (NULL == newNode)
{
printf("申请失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//将新节点入到队尾
newNode->_data = data; //数据data赋值给新节点
newNode->_next = NULL; //新节点会作为队尾节点,因此对新节点_next置空
if (pq->_front)
{
pq->_rear->_next = newNode; //队列不为空,队尾结点先链接新结点
pq->_rear = newNode; //再将队尾指向新节点
}
else
{
pq->_front = pq->_rear = newNode; //如果队列为空,则队头队尾都指向新节点
}
}
2.4 队头出队列
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_front); //出队列判断队列是否为空
QNode* next = pq->_front->_next; //next保存新队头结点
free(pq->_front);
pq->_front = next;
//出队列后需要判断队列是否为空
if (NULL == pq->_front)
{
pq->_rear = NULL; //如果为空,则队尾也为空
}
}
2.5 获取队列头部元素
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_front);
return pq->_front->_data;
}
2.6 获取队列队尾元素
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_rear);
return pq->_rear->_data;
}
2.7 获取队列中有效元素个数
O(n)
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->_front;
//遍历一遍链表
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return size;
}
2.8 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->_front == NULL ? 1 : 0;
}
2.9 销毁队列
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//从头节点开始遍历每一个节点并free
QNode* cur = pq->_front;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->_next; //cur指向下一个节点
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->_front = pq->_rear = NULL;
}
三、队列的接口测试
#include "Queue.h"
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
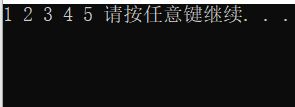
while (!(QueueEmpty(&q)))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
//TestStack();
TestQueue();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
四、代码清单
4.1 Queue.h
#pragma once
#include4.2 Queue.c
#include "Queue.h"
// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->_front = pq->_rear = NULL; //队头队尾置空即可
}
// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType data)
{
assert(pq);
QNode * newNode = (QNode *)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); //向内存申请一个结点
//判断是否申请成功
if (NULL == newNode)
{
printf("申请失败!\n");
exit(-1);
}
//将新节点入到队尾
newNode->_data = data; //数据data赋值给新节点
newNode->_next = NULL; //新节点会作为队尾节点,因此对新节点_next置空
if (pq->_front)
{
pq->_rear->_next = newNode; //队列不为空,队尾结点先链接新结点
pq->_rear = newNode; //再将队尾指向新节点
}
else
{
pq->_front = pq->_rear = newNode; //如果队列为空,则队头队尾都指向新节点
}
}
// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_front); //出队列判断队列是否为空
QNode* next = pq->_front->_next; //next保存新队头结点
free(pq->_front);
pq->_front = next;
//出队列后需要判断队列是否为空
if (NULL == pq->_front)
{
pq->_rear = NULL; //如果为空,则队尾也为空
}
}
// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_front);
return pq->_front->_data;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->_rear);
return pq->_rear->_data;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->_front;
//遍历一遍链表
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->_next;
}
return size;
}
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->_front == NULL ? 1 : 0;
}
// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//从头节点开始遍历每一个节点并free
QNode* cur = pq->_front;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->_next; //cur指向下一个节点
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->_front = pq->_rear = NULL;
}
4.3 test.c
#include "stack.h"
#include "Queue.h"
void TestStack()
{
Stack ps;
StackInit(&ps);
StackPush(&ps, 1);
StackPush(&ps, 2);
StackPush(&ps, 3);
StackPush(&ps, 4);
StackPush(&ps, 5);
while (!StackEmpty(&ps))
{
printf("%d, %d\n", StackTop(&ps),StackSize(&ps));
StackPop(&ps);
}
}
void TestQueue()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
QueuePush(&q, 5);
while (!(QueueEmpty(&q)))
{
printf("%d ", QueueFront(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
int main()
{
//TestStack();
TestQueue();
system("pause");
return 0;
}