修改github上yolo源码实现自建数据集的目标检测任务
本项目自建猫狗数据集,搭建Yolov5,实现猫狗检测
一、环境搭建
1.在Anaconda中创建pytorch环境
conda create -n pytorch python=3.82.激活pytorch环境
conda activate pytorch
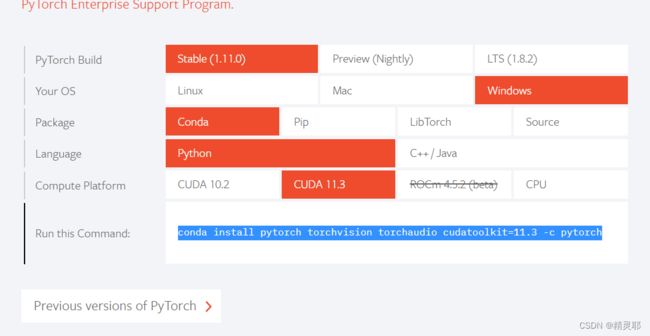
3.进入PyTorch
复制命令,安装支持包
conda install pytorch torchvision torchaudio cudatoolkit=11.3 -c pytorch4.安装pycharmDownload PyCharm: Python IDE for Professional Developers by JetBrains
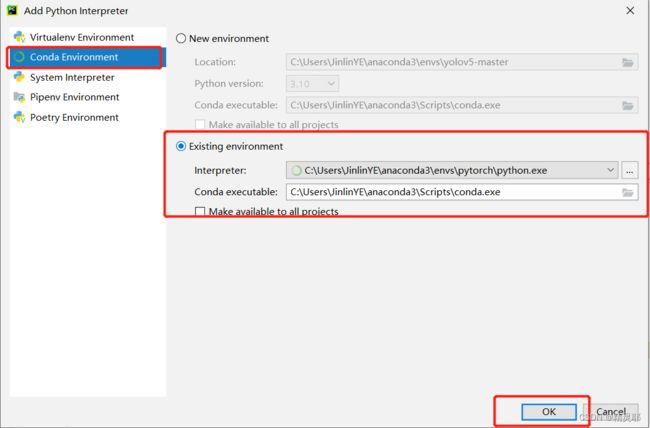
5.在pycharm中创建pytorch环境的工程项目文件
二、数据集制作
采用labelimg进行数据集标注
1.安装labelimg
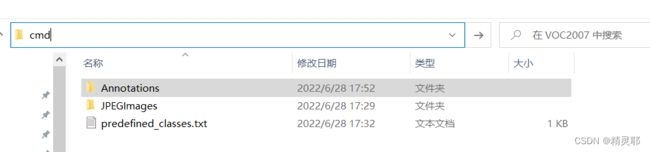
cmd中输入指令
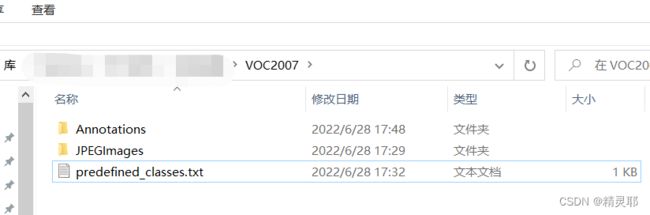
pip install labelimg -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple2.创建数据集文件夹VOC2007并创建子文件
JPEGImages存放需要打标签的图片文件
Annotations存放标注的标签文件
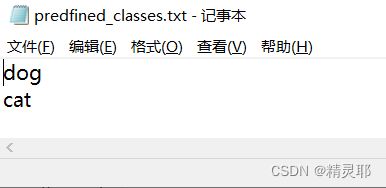
predefined_classes.txt存放类别名称
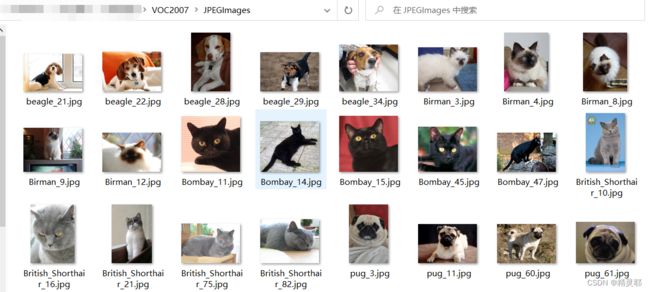
3.在JPEGImages中放入待标注的图片,分别是猫、狗,然后在predefined_classes.txt内输入定义的类别
4.在cmd中进入数据集文件夹目录下打开labelimg
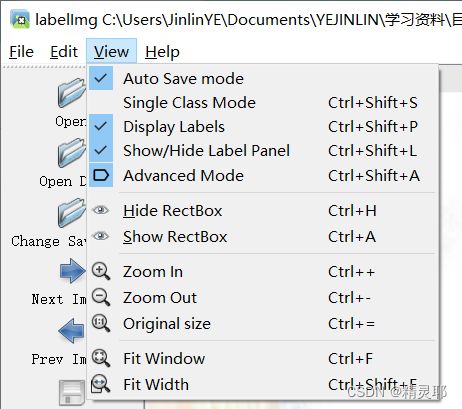
labelimg JPEGImages predefined_classes.txt在view中勾选
Auto Save mode 切换下一张图时自动保存标签
Display Labels 显示标注框和标签
Advanced Mode 标注的十字架一直悬浮在窗口
5.开始标注
三、VOC标签格式转YOLO格式并划分训练集和测试集
1.Yolov5训练所需要的文件格式是yolo(txt)格式的,在此对xml格式的标签文件转换为txt文件,同时训练将数据集按比例划分为训练集和验证集。(注:需要修改标签名称)
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
import random
from shutil import copyfile
#标签名称
classes = ["dog", "cat"]
#80%划分给训练集,20%划分给验证集
TRAIN_RATIO = 80
def clear_hidden_files(path):
dir_list = os.listdir(path)
for i in dir_list:
abspath = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(path), i)
if os.path.isfile(abspath):
if i.startswith("._"):
os.remove(abspath)
else:
clear_hidden_files(abspath)
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return (x, y, w, h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('VOCdevkit/VOC2007/Annotations/%s.xml' % image_id,encoding='UTF-8')
out_file = open('VOCdevkit/VOC2007/YOLOLabels/%s.txt' % image_id, 'w',encoding='UTF-8')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
in_file.close()
out_file.close()
wd = os.getcwd()
wd = os.getcwd()
data_base_dir = os.path.join(wd, "VOCdevkit/")
if not os.path.isdir(data_base_dir):
os.mkdir(data_base_dir)
work_sapce_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "VOC2007/")
if not os.path.isdir(work_sapce_dir):
os.mkdir(work_sapce_dir)
annotation_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "Annotations/")
if not os.path.isdir(annotation_dir):
os.mkdir(annotation_dir)
clear_hidden_files(annotation_dir)
image_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "JPEGImages/")
if not os.path.isdir(image_dir):
os.mkdir(image_dir)
clear_hidden_files(image_dir)
yolo_labels_dir = os.path.join(work_sapce_dir, "YOLOLabels/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolo_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolo_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolo_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "images/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_dir)
yolov5_labels_dir = os.path.join(data_base_dir, "labels/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_dir)
yolov5_images_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, "train/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_train_dir)
yolov5_images_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_images_dir, "val/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_images_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_images_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_images_test_dir)
yolov5_labels_train_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, "train/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_train_dir)
yolov5_labels_test_dir = os.path.join(yolov5_labels_dir, "val/")
if not os.path.isdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir):
os.mkdir(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
clear_hidden_files(yolov5_labels_test_dir)
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_train.txt"), 'w')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_val.txt"), 'w')
train_file.close()
test_file.close()
train_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_train.txt"), 'a')
test_file = open(os.path.join(wd, "yolov5_val.txt"), 'a')
list_imgs = os.listdir(image_dir) # list image files
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probability: %d" % prob)
for i in range(0, len(list_imgs)):
path = os.path.join(image_dir, list_imgs[i])
if os.path.isfile(path):
image_path = image_dir + list_imgs[i]
voc_path = list_imgs[i]
(nameWithoutExtention, extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(image_path))
(voc_nameWithoutExtention, voc_extention) = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(voc_path))
annotation_name = nameWithoutExtention + '.xml'
annotation_path = os.path.join(annotation_dir, annotation_name)
label_name = nameWithoutExtention + '.txt'
label_path = os.path.join(yolo_labels_dir, label_name)
prob = random.randint(1, 100)
print("Probability: %d" % prob)
if (prob < TRAIN_RATIO): # train dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
train_file.write(image_path + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_train_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_train_dir + label_name)
else: # test dataset
if os.path.exists(annotation_path):
test_file.write(image_path + '\n')
convert_annotation(nameWithoutExtention) # convert label
copyfile(image_path, yolov5_images_test_dir + voc_path)
copyfile(label_path, yolov5_labels_test_dir + label_name)
train_file.close()
test_file.close()2.将之前做好的数据集复制到VOCdevkit-VOC2007下的Annotations和JPEGImages中
(注:运行完上述代码后,会建立空的文件,将数据集复制进去后,再次运行文件即可完成转换与划分)
四、利用Yolov5训练目标检测模型
1.在github上下载yolov5源码
GitHub - ultralytics/yolov5 at v5.0
2.pycharm的命令终端中输入如下命令,安装依赖包
pip install -r requirements.txt3.将数据集(VOCdevkit文件)复制到工程文件中
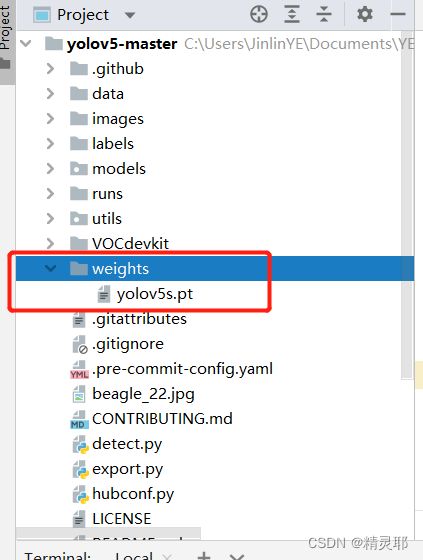
4.在下载预训练权重,以yolov5s.pt为例,下载后放入weights文件中
Releases · ultralytics/yolov5 · GitHub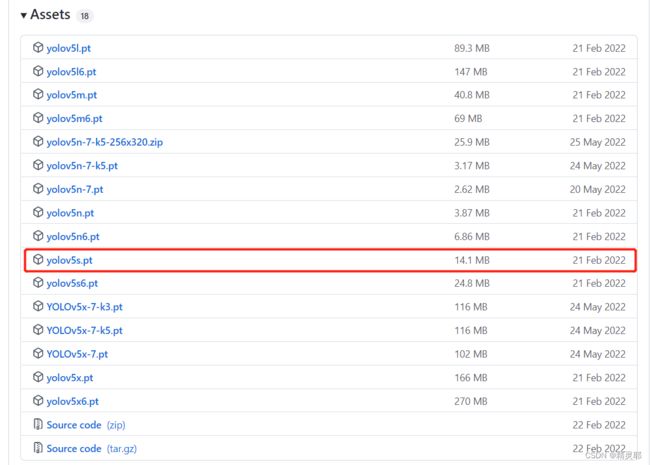
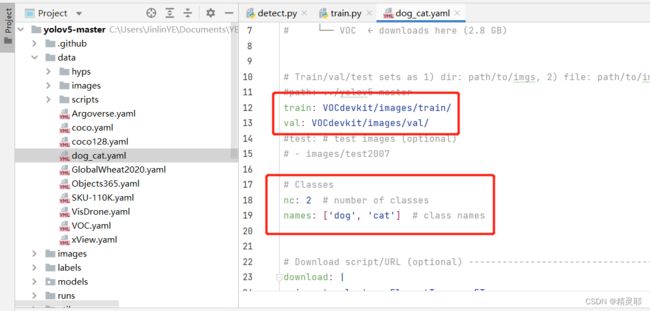
5.修改data目录下的yaml文件
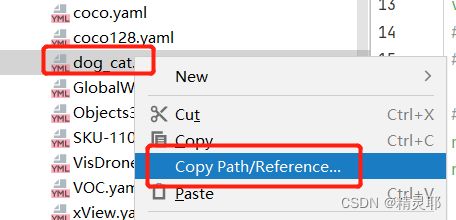
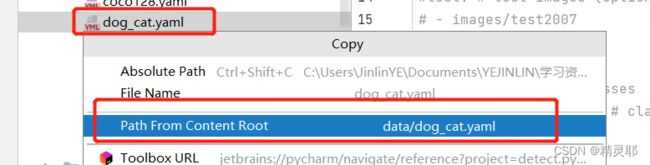
复制VOC.yaml文件,将复制后的文件重命名为dog_cat.yaml,之后对dog_cat.yaml中的参数进行修改(路径修改方式如下)
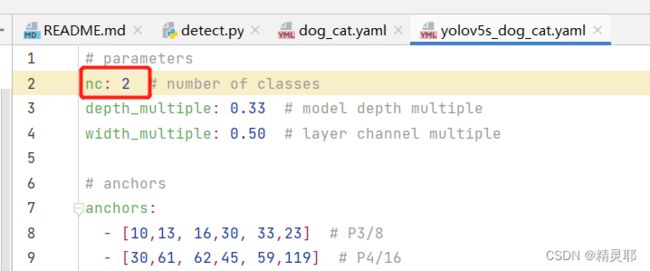
6.修改models下的yaml文件
复制yolov5s.yaml文件,将复制后的文件重命名为yolo5s_dog_cat.yaml,之后对yolo5s_dog_cat.yaml中的参数进行修改
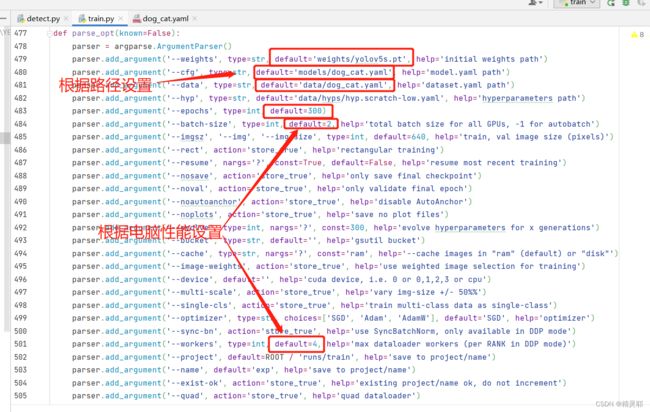
7.修改train.py中的参数后运行train.py
(注:遇到“页面文件太小,无法完成操作”的红字不用管,只要程序在运行,等待一会就会开始训练)
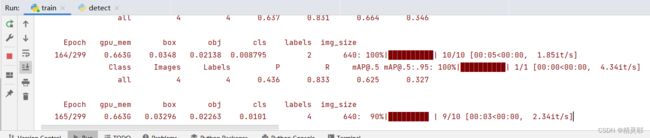
可以通过如下命令查看训练参数
tensorboard --logdir=runs/train # 训练过程中查看参数
tensorboard --logdir=runs # 训练完查看参数
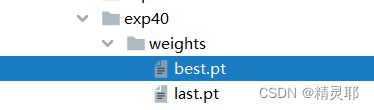
8.训练完成后,最佳参数保存在runs-train-exp40-weights中
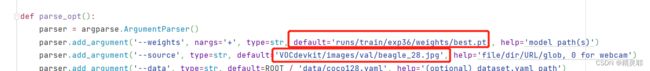
9.修改detect.py中参数并运行
(注:以照片为例进行预测)
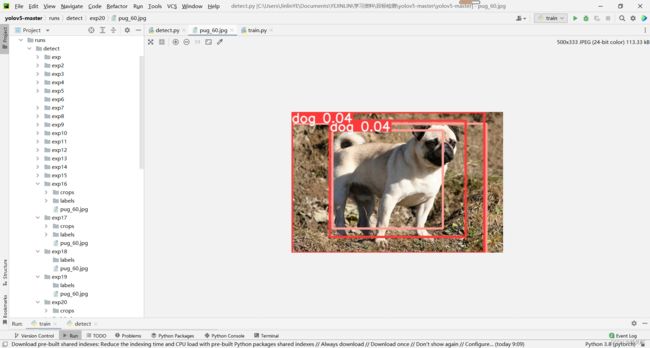
10.检测结果保存在runs-detect-exp20中
(注:由于本实例只演示操作,数据集很少,训练轮数也很少,所以精度很低,调小detect.py中的置信度参数,如果不调可能无法框出预测结果)