SpringSecurity框架
用户登录系统时我们协助 SpringSecurity 把 用户对应的角色、权限组装好,同时把各个资源所要求的权限信息设定好,剩下的“登录验证”、“权限验证”等等工作都交给SpringSecurity。
1.SpringSecurity框架使用简介
2.权限管理过程中的相关概念
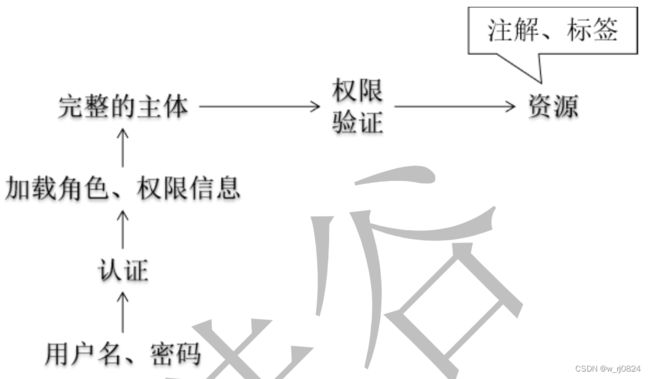
2.1主体:principal,使用系统的用户、设备或从其他系统远程登录的用户等等。简单说就是谁使用系统谁就是主体。
2.2认证:authentication,权限管理系统确认一个主体的身份,允许主体进入系统。简单说就是“主体”证明自己是谁。笼统的认为就是以前所做的登录操作。
2.3授权:authorization,将操作系统的“权力”“授予”“主体”,这样主体就具备了操作系统中特定功能的能力。所以简单来说,授权就是给用户分配权限。
2.4权限管理的主流框架:
①SpringSecurity:Spring 技术栈的组成部分。
SpringSecurity 特点:
- 和 Spring 无缝整合。
- 全面的权限控制。
- 专门为 Web 开发而设计。
- 旧版本不能脱离 Web 环境使用。
- 新版本对整个框架进行了分层抽取,分成了核心模块和 Web 模块。单独引入核心模块就可以脱离 Web 环境。
- 重量级。
②Shiro:Apache 旗下的轻量级权限控制框架。
特点:
- 轻量级。Shiro 主张的理念是把复杂的事情变简单。针对对性能有更高要求的互联网应用有更好表现
- 通用性。
- 好处:不局限于 Web 环境,可以脱离 Web 环境使用。
- 缺陷:在 Web 环境下一些特定的需求需要手动编写代码定制。
3. SpringSecurity的使用
3.1引入框架依赖
org.springframework.security
spring-security-web
5.4.2
org.springframework.security
spring-security-config
5.4.2
org.springframework.security
spring-security-taglibs
5.4.2
3.2加入 SpringSecurity 控制权限的 Filter
SpringSecurity使用的是过滤器Filter而不是拦截器Interceptor,意味着SpringSecurity能够管理的不仅仅是 SpringMVC 中的 handler 请求,还包含 Web 应用中所有请求。比如:项目中的静态资源也会被拦截,从而进行权限控制。
springSecurityFilterChain
org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy
springSecurityFilterChain
/*
特 别 注 意 :
3.3加入配置类
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebAppSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
}
//Enable 理解为启用。
//@EnableWebSecurity 注解表示启用 Web 安全功能。
//以后会接触到很多@EnableXxx 注解,用来启用对应的功能。3.4效果
- 所有请求都被 SpringSecurity 拦截,要求登录才可以访问。
- 静态资源也都被拦截,要求登录。
- 登录失败有错误提示。
4.SpringSecurity 操作实验
下面的操作都是在spring-security-new工程的的基础上逐步增加权限控制设置,循序渐进学习SpringSecurity用法。
4.1实验1:放行首页和静态资源
设置授权信息时需注意:范围小的放在前面、范围大的放在后面
在配置类中重写父类的 configure(HttpSecurity security)方法
重写前:
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
this.logger.debug("Using default configure(HttpSecurity). If subclassed this will potentially override subclass configure(HttpSecurity).");
http.authorizeRequests((requests) -> requests.anyRequest().authenticated());
http.formLogin();
http.httpBasic();
}
重写后:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity security) throws Exception {
security
.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.antMatchers("/layui/**","/") //针对"/layui/**","/"路径进行授权(匹配请求路径)
.permitAll() //permitAll表示可以无条件的访问,
.and()
.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.anyRequest() //任意请求
.authenticated(); //需要登陆以后才可以访问
}
效果:未认证的请求会跳转到 403 错误页面。
4.2 实验 2:未认证请求跳转到登录页
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity security) throws Exception {
security
.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.antMatchers("/layui/**","/") //针对"/layui/**","/"路径进行授权(匹配请求路径)
.permitAll() //permitAll表示可以无条件的访问,
.and()
.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.anyRequest() //任意请求
.authenticated() //需要登陆以后才可以访问
.and()
.formLogin() //设置未授权请求跳转到登录页面,使用表单形式登录
// 关于loginPage()方法的特殊说明
// 指定登录页的同时会影响到:"提交登录表单的地址","退出登录的地址","登陆失败的地址"以及"登录页本身"
// 去登录页面: /login GET - the login form
// 提交登录表单:/login POST - process the credentials and if valid authenticate the user
// 登陆失败: /login?error GET - redirect here for failed authentication attempts
// 退出登录: /login?logout GET - redirect here after successfully logging out
.loginPage("/login") //指定登录页,如果没有指定会访问springsecurity自带的登录页
// loginProcessingUrl()方法指定了登录地址,就会覆盖loginPage()方法中设置的默认值/login POST
.loginProcessingUrl("/do/login")
.permitAll(); //调用permitAll()方法是为了允许访问登录地址(表单提交地址),不然这个登录地址也需要登录后才能访问
}4.3 实验 3:设置登录系统的账号、密码
4.3.1账号、密码的请求参数名
SpringSecurity 默认账号的请求参数名:username
SpringSecurity 默认密码的请求参数名:password
如果想更改请求参数名:
要么修改页面上的表单项的 name 属性值,要么修改配置。
如果修改配置可以调用usernameParameter()和 passwordParameter()方法。
...
.permitAll()
.usernameParameter("loginAcct") //定制登录账号的请求参数名
.passwordParameter("userPswd"); //定制登录密码的请求参数名
.defaultSuccessUrl("/main"); //登陆成功后前往的地址4.3.2重写另外一个父类的方法,来设置登录系统的账号密码(假数据)
// 用以指定正确的账号和正确的密码
// Cannot pass a null GrantedAuthority collection 问 题 是 由 于 没 有 设 置 roles() 或 authorities()方法导致的。
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder builder) throws Exception {
builder.inMemoryAuthentication() // 在内存中完成账号、密码的检查
// 用以解决"java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null""报错问题
.passwordEncoder(new MyPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("tom").password("123123") //设置账号密码
.roles("ADMIN") //设置角色
.and()
.withUser("jerry").password("456456")//设置另一个账号密码
.authorities("SAVE","EDIT"); //设置权限
}Cannot pass a null GrantedAuthority collection 问 题 是 由 于 没 有 设 置 roles() 或 authorities()方法导致的。
4.3.3设置登录成功后默认前往的页面
.defaultSuccessUrl("/main"); //设置登录成功后默认前往的 URL 地址实现的最后效果:登录成功后具体资源都可以访问了。
4.4实验 4:用户注销
通过调用 HttpSecurity 对象的一系列方法设置注销功能。
logout()方法:开启注销功能
logoutUrl()方法:自定义注销功能的 URL 地址
如果 CSRF 功能没有禁用,那么退出请求必须是 POST 方式。如果禁用了 CSRF功能则任何请求方式都可以。
logoutSuccessUrl()方法:退出成功后前往的 URL 地址
addLogoutHandler()方法:添加退出处理器
logoutSuccessHandler()方法:退出成功处理器
退出
.and()
.csrf()
.disable() // 禁用CSRF功能
.logout() // 开启退出功能
.logoutUrl("/do/logout") // 指定处理退出请求的url地址
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login"); // 退出成功之后前往的地址
退出
//.and()
//.csrf()
//.disable() // 禁用CSRF功能
.and()
.logout() // 开启退出功能
.logoutUrl("/do/logout") // 指定处理退出请求的url地址
.logoutSuccessUrl("/login"); // 退出成功之后前往的地址
4.5实验 5:基于角色或权限进行访问控制
通过 HttpSecurity 对象设置资源的角色要求
//设置资源的角色要求:
security.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.antMatchers("/layui/**","/") //针对"/layui/**","/"路径进行授权(匹配请求路径)
.permitAll() //permitAll表示可以无条件的访问,
.antMatchers("/level1/**") //针对 "/level1/**" 路径设置访问要求
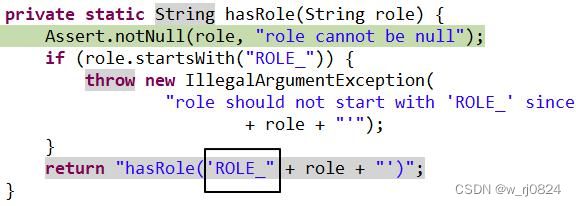
.hasRole("学徒") //要求用户具备学徒的角色才可以访问
.antMatchers("/level2/**") //针对 "/level2/**" 路径设置访问要求
.hasAuthority("内门弟子") //要求用户具备内门弟子的权限才可以访问
.and()
.authorizeRequests() //对请求进行授权
.anyRequest() //任意请求
.authenticated() //需要登陆以后才可以访问
//给账号设置角色或权限
builder.inMemoryAuthentication() // 在内存中完成账号、密码的检查
// 用以解决"java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id "null""报错问题
.passwordEncoder(new MyPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("tom").password("123123") //设置账号密码
.roles("ADMIN","学徒") //设置角色
.and()
.withUser("jerry").password("456456")//设置另一个账号密码
.authorities("SAVE","内门弟子"); //设置权限
注意:调用顺序 (设置授权信息时需注意:范围小的放在前面、范围大的放在后面)
// ①
.antMatchers("/level1/**") // 设置匹配/level1/** 的地址
.hasRole(" 学徒") // 要求具备 “ 学徒 ” 角色
// ②
.anyRequest() // 其实未设置的所有请求
.authenticated()
②代码设置范围更大
①代码设置范围相对小
如果②代码先调用,会把后面①代码的设置覆盖,导致①代码无效。
所以要先做具体小范围设置,再做大范围模糊设置。
注意 :SpringSecurity 会在角色字符串前面加“ROLE_”前缀,之所以要强调这个事情,是因为将来从数据库查询得到的用户信息、角色信息、权限信息需要我们自己手动组装。手动组装时需要我们自己给角色字符串前面加“ROLE_”前缀。
4.6实验 6 :自定义 403 错误页面
自定义的错误页面的主体:
抱歉!您没有权限访问此功能!
前往自定义页面方式一:
@RequestMapping("/to/no/auth/page")
public String toNoAuthPage() {
return "/views/no_auth";
}
HttpSecurity.exceptionHandling()
.accessDeniedPage("/to/no/auth/page"); 前往自定义页面方式二:
@RequestMapping("/to/no/auth/page")
public String toNoAuthPage() {
return "/views/no_auth";
}
.and()
.exceptionHandling() // 指定异常处理器
//.accessDeniedPage("/to/no/auth/page");//出现异常时,前往自定义的错误页面
.accessDeniedHandler(new AccessDeniedHandler() {
@Override
public void handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AccessDeniedException e) throws IOException, ServletException {
request.setAttribute("message","抱歉!您无法访问这个资源!☆☆☆");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/to/no/auth/page").forward(request,response);
}
});
4.7 实验 7 :记住我-内存版(不重要)
HttpSecurity 对象调用 rememberMe()方法。
登录表单携带名为 remember-me 的请求参数。具体做法是将登录表单中的 checkbox 的 name 设置为 remember-me
如果不能使用“remember-me”作为请求参数名称,可以使用rememberMeParameter()方法定制。
4.8 实验 8 :记住我-数据库版(不重要)
为了让服务器重启也不影响记住登录状态,将用户登录状态信息存入数据库。
4.8.1 建立数据库连接
①依赖
org.springframework
spring-orm
5.3.17
mysql
mysql-connector-java
8.0.28
com.alibaba
druid
1.2.8
②数据源
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=abc123
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/security?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
③在 WebAppSecurityConfig类中注入数据源
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource;4.8.2 启用令牌仓库功能
JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl repository = new JdbcTokenRepositoryImpl();
repository.setDataSource(dataSource);
security.tokenRepository(repository);4.9 实验 9:查询数据库完成认证
4.9.1 了解:SpringSecurity 默认实现
builder.jdbcAuthentication().usersByUsernameQuery("tom");
在usersByUsernameQuery("tom")等方法中最终调用JdbcDaoImpl类的方法查询数据库。
SpringSecurity 的默认实现已经将 SQL 语句硬编码在了 JdbcDaoImpl 类中。这种
情况下,我们有下面三种选择:
- 按照 JdbcDaoImpl类中 SQL 语句设计表结构。
- 修改 JdbcDaoImpl类的源码。
- 不使用 jdbcAuthentication()。
4.9.2 自定义数据库查询方式
builder.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)
其中userDetailsService需要自定义实现UserDetailsService接口的类并自动装配。
①实现UserDetailsService接口的类(在这之前需要根据t_admin表创建Admin实体类)
@Component
public class MyUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
// 总目标:根据表单提交的用户查询User对象,并装配角色、权限等信息
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(
// 表单提交的用户名
String username
) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 1.从数据库查询admin对象
String sql = "SELECT id,loginacct,userpswd,username,email FROM t_admin WHERE loginacct = ?";
List list = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Admin.class), username);
Admin admin = list.get(0);
// 2.给admin设置角色权限信息
ArrayList authorities = new ArrayList<>();
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("ROLE_ADMIN"));
authorities.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority("UPDATE"));
// 3.把admin对象和authorities封装到UserDetails中
String userpswd = admin.getUserpswd();
return new User(username,userpswd,authorities);
}
} ② 使用自定义 UserDetailsService 完成登录
// 装配userDetailsService
builder.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(new MyPasswordEncoder());4.10 实验 10:应用自定义密码加密规则
4.10.1MD5加密
①自定义类实现 org.springframework.security.crypto.password.PasswordEncoder(使用没有过时的)接口。
@Component
public class MyPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder {
//encode()方法对明文进行加密。
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence rawPassword) {
return privateEncode(rawPassword);
}
//matches()方法对明文加密后和密文进行比较。
@Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence rawPassword, String encodedPassword) {
// 1.对明文密码进行加密
String formPassword = privateEncode(rawPassword);
// 2.声明数据库查询出来的密码
String databasePassword = encodedPassword;
// 3.比较
return Objects.equals(formPassword,databasePassword);
}
private String privateEncode(CharSequence rawPassword){
try {
// 1.创建MessageDigest对象
String algorithm = "MD5";
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
// 2.获取rawPassword的字节数组
byte[] input = ((String) rawPassword).getBytes();
// 3.加密
byte[] output = messageDigest.digest(input);
// 4.创建 BigInteger 对象
int signum = 1;//控制bigInteger是正数
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger(signum, output);
// 5.按照 16 进制将 bigInteger 的值转换为字符串
int radix = 16;
String encoded = bigInteger.toString(radix).toUpperCase();
return encoded;
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}②在配置类中的 configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder)方法中应用自定义密码加密规则
// 装配userDetailsService
uilder.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);③潜在问题
固定的明文对应固定的密文,虽然很难从密文通过算法破解反推回明文。但是可以借助已有的明文和密文的对应关系猜解出来。123123 → 4297F44B13955235245B2497399D7A93
4.10.2带盐值的加密
在加密时每次使用一个随机生成的盐值,让每次的加密结果都不同,能够避免密码的明文被猜到。
@Autowired
private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder getBBCryptPasswordEncoder(){
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
// 装配userDetailsService,passwordEncoder
builder.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder);