Idea通过jdbc连接Mysql8.0,JDBC的API使用
目录
首先下载jar包,点击下面的官网链接下载
连接的代码:(Mysql5.0以后,可以省略注册驱动那一步)
DriverManager
事务处理
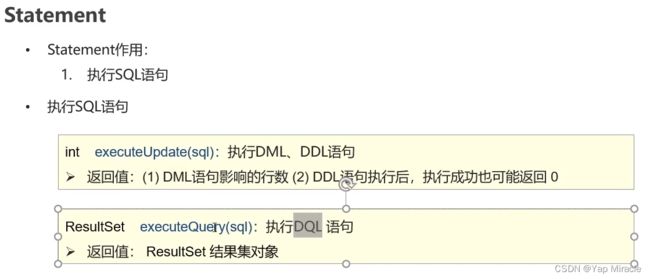
Statement
PrepareStatement
首先下载jar包,点击下面的官网链接下载
MySQL :: Download Connector/J
下载完成后记得在项目里面Add as library。
JDBC的步骤:
连接的代码:(Mysql5.0以后,可以省略注册驱动那一步)
jar包里面包含了注册的代码
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//注册驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("哈哈哈");
// String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student&ussl=false";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String username="root";
String password="123456";
//获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String sql = "select * from admin";
//获取执行对象
Statement stat = connection.createStatement();
boolean execute = stat.execute(sql);
// while()
System.out.println(execute);
stat.close();
connection.close();
}
}
打印成功的信息
DriverManager
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");这个是最常见的注册驱动的方法,但是要注意版本(尤其注意cj加与不加)。
另外一种注册驱动的方法:
System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
System.setProperty("jdbc.driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//系统属性指定数据库驱动
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/databasename";//数据库连接子协议
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,"username","password"); 可以同时导入多个jdbc驱动,中间用冒号“:”分开
比如System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers","XXXDriver:XXXDriver:XXXDriver");
这样就一次注册了三个数据库驱动
事务处理
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//注册驱动
// Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
System.out.println("哈哈哈");
// String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student&ussl=false";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String username="root";
String password="123456";
//获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String sql0="update admin set password=123456 where id=1";
String sql = "update admin set password=12345 where id=2";
//获取执行对象
Statement stat = connection.createStatement();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//执行sql
try {
int count1 = stat.executeUpdate(sql0);
System.out.println(count1);
int i=1/0;
int count2 = stat.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(count2);
connection.commit();
}
catch(Exception e){
connection.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}
stat.close();
connection.close();
}
}
这里故意抛出1/0的错误,看看是否执行了roolback(),结果证明是正确的。try块里面的数据都没有成功执行,回滚了。
Statement
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//注册驱动
//Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
//String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student&ussl=false";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String username="root";
String password="123456";
//获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
String sql0="select * from admin";
// String sql = "update admin set password=12345 where id=2";
//获取执行对象
Statement stat = connection.createStatement();
ResultSet res=stat.executeQuery(sql0);
while(res.next()){
// Account a=new Account();
System.out.println("id=" + res.getInt("id"));
System.out.println("name=" + res.getString("name"));
System.out.println("password=" + res.getString("password"));
}
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(now);
res.close();
stat.close();
connection.close();
}
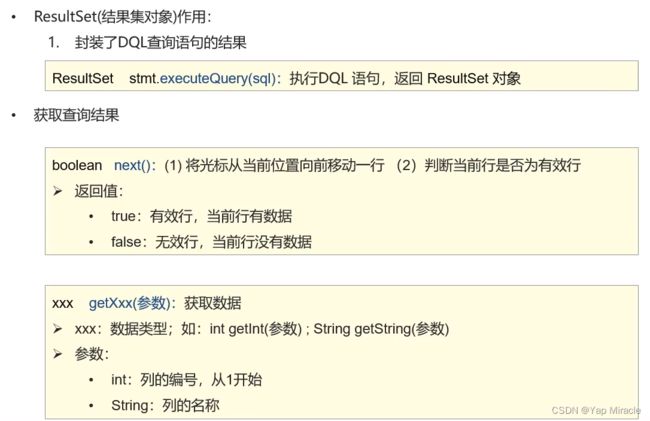
}boolean next() throws SQLException;注意ResultSet (结果集)的next的方法返回值是boolean类型,表示还有数据的话即输出来。
PrepareStatement
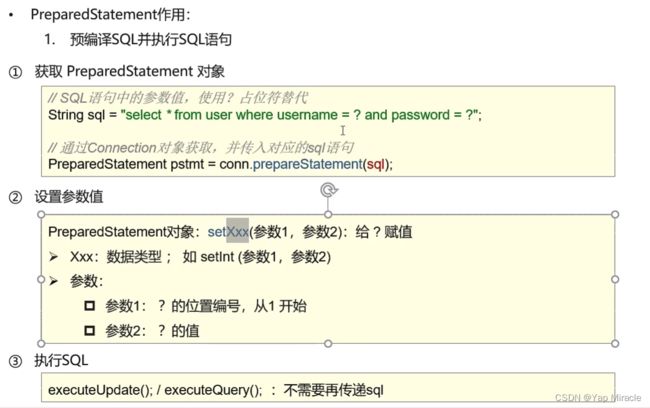
作用:预编译SQL语句并且执行,预防SQL注入问题,继承于Statement。
SQL注入问题:通过操作事先设置好的SQL语句,用以达到执行代码对服务器进行攻击的方法。
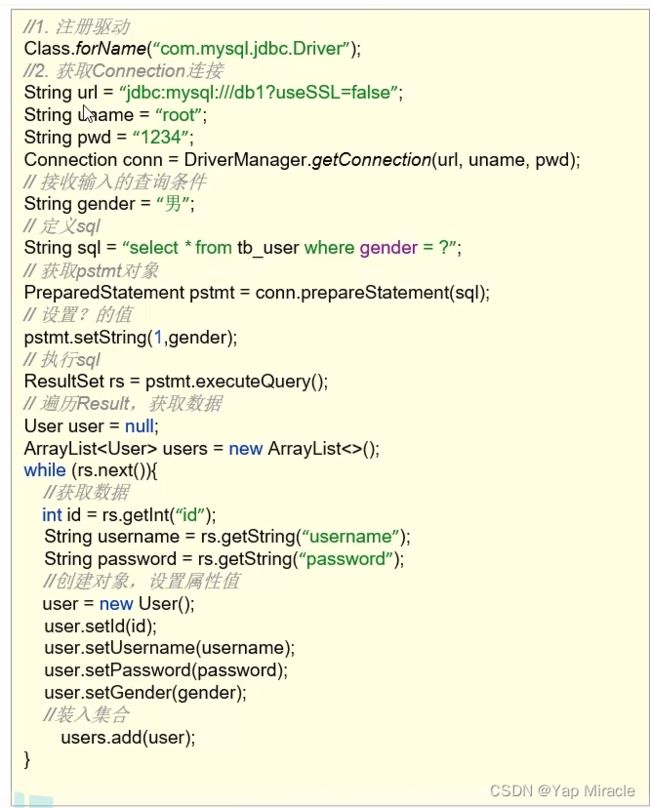
常见的就是如下图所示的代码,只要输入的密码是下面那种情况的,都可以登录成功,不管你有没有那个用户名。
演示:
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import com.mysql.cj.protocol.Resultset;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 模拟SQL注入问题
*/
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
String name="124";
String pas = "' or '1' = '1";
String sql = "select * from admin where name='"+name+"' and password = '"+pas+"'";
Statement stat = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet res = stat.executeQuery(sql);
String[] a=new String[10];
int i=0;
while(res.next()){
String id= res.getString("id");
String name1 = res.getString("name");
String pass = res.getString("password");
a[i++]=id;
a[i++]=name1;
a[i++]=pass;
}
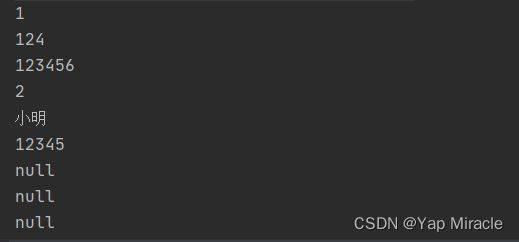
for (i=0; i输出结果:
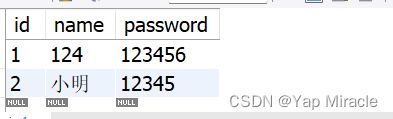
数据库里面的数据:
明明是密码错误,怎么会输出数据呢?
我们打印一下sql语句:
select * from admin where name='124' and password = '' or '1' = '1'原来where的条件一直显示为真,所以相当于:
select * from admin解决办法:
示例:
package com.itheima.jdbc;
import com.mysql.cj.protocol.Resultset;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* 模拟SQL注入问题
*/
public class JDBCDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC";
String user = "root";
String pwd = "123456";
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pwd);
String name="124";
String pas = "' or '1' = '1";
String sql = "select * from admin where name=? and password =?";
PreparedStatement stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
stat.setString(1, name);
stat.setString(2, pas);
ResultSet res = stat.executeQuery();
String[] a=new String[10];
int i=0;
while(res.next()){
String id= res.getString("id");
String name1 = res.getString("name");
String pass = res.getString("password");
a[i++]=id;
a[i++]=name1;
a[i++]=pass;
}
System.out.println(sql);
for (i=0; i执行结果:
使用? 号当作sql的占位符就可以完美解决SQL注入的问题。