代码随想录算法训练营第四天|24. 两两交换链表中的节点 19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点 面试题02.07. 链表相交 142.环形链表II
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
给你一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后链表的头节点。你必须在不修改节点内部的值的情况下完成本题(即,只能进行节点交换)。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[2,1,4,3]
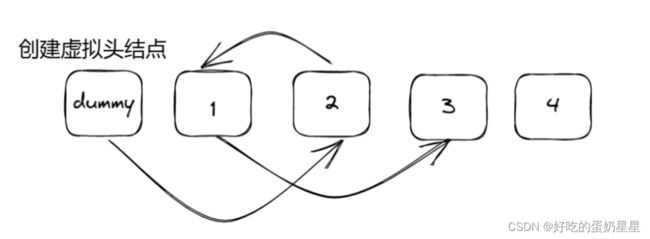
通过设置虚拟头结点,个节点的指向如下
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode cur=dummy;
while(cur.next!=null&&cur.next.next!=null){
ListNode temp=cur.next.next.next;
ListNode fristnode=cur.next;
ListNode secondnode=cur.next.next;
cur.next=secondnode;
secondnode.next=fristnode;
fristnode.next=temp;
cur=fristnode;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}
这里可以多设置几个temp等节点,可以防止在节点变换过程中发生的改变,这样更加方便快捷。
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第
n**个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
思路1:首先要确定列表的size,然后index=size-n,之后按照index索引去删除即可
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
//1.判断链表的长度size
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode temp=head;
int size=0;
while(cur!=null){
size++;
cur=cur.next;
}
int index=size-n;
//删除第一个数headsize为2
if(index==0){
return head=head.next;
}
//head的size为1
if(size==1&&n==1){
return head=head.next;
}
for(int i=0;i这个方法思考起来不难,但是有几处细节需要考虑到
思路2:虚拟头结点+双指针
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy=new ListNode(0,head);
ListNode fastindex=dummy;
ListNode lowindex=dummy;
for(int i=0;i- 设置虚拟头结点dummy和快慢指针节点
- 让快指针走n+1步
- 再让快慢指针一同去走,当快指针走到最后一个节点即
fastindex.next==null时慢指针的后一个节点就是需要删除的 - 删除慢指针的后一个节点即可
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
给你两个单链表的头节点
headA和headB,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回null。
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at '8'
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
这道题仍然是要求善用双指针的方法
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode tempA=headA;
ListNode tempB=headB;
int sizeA=0;
int sizeB=0;
//1.求headA的长度
while(tempA!=null){
tempA=tempA.next;
sizeA++;
}
//2.求headB的长度
while(tempB!=null){
tempB=tempB.next;
sizeB++;
}
//3.让curA称为最长链表的头
if(sizeB>sizeA){
int temp=sizeA;
sizeA=sizeB;
sizeB=temp;
ListNode tempNode=headA;
headA=headB;
headB=tempNode;
}
//4.求长度差
int gap=sizeA-sizeB;
//5.两个链表处于相同节点出发
while (gap-->0){
headA=headA.next;
}
while (headA!=null){
if(headA==headB){
return headA;
}
headA=headA.next;
headB=headB.next;
}
return null;
}
}
- 分别求出headA和headB链表的长度为sizeA和sizeB
- 让链表headA为最长的链表,所以判断是否满足,不满足就交换链表和size大小
- 求出sizeA和sizeB的长度差
- 让headA先走gap步,让两个链表位于相同的出发点
- 遍历剩下的链表节点并判断链表是否相同,相同返回headA,不同返回null
142.环形链表II
给定一个链表的头节点
head,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回null。
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:返回索引为 1 的链表节点
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
首先需要判断是否有环:
定义两个指针fast和slow,让fast每次走两个节点,slow每次走一个节点,如果有环则fast和slow在环内相遇
其次判断入环节点:
定义两个指针index1,index2让index1从相遇节点出发,index从头节点出发,每次走一步则index1,index会在入环处相遇
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode fastNode=head;
ListNode slowNode=head;
while(fastNode!=null&&fastNode.next!=null){
fastNode=fastNode.next.next;
slowNode=slowNode.next;
if(slowNode==fastNode){
ListNode index1=fastNode;
ListNode index2=head;
while(index1!=index2){
index1=index1.next;
index2=index2.next;
}
return index1;
}
}
return null;
}
}