Netty组件-Handler和Pipeline
在netty中,可以使用pipeline和handler配合使用,对入栈数据和出栈数据进行链式的操作。就像大家理解的pipeline是管道、handler是工人,在管道上每个工人都坐着自己的工作。
netty中提供了很多handler,同时使用者也可以根据自己的需求,对handler进行实现,本章主要讲述handler的执行顺序和相关的注意点。
简单代码:
package com.test.netty.c4;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.*;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
@Slf4j
public class HandlerServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ServerBootstrap()
.group(new NioEventLoopGroup(), new NioEventLoopGroup(2))
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(NioSocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//1、channel 拿到 pipeline
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//2、添加处理器 head->h1->h2->h3 tail 这两个 handler之间
pipeline.addLast("h1", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("1");
ByteBuf byteBuf = (ByteBuf) msg;
String str = byteBuf.toString(Charset.defaultCharset());
super.channelRead(ctx, str);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h2", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("2");
String str = (String) msg;
super.channelRead(ctx, new Student(str));
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h6", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("6");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h3", new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("3,结果:{}, 类型:{}", msg, msg.getClass());
//交给下一个入站处理器,因为是最后一个,所以没有必要再次调用了,下面两个方法都可以
//super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
//ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
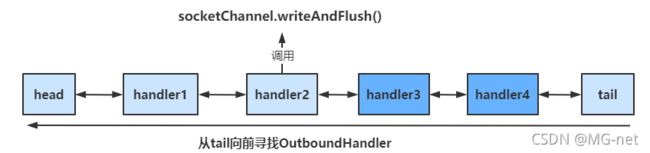
//ch writeAndFlush 是从当前处理器向后找出栈处理器
//ch.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("服务器".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
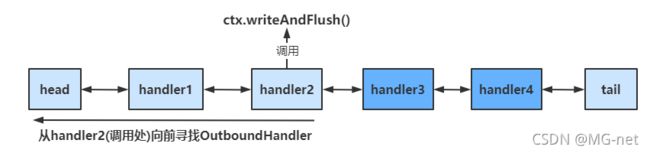
//ctx writeAndFlush 是从当前处理器向前找出栈处理器
ctx.writeAndFlush(ctx.alloc().buffer().writeBytes("hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
}
});
//出栈处理器,向channel写入数据,才回触发,并且是从后向前,也就是 h6->h5->h4
pipeline.addLast("h4", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("4");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
pipeline.addLast("h5", new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter(){
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("5");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
});
}
}).bind(8080);
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
static class Student{
String name;
}
}
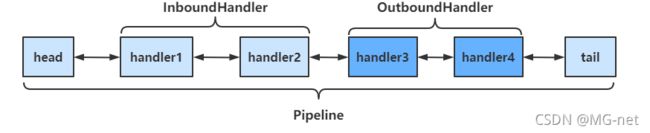
netty会先创建两个handler,一个是head,另一个是tail,也就是头和尾,所有的handler都是增加到这两个handler之间。在使用pipeline添加handler的时候,需要进行命名,这样可以更加方便的调用addBefore和addAfter,也就是更加灵活的调用handler之间的顺序,结构如下:
- 入栈的时候,会从head向后调用每个InboundHandler,但是要注意调super.channelRead(ctx, msg);或者ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);继续执行
- 出栈的时候,会从tail向前调用每个OutBoundHandler,但是要注意调用super.write(ctx, msg, promise);或者ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);继续执行
- 想要执行OutBoundHandler,就需要channel执行write方法
-
channelHandlerContext.writeAndFlush(),是从当前handler向前执行OutBoundHandler
EmbeddedChannel
是为了在不用编写服务器端代码,直接执行pipeline链的测试方法
示例如下:
package com.test.netty.c4;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelPromise;
import io.netty.channel.embedded.EmbeddedChannel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
@Slf4j
public class TestEnbeddedChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h1 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("1");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter h2 = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
log.debug("2");
super.channelRead(ctx, msg);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h3 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("3");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter h4 = new ChannelOutboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception {
log.debug("4");
super.write(ctx, msg, promise);
}
};
//可以模拟入栈、出栈的执行
EmbeddedChannel embeddedChannel = new EmbeddedChannel(h1, h2, h3, h4);
embeddedChannel.writeInbound("小小子");
embeddedChannel.writeOutbound("小妮子");
}
}