一、SpringBoot高级之缓存
Table of Contents
一、Spring缓存抽象
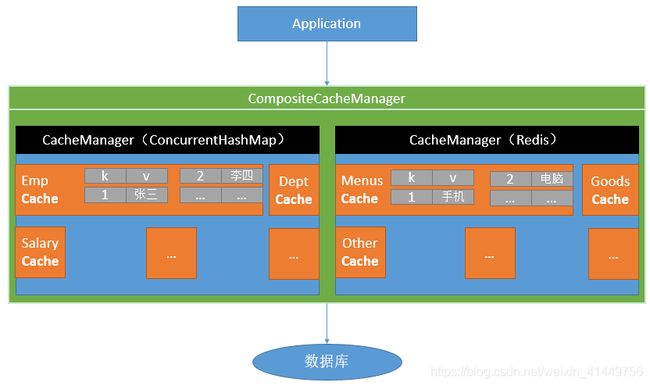
1、原理:CacheManager按照名字得到cache缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
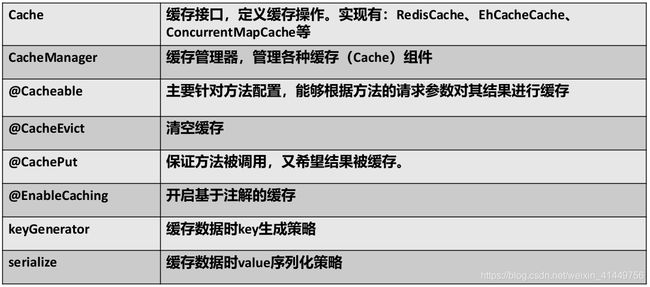
2、几个重要概念&缓存注解
二、缓存使用
1、步骤
2、实例
三、整合redis实现缓存
1、引入依赖
2. 在配置文件中配置redis连接地址
3. 使用RestTemplate操作redis
4、自定义CacheManager
一、Spring缓存抽象
1、原理:CacheManager按照名字得到cache缓存组件来实际给缓存中存取数据
2、几个重要概念&缓存注解
二、缓存使用
1、步骤
1、引入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
2、@EnableCaching开启缓存
/**
* 一、快速体验缓存
* 步骤:
* 1、开启基于注解的缓存 @EnableCaching
* 2、标注缓存注解
* @Cacheable
* @CacheEvict
* @CachePut
* 默认使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager==ConcurrentMapCache;将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中
* 开发中使用缓存中间件:redis、memcached、ehcache;
*/
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.zm.mapper")
public class Springboot01CacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01CacheApplication.class, args);
}
}3、使用缓存注解
@Cacheable、@CacheEvict、@CachePut
package com.zm.service.impl;
import com.zm.bean.Department;
import com.zm.mapper.DepartmentMapper;
import com.zm.service.IDepartmentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "dept")
@Service
public class DepartmentServiceImpl implements IDepartmentService {
@Autowired
private DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@Cacheable(value = "dept")
@Override
public Department getDept(Integer id) {
return departmentMapper.getDept(id);
}
}
4、切换为其他缓存(redis)
2、实例
1、代码展示
package com.zm.config;
import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Configuration
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean("myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return (o, method, objects) -> method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(objects).toString() + "]";
}
}
package com.zm.service.impl;
import com.zm.bean.Employee;
import com.zm.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.zm.service.IEmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "emp") // 统一指定Cache组件
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements IEmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
/**
* 将方法的运行结果进行缓存;以后再要有相同的数据,就直接从缓存中获取,不用调用方法
* CacheManager管理多个Cache组件的,对缓存的真正CRUD操作在cache组件中,每一个缓存组件都有自己唯一的一个名字;
* 几个属性:
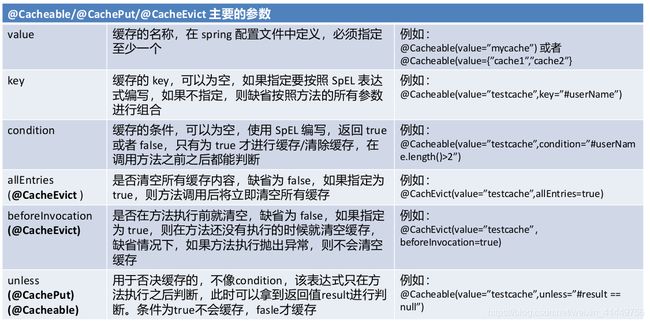
* cacheNames/value 指定缓存组件的名字;指定将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,以数组的方式,可以指定多个缓存
* key:缓存数据使用的key:可以用它来指定。默认使用方法参数的值;缓存的数据默认是以键值对形式存储的
* 编写SpEl:#id(参数id的值) #root.args[0]/#a0/#p0(第一个参数,0代表参数的索引)
* keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
* key/keyGenerator:二选一
* cacheManager:指定缓存管理器与cacheResolver类似
* condition:指定符合调节的情况下才缓存: condition = "#id>0"
* unless:否定缓存,当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值不会缓存:unless = "#result==null"
* sync:是否使用异步
* 原理:
* 1、自动配置类:CacheAutoConfiguration
* 2、缓存的配置类:
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration
* org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
* 3、哪个配置类默认会生效:SimpleCacheConfiguration
* 4、给容器中注册了一个CacheManager:ConcurrentMapCacheManager
* 5、可以获取创建和创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的组件;他的作用是将数据保存到ConcurrentMap中
* @Cacheable 运行流程:
*
* 1、运行之前,先查看Catch(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的位置获取;
* (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存组件),第一次没有获取到,会创建缓存组件
* 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
* key按照某种策略生成,默认是使用KeyGenerator生成的,默认使用的是SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;
* SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的策略:
* 如果没有参数:key= new SimpleKey()
* 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
* 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params)
* 3、没有查找到缓存就调用目标方法;
* 4、将目标方法的返回结果放进缓存中
* @Cacheable标注的方法之前先检查缓存中是否有数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存, 如果没有就运行目标方法,并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就直接从缓存中获取
* 核心:
* 1、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到cache【CurrentMapCache】组件
* 2、key使用KeyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleGenerator
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"emp"})
public Employee getEmp(Integer id) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
}
/**
* @CachePut:即调用方法,又更新缓存数据; 修改数据库的某个数据,同事更新缓存
* 运行时机:
* 1、先调用目标方法
* 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来
* 测试:
* 1、查询1号员工,查到的结果会放到缓存中
* 2、以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3、更新1号员工:
* 将方法的返回值也存入到缓存:要达到查询的结果是最新的需要查询的key和更新的key要一致
* 4、查询1号员工?
* 应该是更新后的员工信息
* key="#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
* key="#result.id":使用返回后的id
* @Cacheable的key是不能使用#result.id的:因为@Cacheable方法还未运行之前就要得到key去缓存中查找
*/
@CachePut(key = "#employee.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
/**
* @CacheEvict:缓存清除 key:指定要清除的数据
* allEntries=true:会清空当前缓存中间中的所有数据
* beforeInvocation=false(默认值):在方法执行之后清除缓存,出错了就不会清空缓存
*/
@CacheEvict(key = "#id")
public void deleteEmp(Integer id) {
System.out.println("deleteEmp" + id);
}
/**
* Caching给一个函数添加多种缓存模式
*
* @CachePut标注的目标函数不管有没有缓存都会被调用
*/
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(key = "#last_name")
},
put = {
@CachePut(key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String last_name) {
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(last_name);
}
}
2、原理分析
1)自动配置类CacheAutoConfiguration默认导入的缓存的配置类
默认生效的是哪一个可以在配置文件中指定:debug=true,查看--->SimpleCacheConfiguration
2、缓存分析
1)SimpleCacheConfiguration会注册一个ConcurrentMapCacheManager(CacheManager管理器)
2)ConcurrentMapCacheManager类
@Nullable// 根据Cache组件的名称获取Cache组件
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized(this.cacheMap) {
cache = (Cache)this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
// 没有就创建组件
cache = this.createConcurrentMapCache(name);
// 将组件存入管理器
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
protected Cache createConcurrentMapCache(String name) {
SerializationDelegate actualSerialization = this.isStoreByValue() ? this.serialization : null;
return new ConcurrentMapCache(name, new ConcurrentHashMap(256), this.isAllowNullValues(), actualSerialization);
}3)ConcurrentMapCache类
// 创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的组件
protected ConcurrentMapCache(String name, ConcurrentMap store, boolean allowNullValues, @Nullable SerializationDelegate serialization) {
super(allowNullValues);
Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null");
Assert.notNull(store, "Store must not be null");
this.name = name;
this.store = store;
this.serialization = serialization;
}
@Nullable
// 根据key获取值
protected Object lookup(Object key) {
return this.store.get(key);
}
// 将值以k-v的形式存入到缓存中
// store的类型为:private final ConcurrentMap store;
public void put(Object key, @Nullable Object value) {
this.store.put(key, this.toStoreValue(value));
} 4)CacheAspectSupport生成key
@Nullable
// 使用keyGenerator生成key
protected Object generateKey(@Nullable Object result) {
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.metadata.operation.getKey())) {
EvaluationContext evaluationContext = this.createEvaluationContext(result);
return CacheAspectSupport.this.evaluator.key(this.metadata.operation.getKey(), this.metadata.methodKey, evaluationContext);
} else {
return this.metadata.keyGenerator.generate(this.target, this.metadata.method, this.args);
}
}三、整合redis实现缓存
1、引入依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
当引入了redis依赖,RedisCacheConfiguration就会起作用
2. 在配置文件中配置redis连接地址
spring.redis.host=localhost3. 使用RestTemplate操作redis
Redis常见的五大数据类型
String、List、Set、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set 无序集合]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet 有序集合]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash 散列]4、自定义CacheManager
让对象以json字符串的形式存储在redis数据库中
package com.zm.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer