C++下“哈希”,“位图”,“布隆过滤器”的简单介绍
目录
- 1. unordered系列关联式
- 2. C++下“hash“的简单模拟实现以及实现中遇见的问题
- 3.哈希的应用
-
- 位图
- 位图模拟实现
- 布隆过滤器
-
- Set
- N的大小
- 删除
- 需求
- 布隆过滤器代码
- 4.海量数据处理面试题
-
- 位图应用
- 布隆过滤器
- 哈希切割
1. unordered系列关联式
区别:
1.unordered_XXX 遍历不按key排序,命名体现
2.unordered_XXX单向迭代器
3.unordered_XXX综合效率略胜map和set
数据重复量比较多的时候,unordered_set更好
重复量比较少的时候,有序的时候,set比较好
2. C++下“hash“的简单模拟实现以及实现中遇见的问题
链接: C++下“hash“的简单模拟实现以及实现中遇见的问题
3.哈希的应用
位图
给40亿个不重复的无符号整数,没排过序。给一个无符号整数,如何快速判断一个数是否在这40亿个数中。
解决:
- 遍历,时间复杂度O(N)
- 排序(O(NlogN)),利用二分查找: logN
- 位图解决
数据是否在给定的整形数据中,结果是在或者不在,刚好是两种状态,那么可以使用一个二进制比特位来代表数据是否存在的信息,如果二进制比特位为1,代表存在,为0代表不存在。比如:
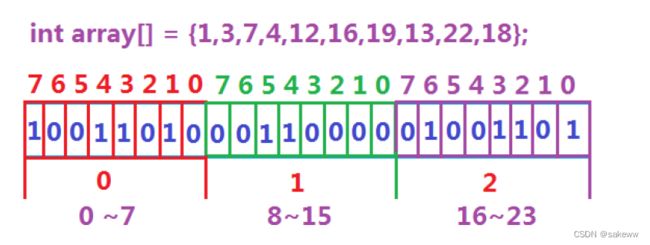
位图概念
所谓位图,就是用每一位来存放某种状态,适用于海量数据,数据无重复的场景。通常是用来判断某个数据存不存在的
优点:节省空间,效率高
局限性:正能处理整数
位图模拟实现
#pragma once
#include 布隆过滤器
一个值映射多个位置
Set
#pragma once
#includeN的大小
删除
不能删除
如果硬要?
每个标记位使用多个比特位,存储引用计数(有几个值映射了当前位置)
也可以对特殊位置增加map存储,
支持删除,整体而言消耗空间变多了,布隆过滤器的优势下降了
需求
数据量大,节省空间,允许误判
举个栗子:
昵称:注册信息的时候,判断昵称有没有人用过?
可以将数据库中的昵称,放到布隆过滤器
在是存在误判的,不在是不存在误判的
昵称判断在的情况下,可以再在数据库中查一下,这样对用户更加负责
垃圾邮件:
每个邮件都有一个发件地址,可以制作一个黑名单,
可以对垃圾邮件进行标记,将其放进布隆过滤器中,
下一封邮件,如果不在布隆过滤器中,那么一定不是垃圾邮件。
利用布隆过滤器减少磁盘IO或者网络请求,因为一旦一个值必定不存在的话,我们可以不用进行后续昂贵的查询请求
布隆过滤器代码
#pragma once
#include4.海量数据处理面试题
位图应用
- 给定100亿个整数,设计算法找到只出现一次的整数?
template<size_t N>
class TwoBitSet
{
public:
void Set(size_t x)
{
if (!_bs1.test(x) && !_bs2.test(x)) // 00 -> 01
{
_bs2.set(x);
}
else if (!_bs1.test(x) && _bs2.test(x)) // 01 -> 10
{
_bs1.set(x);
_bs2.reset(x);
}
// 10 表示已经出现2次或以上,不用处理
}
void PrintOnceNum()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
if (!_bs1.test(i) && _bs2.test(i)) // 01
{
cout << i << endl;
}
}
}
private:
sakeww::bitset<N> _bs1;
sakeww::bitset<N> _bs2;
};
void TestTwoBitSet()
{
int a[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,4,5,6,3,2,1,6};
TwoBitSet<100> bs;
for (auto e : a)
{
bs.Set(e);
}
bs.PrintOnceNum();
}
- 给两个文件,分别有100亿个整数,我们只有1G内存,如何找到两个文件交集?
一个文件中整数,set到一个位图,读取第二个文件中的整数判读在不在位图,再就是交集,不在就不是
缺陷:交集会把重复值找出来,多次出现
改进:
一个文件中整数,set到一个位图bs1,另一个文件中整数,set到一个位图bs2
a.遍历bs2中值,看在不在bs1,在就是交集
b.bs1中的值依次跟bs2中的值与一下,再去看与完是1的位置值就是交集
- 位图应用变形:1个文件有100亿个int,1G内存,设计算法找到出现次数不超过2次的所有整数
用两个位图
出现0:00
出现1:01
出现2:10
出现3及以上:11
布隆过滤器
给两个文件,分别有100亿个query,我们只有1G内存,如何找到两个文件交集?分别给出精确算法和近似算法?
近似算法:将100亿个query放进一个布隆过滤器,另外一个文件在就是交集,不在就不是;
交集里面:存在不是交集的query
精确算法:
(query是字符串,比如是SQL语句,是网络请求url)
假设每个quert是10byte,100亿个query需要100G左右存储空间
哈希切分:
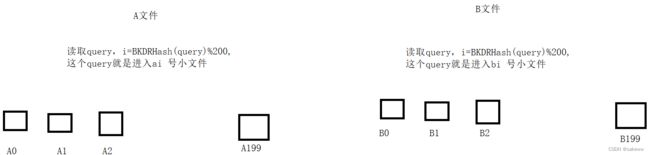
ai和bi小文件找交集就可以
A和B中相同的query一定进入编号相同的小文件
为什么是200?
取决于你有多少内存和 需要多少存储空间,
平均下来100G 切200份,一份500MB ,我们有1G内存,应该是够用的
但是有一些小文件比较大,例如:A123 有1G以上,那么就需要再切分一次,或者切的更多点(增大200)
这个方法还有什么问题?
如果Ai和Bi都太大,超过内存,可以考虑换个哈希算法,在切分一次。
哈希切割
给一个超过100G大小的log file, log中存着IP地址, 设计算法找到出现次数最多的IP地址? 与上题条件相同,如何找到top K的IP?
哈希切分:
依次读取ip,i=BKDRHash(ip)%100
i是多少,ip就进入对应的编号i小文件中
相同的ip一定进入了同一个小文件,那么我们使用map统计一个小文件中的ip的次数,就是它准确的次数
pair
出现次数最多的,top K的IP?
priority_queue
