一文全解ThreadLocal
文章目录
-
- 一、Thread简介
-
- 1.什么是ThreadLocal
- 2.为什么要是用ThreadLocal
-
- 2.1Synchronized、Lock保证线程安全
- 2.2ThreadLocal保证线程安全
- 3.ThreadLocal和Synchronized的区别
- 二、ThreadLocal原理
-
- 1.Thread抽象内部结构
- 2.ThreadLocal源码
-
- 2.1Thread、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap、Entry之间关系
- 2.2ThreadLocal类的set()方法
- 2.3ThreadLocal类的get()方法
- 2.4ThreadLocal类的remove()方法
- 2.5面试:说一说ThreadLocal原理、Thread如何实现线程隔离的
- 三、深究ThreadLocal
-
- 1.为什么不直接用线程id作为ThreadLocalMap的key呢?
- 2.ThreadLocal导致内存泄漏的原因
- 3.ThreadLocalMap在设计中有没有考虑到内存泄漏这点呢?
- 4.在使用ThreadLocal中,我们应该注意什么
- 5.key是弱引用,GC回收会影响ThreadLocal的正常工作嘛
- 6.Entry的key为什么要设计成弱引用呢,为什么不使用强引用
-
- 6.1Entry的key如果使用强引用
- 6.2为什么要设计成弱引用
- 6.3四种引用类型
- 7.我们希望父子线程之间共享数据,应该怎么做呢
-
- 7.1InheritableThreadLocal
- 7.2InheritableThreadLocal是如何实现父子线程之间共享的
- 使用InheritableThreadLocal,父线程修改数据,子线程是否可见?
- 8.线程池中如何是实现数据共享呢?
- 9.ThreadLocal有哪些用途?
- 10.ThreadLocal如何定位数据的
- 11.ThreadLocal是如何扩容的
一、Thread简介
1.什么是ThreadLocal
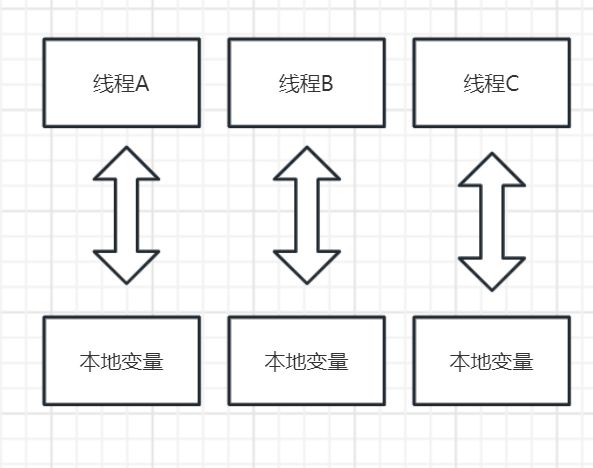
ThreadLocal,即线程本地变量。如果你创建了一个ThreadLocal变量,那么访问这个变量的每个线程都会有这个变量的一个本地拷贝,多个线程操作这个变量的时候,实际是在操作自己本地内存里面的变量,从而起到线程隔离的作用,保证了线程安全。
- 因为每个 Thread 内有自己的实例副本,且该副本只能由当前 Thread 使用。这是也是 ThreadLocal 命名的由来。
- 每个 Thread 有自己的实例副本,且其它 Thread 不可访问,那就不存在多线程间共享的问题。
2.为什么要是用ThreadLocal
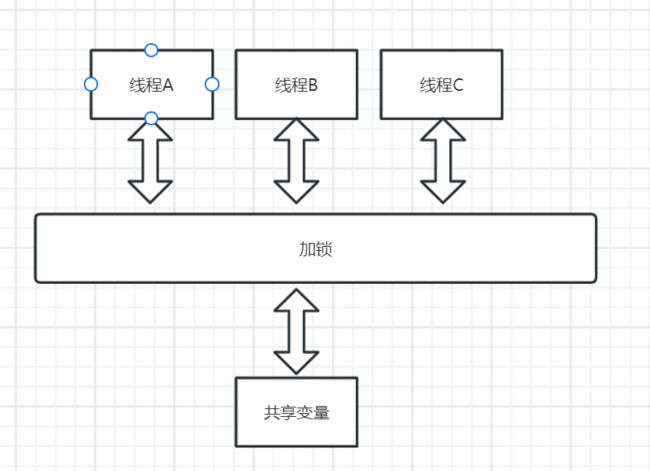
保证线程安全,并发场景下,会出现多个线程共享一个变量的场景,这种场景可能会出现线程安全性问题,我们可以采取加锁的方式(Synchronized、Lock)方式,也可以使用使用ThreadLocal方式来避免线程安全问题。
2.1Synchronized、Lock保证线程安全
采用加锁方式保证线程安全到导致系统变慢。共享变量某个时刻只能由一个线程访问,其他线程需要等到该线程释放锁才能访问,影响系统性能。
2.2ThreadLocal保证线程安全
使用ThreadLocal。使用ThreadLocal类访问共享变量时,会在每个线程的本地,都保存一份共享变量的拷贝副本。多线程对共享变量修改时,实际上操作的是这个变量副本,从而保证线性安全。
3.ThreadLocal和Synchronized的区别
- ThreadLocal和Synchronized都是为了解决并发问题。
- Synchronized用于线程共享, 而ThreadLocal用于线程隔离。
- Synchronized是时间换空间,ThreadLocal是空间换时间。
- Synchronized是利用锁的机制,使变量或代码块在某一时该只能被一个线程访问。而ThreadLocal为每一个线程都提供了变量的副本,使得每个线程在某一时间访问到的并不是同一个对象,这样就隔离了多个线程对数据的数据共享。
二、ThreadLocal原理
1.Thread抽象内部结构
简单理解(看不懂先往下看再回顾):
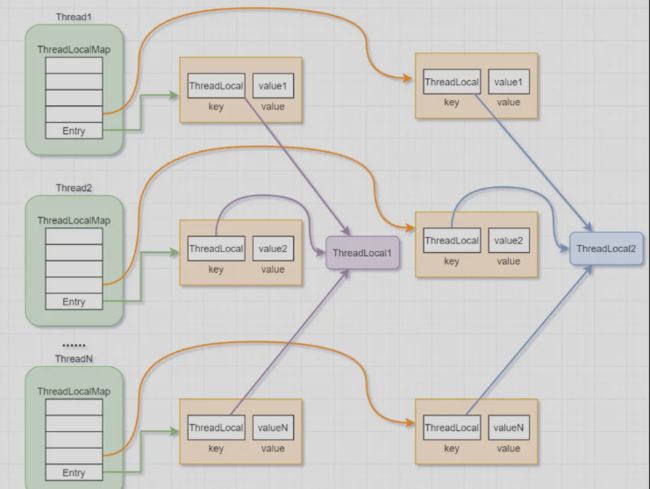
- Thread类中有ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals属性
- ThreadLocalMap 是Thread的静态内部类,它维护着Entry对象数组,每个Entry代表一个ThreadLocalMap对象
- Entry是ThreadLocalMap的静态内部类,存储采用的是k-v形式,key为ThreadLocal,value为set的value
2.ThreadLocal源码
2.1Thread、ThreadLocal、ThreadLocalMap、Entry之间关系
先根据源码砍砍他们之间的关系
- Thread的成员变量ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
- ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类
- Entry是ThreadLocalMap的静态内部类,Entry继承了弱引用,也就是说,如果外部没有强引用关联的话,下一次GC时会被回收。
- 在Entry是一个k-v形式,内部使用ThreadLocal作为key,使用我们设置的value作为value。
- Entry[] table为ThreadLocal的属性,由ThreadLocalMap维护
//Thread类
class Thread implements Runnable {
//ThreadLocalMap是Thread的成员变量
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}
//ThreadLocal类
public class ThreadLocal<T> {
//Entry数组是ThreadLocal的成员变量,该数组由ThreadLocalMap维护
private Entry[] table;
//静态内部类ThreadLocalMap
static class ThreadLocalMap {
//Entry是ThreadLocalMap的静态内部类,注意,Entry继承了弱引用(如果没有被强引用关联,下一次GC会被回收)
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
}
}
2.2ThreadLocal类的set()方法
通过源码可以看到,ThreadLocalMap维护了Entry数组,Entry是k-v形式,key为ThreadLocal,value为我们传入的值,当同一个线程对同一个ThreadLocal进行两次set时,value会被覆盖。
- 获取当前线程,根据当前线程获取ThreadLocalMap
- 判断ThreadLocalMap是否存在
- 存在则将ThreadLocal作为key,传入的值为value,存入ThreadLocalMap的Entry中
- 不存在则根据ThreadLocalMap构造函数创建ThreadLocalMap并将ThreadLocal作为key,传入的值为value,存入ThreadLocalMap的Entry中
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程t
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);//根据当前线程获取到ThreadLocalMap
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);//如果map不为空,则将当前对象ThreadLocal作为key,传入的值为value存入ThreadLocalMap中
else
createMap(t, value);//如果map为空,则创建ThreadLocalMap对象后,再将k-v存入ThreadLocalMap中
}
//该方法位于ThreadLocal中
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;//根据线程t获取Thrad的ThreadLocalMap
}
//该方法位于ThreadLocal中
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);//调用ThreadLocalMap构造函数,this表示当前类ThreadLocal
}
//该方法位于ThreadLocal中,该方法位于ThreadLocal中构造函数维护这Entry数组table
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
2.3ThreadLocal类的get()方法
- 获取当前线程t
- 根据线程t获取ThradLocalMap map
- map存在则获取Entry,Entry存在获取value
- map不存在,初始化ThradLocalMap并将ThreadLocal作为kay,valeu为null存进ThreadLocalMap中,返回value也就是null。
- (调用get()方法时,ThreadLocalMap没有初始化则会初始化并ThreadLocal作为key,valeu为null存进ThreadLocalMap中)
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();//获取当前线程
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);//map不为空,获取Entry
if (e != null) {//entry不为空。返回value
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();//map为空,初始化threadLocals成员变量的值,也就是初始化把thread Local为key,value=null塞进entry
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue(); //初始化value的值
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); //以当前线程为key,获取threadLocals成员变量,它是一个ThreadLocalMap
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value); //K,V设置到ThreadLocalMap中
else
createMap(t, value); //实例化threadLocals成员变量
return value;//返回null
}
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
2.4ThreadLocal类的remove()方法
- 获取当前线程,根据当前线程获取ThreadLocalMap
- 如果map不为空,则删除map中指定的的Entry
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());//获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap变量
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);//对象不为空,则删除
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
2.5面试:说一说ThreadLocal原理、Thread如何实现线程隔离的
ThreadLocal叫本地线程变量,作用就是当多线程访问共享变量时,起到线程隔离的作用,每个线程都有自己的一个副本,且之间不被共享,这种方式采用的是空间换时间的方式。目的是保证线程安全,采用空间换时间的方式保证线程安全。
每个线程Thread都有一个成员变量ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap thradLocals。也就是说每个线程都有一个ThreadLocalMap,这个ThreadLocalMap是ThreadLocal的静态内部类,他维护者Entry对象数组,Entry对象存储方式是k-v的形式。k为ThreadLocal,V为我我们set进去的值。
在并发场景下,每个线程在往ThreadLocal里面设置值得时候,实际就是存进自己的thradLocals属性中,以ThreadLocal为key,set进去的值为value。实现线程隔离。
三、深究ThreadLocal
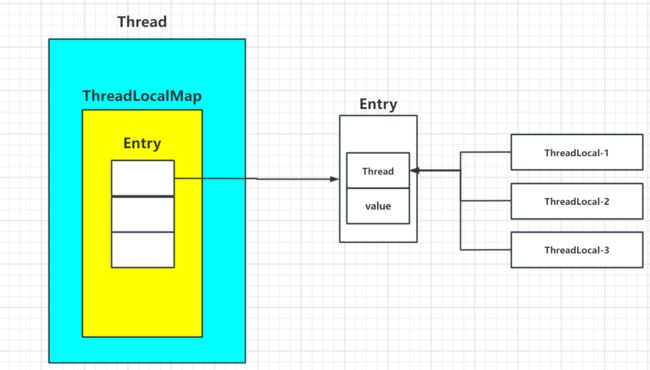
1.为什么不直接用线程id作为ThreadLocalMap的key呢?
ThreadLocalMap是Thread的属性,维护着Entry数组,Entry的key是ThradLocal,value为我们set入的值。
如果将线程id作为key,那么当一个Thread有多个ThreadLocal进行set()的时候,无法区分value是哪个ThreadLocal的,或者说无论多少个ThreadLocal,每次set进去,由于key都是ThreadId,会导致每次set都会被覆盖。
如图所示,一个key对应多个ThreadLocal。ThreadLocal-1 set()的时候key为Thread,ThreadLocal-1 set()的时候key依然为Thread
2.ThreadLocal导致内存泄漏的原因
ThreadLocal导致内存泄漏愿意你有两个
- 使用完后没有remove(), 由于ThreadLocalMap 的生命周期跟 Thread 一样长,对于重复利用的线程来说(例如核心线程池中的线程),如果没有手动删除(调用remove()方法),会导致Entry对象越来越多,从而导致内存泄漏.
- 第二种原因下面讲解
Entry类继承了弱引用,super(k);使ThreadLocal也是一个弱引用
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
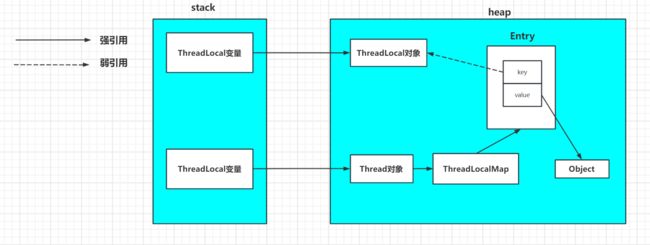
ThreadLocal引用示意图
- ThreadLocalMap使用ThreadLocal的弱引用作为key,当ThreadLocal变量被手动设置为null,即一个ThreadLocal没有外部强引用来引用它,当系统GC时,ThreadLocal一定会被回收。
- 这样的话,ThreadLocalMap中就会出现key为null的Entry,就没有办法访问这些key为null的Entry的value
- 如果当前线程再迟迟不结束的话(比如线程池的核心线程),这些key为null的Entry的value就会一直存在一条强引用链:Thread变量 -> Thread对象 -> ThreaLocalMap -> Entry -> value -> Object 永远无法回收,造成内存泄漏。
当Thread手动设置为null后的因用链
此时,堆中的ThreadLocal只存在弱引用,再下一次GC时会被回收。回收后,Entry中的key=null,这个Entry就没有办法被访问。导致内存泄漏。
3.ThreadLocalMap在设计中有没有考虑到内存泄漏这点呢?
实际上ThreadLocalMap在设计的时候就考虑到这个情况了,所以ThreadLocal的get、set方法中加了一些防护措施。在执行set、get方法的时候,会清楚线程中ThreadLocalMap中key为null的Entry。但是这些措施并不能完全保证不会内存泄漏**
ThreadLocal的set()方法防止内存泄漏措施
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
//触发一次Log2(N)复杂度的扫描,目的是清除过期Entry
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
ThreadLocal的get()方法防止内存泄露措施
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//去ThreadLocalMap获取Entry,方法里面有key==null的清除逻辑
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//其中有key为null的清楚逻辑
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
if (k == null)
// Entry的key为null,则表明没有外部引用,且被GC回收,是一个过期Entry
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
4.在使用ThreadLocal中,我们应该注意什么
- 将ThreadLocal变量定义成private static的,这样的话ThreadLocal的生命周期就更长,由于一直存在ThreadLocal的强引用,所以ThreadLocal也就不会被回收,也就能保证任何时候都能根据ThreadLocal的弱引用访问到Entry的value值,然后remove它,防止内存泄露
- 每次使用完ThreadLocal,都调用它的remove()方法,清除数据。
5.key是弱引用,GC回收会影响ThreadLocal的正常工作嘛
- 弱引用:具有弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。如果一个对象只有弱引用存在了,则下次GC将会回收掉该对象(不管当前内存空间足够与否)
当然不会,因为还有ThreadLocal强引用着它,是不会被GC回收的,除非手动将ThradLocal置为null
验证
package com.jhq.threadLocal;
import java.lang.ref.WeakReference;
/**
* @BelongsProject: study
* @BelongsPackage: com.jhq.threadLocal
* @Author: jianghq
* @CreateTime: 2023-02-24 17:02
* @Description: ThreadLocal的key既然是弱引用.会不会GC贸然把key回收掉,进而影响ThreadLocal的正常使用? 不会
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class WeakReferenceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object object = new Object();
WeakReference<Object> testWeakReference = new WeakReference<>(object);
System.out.println("GC回收之前,弱引用:"+testWeakReference.get());
//触发系统垃圾回收
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
//我们只能建议GC回收,并不能百分之百保证真的回收
System.gc();
}
System.out.println("GC回收之后,弱引用:"+testWeakReference.get());
//手动设置为object对象为null
object=null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("对象object设置为null,GC回收之后,弱引用:"+testWeakReference.get());
}
}
输出:
GC回收之前,弱引用:java.lang.Object@cc34f4d
GC回收之后,弱引用:java.lang.Object@cc34f4d
对象object设置为null,GC回收之后,弱引用:null
6.Entry的key为什么要设计成弱引用呢,为什么不使用强引用
官方回答
o help deal with very large andlong-lived usages, the hash table entries use WeakReferences for keys.
为了应对非常大和长时间的用途,哈希表使用弱引用的 key。
6.1Entry的key如果使用强引用
先看看引用图
正这种情况,由于ThreadLocalMap生命周期和Thread一样长,使用强引用之后,只要Thrad存在,那么Entry就会一直存在内存中,如果线程为核心线程池中的线程,Entry就会一直存在,导致内存泄漏。
6.2为什么要设计成弱引用
如果Key使用弱引用:ThreadLocal置为null,因为ThreadLocalMap持有ThreadLocal的弱引用,即使没有手动删除,ThreadLocal也会被回收。value则在下一次ThreadLocalMap调用set,get,remove的时候会被清除。
6.3四种引用类型
- 强引用:我们new出来的对象就是强引用,例如Object o=new Onject();强引用不会被GC回收。
- 软引用:一个对象只有软引用时,内存空间足够的情况下不会被回收,当内存不足时会被回收。
- 弱引用:当对象只有弱引用时,下一次GC时会被回收。
- 虚引用:如果一个对象仅持有虚引用,那么它就和没有任何引用一样,在任何时候都可能被垃圾回收器回收。虚引用主要用来跟踪对象被垃圾回收器回收的活动。
7.我们希望父子线程之间共享数据,应该怎么做呢
7.1InheritableThreadLocal
使用InheritableThreadLocal
public class InheritableThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal threadLocal=new ThreadLocal();
InheritableThreadLocal inheritableThreadLocal=new InheritableThreadLocal();
threadLocal.set("main线程.ThreadLocal");
inheritableThreadLocal.set("main线程.InheritableThreadLocal");
new Thread(()->{
threadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"ThreadLocal");
inheritableThreadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"InheritableThreadLocal");
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("当前线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+threadLocal.get());
System.out.println("当前线程"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"===="+inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
//输出
当前线程Thread-0====null
当前线程Thread-0====main线程.InheritableThreadLocal
可以看出,ThreadLocal在父子线程之间是不共享的。InheritableThreadLocal可以在父子线程之间共享。但仅限于父子线程之间。
7.2InheritableThreadLocal是如何实现父子线程之间共享的
InheritableThreadLocal是Thread的成员变量,返回类型也是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
/*
* InheritableThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is
* maintained by the InheritableThreadLocal class.
*/
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap inheritableThreadLocals = null;
Thread的init方法
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc) {
//>.....衡略
//如果父线程的inheritableThreadLocals不为空,则将inheritableThreadLocals赋值给子类
if (parent.inheritableThreadLocals != null)
this.inheritableThreadLocals =
ThreadLocal.createInheritedMap(parent.inheritableThreadLocals);
/* Stash the specified stack size in case the VM cares */
this.stackSize = stackSize;
/* Set thread ID */
tid = nextThreadID();
}
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
使用InheritableThreadLocal,父线程修改数据,子线程是否可见?
创建两个线程方式验证,父线程修改数据,子线程是可见
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InheritableThreadLocal inheritableThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal();
inheritableThreadLocal.set("AA");
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==get()=="+inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}).start();
inheritableThreadLocal.set("BB");
new Thread(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"==get()=="+inheritableThreadLocal.get());
}).start();
}
}
//输出
Thread-0==get()==AA
Thread-1==get()==BB
线程池复用线程方式验证,父线程修改数据,子线程不可见
public class demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InheritableThreadLocal inheritableThreadLocal = new InheritableThreadLocal();
inheritableThreadLocal.set("AA");
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;
//为了模拟这种场景,核心线程池和线程池容量设置为1
threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES, blockingQueue, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==get()==" + inheritableThreadLocal.get());
});
inheritableThreadLocal.set("BB");
threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "==get()==" + inheritableThreadLocal.get());
});
}
}
//输出
pool-1-thread-1==get()==AA
pool-1-thread-1==get()==AA
通过上面两个案例,说明如果使用了线程池,不能通过InheritableThreadLocal来实现父子线程数据共享。
8.线程池中如何是实现数据共享呢?
使用TransmittableThreadLocal它并非JDK自带的类,而是阿里巴巴开源jar包中的类。
可以通过如下pom文件引入该jar包:
com.alibaba
transmittable-thread-local
2.11.0
compile
9.ThreadLocal有哪些用途?
- 在spring事务中,保证一个线程下,一个事务的多个操作拿到的是一个Connection。
- 在hiberate中管理session。
- 在JDK8之前,为了解决SimpleDateFormat的线程安全问题。
- 获取当前登录用户上下文。
- 临时保存权限数据。
- 使用MDC保存日志信息。
10.ThreadLocal如何定位数据的
在set()、get()方法都有段代码 int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
再回顾get()方法源码
● 整个过程很好理解
● 通过key取hash再按位取与(table.length-1)计算出下标
● 通过下标,在Entry数组中定位Entry。如果Entry中的key是我们所查找的,定位到数据,返回
● key不是我们所找到的,说明hash冲突了。继续往后找,没有找到数据就从头再来(下标为0开始)
● 知道找到第一Entry的key为null为止。
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
//获取Entry
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
//key的hash再与entry数组长度-1按位取与
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
//获取Entry
Entry e = table[i];
//如果找到的Entry的key是我们需要的key,则返回value
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
//entry返回的key不是我们要的key,就是hash冲突了,导致了两个不同的key定位到了同一个Entry
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal<?> key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
//不断往后找,
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
//如果当前Entry的key正好是我们所需要寻找的key,找到数据
if (k == key)
return e;
//如果key为空,则清理脏数据
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
//如果还是没找到数据,则继续往后找
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
//nextIndex方法,很关键
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
//i+1小于数组长度,则i+1,如果大于等于就为0,从0开始(形成闭环)
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
11.ThreadLocal是如何扩容的
threadLocals默认是null,ThreadLocal中Entry数组初始容量为16,每次扩容2倍。
再回顾set()方法
- 初始为ThreadLocalMap时,Entry长度为16,扩容阈值threshold为长度的三分之二等于10
- 当size长度>=扩容阈值(10),处理key为null的Entry,腾出空间
- 腾出之后,发现size>=threshold(10)的四分之三(向上取整,8)。则扩容
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
//createMap方法,ThreadLocalMap构造函数初始容量为16
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal<?> firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);//设置扩容阈值
}
//设置扩容阈值16*2/3=10
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
//set方法
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
//先尝试回收一次key为null的值,腾出一些空间
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
private void rehash() {
//在此尝试回收一次key为null的值,腾出一些空间
expungeStaleEntries();
// Use lower threshold for doubling to avoid hysteresis
//如果回收之后的size大于等于threshold的3/4时,才需要真正的扩容。
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < oldLen; ++j) {
Entry e = oldTab[j];
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null; // Help the GC
} else {
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
例如:初始Entry数组长度为len=16,threshold为len*2/3=10
到达10时,触发清除key为null的Entry,当size>=10-(10/4)=8时,才真正扩容。倍数为2