初始Vue【Vue】
Vue 简介
1. Vue是什么?
一套用于构建用户界面的
渐进式JavaScript框架
- 渐进式:Vue可以自底向上逐层的应用
简单应用:只需一个轻量小巧的核心库
复杂应用:可以引入各式各样的Vue插件
2. Vue 的特点
- 采用
组件化的模式,提高代码复用率、且让代码更好维护。 - 声明式编码,让编码人员无需直接操作DOM,提高开发效率。
3. 学习 Vue 之前要掌握的 JavaScript 基础知识?
ES6语法规范、ES6模块化、包管理器、原型原型链、数组常用方法、axios、promise…
4. 初识 Vue
4.1 初识 Vue
- 想让Vue工作,就必须创建一个Vue实例,且要传入一个配置对象;
- root容器里的代码依然符合html规范,只不过混入了一些特殊的Vue语法;
- root容器里的代码被称为【Vue模板】
- Vue实例和容器是一一对应的;
- 真实开发中只有一个Vue实例,并且会配合着组件一起使用;
- {{xxx}}中的xxx要写js表达式,且xxx可以自动读取到data中所有的属性;
- 一旦data中的数据发生改变,那么页面中用到该数据的地方也会自动更新;
注意区分:js表达式 和 js 代码(语句)
- 表达式:一个表达式会产生一个值,可以放在任何一个需要值的地方;
(1)a
(2)a+b
(3)demo(1)
(4)x === y ? ‘a’ :’b‘ - js 代码(语句)
(1)if(){}
(2)for(){}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<!-- 初始 Vue -->
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>Hello, {{name}}</h1>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
//创建Vue实例
new Vue({
el: '#root', //el用于指定当前Vue实例未哪个容器服务,值通常为css选择器字符串。
data: { //data中用于存储数据,数据供el所指定的容器去使用。值我们暂时先写成一个对象。
name: '西安文理',
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4.2 模板语法
Vue模板语法有2大类:
- 插值语法:
功能:用于解析标签体内容
写法:{{xxx}},xxx是js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的所有属性 - 指令语法:
功能:用于解析标签(包括:标签属性、标签体内容、绑定事件…)
举例:v-bind:href=“xxx” 或 简写为 :href=“xxx”, xxx同样要写js表达式,且可以直接读取到data中的多有属性。
备注:Vue中有很多的指令,且形式都是:v-???,此处我们只是拿v-bind举个例子。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>插值语法</h1>
<h3>您好, {{name}}</h3>
<hr/>
<h1>指令语法</h1>
<a v-bind:href="school.url.toUpperCase()" :x="school.hello">点我去百度</a> <!-- 遇到v-bind 引号里面的东西当作表达式来引用 -->
<a :href="url" x="hello">点我去{{school.name}}学习2</a>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data:{
name: 'jack',
school:{
url: 'http://baidu.com',
hello: '你好',
name: '西安文理'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
4.3 数据绑定
Vue中有2中数据绑定的方式:
- 单向绑定(v-bind):数据只能从data流向页面
- 双向绑定(v-model):数据不仅能从data流向页面,还可以从页面流向data
备注:
- 双向绑定一般都应用在表单类元素上(如:input、select等)
- v-model:value 可以简写为 v-model,因为v-model默认手机的就是value的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<!-- 普通写法 -->
<!-- 单向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-bind:value="name"><br/>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model:value="name"><br/> -->
<!-- 简写 -->
单向数据绑定:<input type="text" :value="name"><br/>
双向数据绑定:<input type="text" v-model="name"><br/>
<!-- 如下代码是错误的,因为v-model只能应用在表单类元素上 -->
<!-- <h2 v-bind:x="name">你好啊</h2> -->
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: '张三'
}
})
</script>
</html>
4.4 el 与 data 的两种写法
data与el的2种写法:
- el有2种写法
(1)new Vue时候配置 el 属性
(2)先创建Vue实例,随后再通过vm.$mount(‘#root’)指定 el 的值 - data有2种写法
(1)对象式
(2)函数式 - 一个重要的原则
由Vue管理的函数,一定不要写箭头函数,一旦写了箭头函数,this就不再是Vue实例了。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>你好 {{name}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
/*const v = new Vue({
//el: '#root', //第一种写法
data: {
name: '张三'
}
})
console.log(v);
v.$mount('#root') //第二种写法*/
//data两种写法
new Vue({
el: '#root',
//data的第一种写法:对象式
/*data: {
name: '张三'
}*/
//data的第二种写法:函数式
data(){
console.log('@@@', this); //此处的this是Vue实例对象
return {
name: '张三'
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
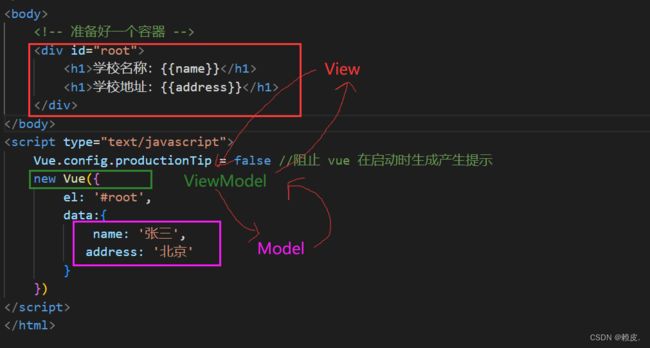
4.5 MVVM模型
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h1>学校名称:{{name}}</h1>
<h1>学校地址:{{address}}</h1>
<h1>测试一下1: {{1+1}}</h1>
<h1>测试一下2: {{$options}}</h1>
<h1>测试一下3: {{$emit}}</h1>
<h1>测试一下4: {{_c}}</h1>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data:{
name: '张三',
address: '北京',
a: 1
}
})
console.log(vm)
</script>
</html>
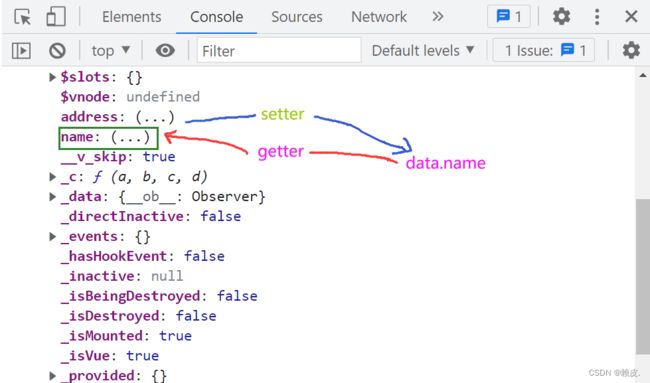
观察发现:
- data中所有的属性,最后都出现在了vm身上
- vm身上所有的属性 及 vue 原型上所有属性,在 Vue模板中都可以直接使用
4.6 数据代理
- 何为数据代理?
通过一个对象代理对另一个对象中属性的操作(读/写)
- 回顾Object.defineProperty方法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script type="text/javascript">
let number = 18
let person = {
name: '张三',
sex: '男',
}
Object.defineProperty(person, 'age', {
// value: 18,
// enumerable: true, //控制属性是否可以枚举,默认值是false
// writable: true, //控制属性是否可以被修改,默认值是false
// configurable: true, //控制属性是否可以被删除,默认值是false
//当有人读取person的age属性时,get(getter)函数就会被调用,且返回值就是age的值
get(){
return number
},
//当有人修改person的age属性时,set(setter)函数就会被调用,且会收到修改的具体值
set(value){
console.log('有人修改了age属性,且值时', value);
number = value
}
})
// console.log(Object.keys(person));
console.log(person);
</script>
</body>
</html>
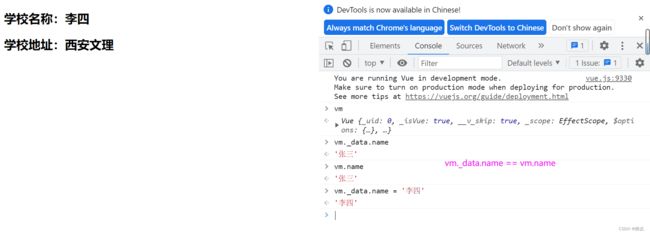
- Vue 中的数据代理
(1)Vue中的数据代理:
通过vm对象来代理data对象中属性的操作(读/写)
(2)Vue中数据代理的好处:
更加方便的操作data中的数据
(3)基本原理:
通过Object.defineProperty()把data对象中所有属性添加到vm上
为每一个添加到vm上的属性,都指定一个getter/setter
在getter/setter内部去操作(读/写)data中对应的属性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>学校名称:{{name}}</h2>
<h2>学校地址:{{address}}</h2>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
let data = {
name: '张三',
address: '西安文理'
}
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data
})
</script>
</html>
5. 事件处理
5.1 事件的基本使用:
- 使用v-on:xxx 或 @xxx 绑定事件,其中xxx是事件名;
- 事件的回调需要配置在methods对象上,最终会在vm上;
- methods中配置的函数,不要用箭头函数!否则this就不是vm了;
- methods中配置的函数,都是被Vue所管理的函数,this的指向是vm 或 组件实例对象;
- @click=“demo” 和 @click=“demo($event)” 效果一致,但后者可以传参;
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}</h2>
<!-- <button v-on:click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button> -->
<button @click="showInfo1">点我提示信息1(不传参)</button>
<button @click="showInfo2(66, $event)">点我提示信息2(传参)</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: '西安文理'
},
methods: {
showInfo1(event){
alert('同学,你好!')
},
showInfo2(number, event){
console.log(number, event);
alert('同学,你好!!')
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
5.2 事件修饰符
Vue中的事件修饰符:
- prevent:阻止默认事件(常用)
- stop:阻止事件冒泡(常用)
- once:事件只触发一次(常用)
- capture:使用事件的捕获模式
- self:只有event.target是当前操作的元素是才触发的事件
- passive:事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
<style>
* {
margin-top: 20px;
}
.demo1{
height: 50px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box1 {
padding: 5px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.box2 {
padding: 5px;
background-color: orange;
}
.list {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: peru;
overflow: auto;
}
li {
height: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}</h2>
<!-- 阻止默认事件(常用) -->
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent="showInfo">点我提示信息</a>
<!-- 阻止事件冒泡(常用) -->
<div class="demo1" @click="showInfo">
<button @click.stop="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
<!-- 修饰符可以连用 -->
<!-- <a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.stop.prevent="showInfo">点我提示信息</a> -->
</div>
<!-- 事件只触发一次 -->
<button @click.once="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
<!-- 使用事件的捕获模式 冒泡阶段由内到外 捕获阶段由外到内-->
<div class="box1" @click.capture="showMsg(1)">
div1
<div class="box2" @click="showMsg(2)">div2</div>
</div>
<!-- 只有event.target是当前操作的元素是才触发的事件 -->
<div class="demo1" @click.self="showInfo">
<button @click="showInfo">点我提示信息</button>
</div>
<!-- 事件的默认行为立即执行,无需等待事件回调执行完毕 -->
<ul @wheel.passsive="demo" class="list">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
</ul>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: '西安文理'
},
methods: {
showInfo(e){
alert('同学你好')
// console.log(e.target);
},
showMsg(msg){
console.log(msg);
},
demo(){
for (let i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
console.log('#');
}
console.log('累坏了');
},
}
})
</script>
</html>
5.3 键盘事件
- Vue中常用的按键别名:
回车 => enter
删除 => delete(捕获“删除”和’退格“键)
退出 => esc
空格 => space
换行 => tab(特殊,必须配合keydown使用)
上 => up
下 => down
左 => left
右 => right - Vue 未提供别名的按键,可以使用按键原始的key值去绑定,但注意要转为kebab-case(短横线命名)
- 系统修饰键(用法特殊):ctrl、alt、shift、meta
(1)配合keyup使用:按下修饰键的同时,再按下其他键,随后释放其他键,事件才被触发。
(2)配合keydown使用:正常触发事件 - 也可以使用keyCode去指定具体的按键(不推荐)
- Vue.config.keyCodes.自定义键名 = 键码,可以去定制按键别名
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>欢迎来到{{name}}</h2>
<input type="text" placeholder="按下回车提示输入" @keyup.enter="showInfo">
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
// Vue.config.keyCodes.huiche = 13 //定义了一个别名按键
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
name: '西安文理'
},
methods: {
showInfo(e){
console.log(e.target.value);
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
6. 计算属性
案例:姓名案例
- 插值语法实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{firstName}}-{{lastName}}</span>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
}
})
</script>
</html>
- methods实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName()}}</span><!-- 把fullName方法调用的返回值插入到这个位置 -->
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
},
methods: {
//只要data中的数据发生改变,那么Vue一定会解析模板的,只有重新解析模板,才能知道模板里的哪个位置用到了这个姓,然后把这个姓给他更新
fullName(){
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 计算属性实现
- 就是拿着已经写完的属性去加工,去计算,然后生成一个全新的属性
- 原理:底层借助了Object.defineproperty方法提供的 getter 和 setter
- get函数什么时候执行?
(1)初次读取时会执行一次。以后再读就不调用了,因为有缓存。
(2)当依赖的数据发生变化时会被再次调用。- 优势:与methods实现相比,内部有缓存机制(复用),效率更高,调试方便。
备注:
(1)计算属性最终会出现在vm上,直接读取使用即可。
(2)如果计算属性要被修改,那必须写set函数去响应修改,且set中要引起计算时依赖的数据发生改变
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
},
computed: {
fullName: {
//get有什么作用? 当有人读取fullName时,get就会被调用,且返回值就作为fullName的值
//get什么时候调用? 1.初次读取fullName时。2.所依赖的数据发生变化时
get(){
console.log('get被调用了');
// console.log(this); //此处的 this 是 vm
return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName
},
//set什么时候调用?当fullName被修改时。
set(value) {
console.log('set', value);
const arr = value.split('-')
this.firstName = arr[0]
this.lastName = arr[1]
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
7. 监视属性
- 天气案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<!-- 绑定事件的时候:事件 @xxx = "yyy" yyy可以写一些简单的语句 -->
<!-- <button @click="isHot = !isHot">切换天气</button> -->
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true,
},
computed: {
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 天气案例_监视属性
监视属性watch:
(1)当被监视的属性发生变化时,回调函数自动调用,进行相关操作
(2)监视的属性必须存在,才能进行监视
(3)监视的两种写法:
- new vue时传入watch配置
- 通过vm.$watch监视
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true,
},
computed: {
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
/*watch: {
isHot: {
immediate: false, //初始化时让 handler 调用一下
//handler什么时候调用? 当isHot发生改变时。
handler(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}
}
}*/
})
vm.$watch('isHot', {
immediate: true, //初始化时让 handler 调用一下
//handler什么时候调用? 当isHot发生改变时。
handler(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 天气案例_深度监视
深度监视:
(1)Vue中的watch默认不检测对象内部值的改变(一层)
(2)配置deep:true可以监测对象内部值改变(多层)
备注:
(1)Vue自身可以监测对象内部值的改变,但Vue提供的watch默认不可以!
(2)使用watch时根据数据的具体结构们决定是否采用深度监测。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
<h2>今天天气很{{info}}</h2>
<button @click="changeWeather">切换天气</button>
<hr/>
<h3>a的值是: {{numbers.a}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.a++">点我让a+1</button>
<h3>b的值是: {{numbers.b}}</h3>
<button @click="numbers.b++">点我让b+1</button>
<button @click="numbers = {a:666, b:888}">彻底替换掉numbers</button>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
isHot: true,
numbers: {
a: 1,
b: 1
}
},
computed: {
info(){
return this.isHot ? '炎热' : '凉爽'
}
},
methods: {
changeWeather() {
this.isHot = !this.isHot
}
},
watch: {
isHot: {
// immediate: false, //初始化时让 handler 调用一下
//handler什么时候调用? 当isHot发生改变时。
handler(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}
},
//监视多级结构中某个属性的变化
// 'numbers.a':{
// handler(){
// console.log('a被改变了');
// }
// }
//监视多级结构中所有属性的变化
numbers: {
deep: true,
handler(){
console.log('numbers改变了');
}
}
}
})
</script>
</html>
- 监视的简写方式
watch: {
//正常写法
/*isHot: {
// immediate: false, //初始化时让 handler 调用一下
// deep: true, //深度监视
handler(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}
},*/
//简写
/*isHot(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}*/
}
})
//正常的写法
/* vm.$watch('isHot', {
immediate: false, //初始化时让 handler 调用一下
deep: true, //深度监视
handler(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
}
}) */
vm.$watch('isHot', function(newValue, oldValue){
console.log('isHot被修改了', newValue, oldValue);
})
- 姓名案例_watch实现
computed和watch之间的区别:
(1)computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成。
(2)watch能完成的功能,computed不一定能完成,例如:watch可以进行异步操作。
两个重要的小原则:
(1)所被Vue管理的函数,最好写成普通函数,这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。
(2)所有不被 Vue 所管理的函数(定时器的回调函数、ajax的回调函数、promise回调函数等),最好携程箭头函数。这样this的指向才是vm 或 组件实例对象。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script type="text/javascript" src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 准备好一个容器 -->
<div id="root">
姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br/><br/>
名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br/><br/>
全名:<span>{{fullName}}</span>
</div>
</body>
<script type="text/javascript">
Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在启动时生成产生提示
const vm = new Vue({
el: '#root',
data: {
firstName: '张',
lastName: '三',
fullName: '张-三'
},
watch: {
firstName(newValue){
this.fullName = newValue + '-' + this.lastName
},
lastName(newValue){
this.fullName = this.firstName + '-' + newValue
}
}
})
</script>
</html>