日撸 Java 三百行day17-20
文章目录
- 说明
- day17 链队列
-
- 1. 链队列特点
- 2. 图示
- day18 循环队列
-
- 1. 循环队列特点
- 2. 取模
- 3.代码
- day19 字符串匹配
-
- 1. 思路
- 2. 代码
- day20 小结
-
- 1.面向对象与面向过程相比, 有哪些优势?
- 2.比较顺序表和链表的异同;分析顺序表和链表的优缺点
- 3.分析调拭程序常见的问题及解决方案
- 4. 分析链队列与循环队列的优缺点.
- 5. 是否合理
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day17 链队列
1. 链队列特点
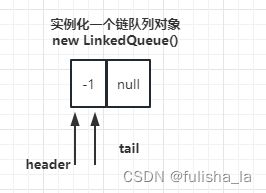
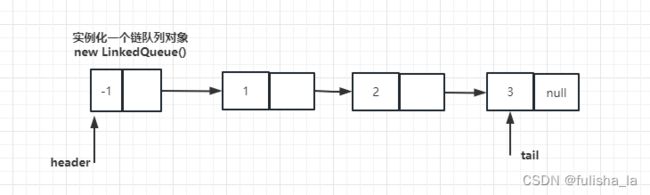
队列相比于栈,它是两端都可以操作,但队头只能进行出队列,队尾只能进行入队列(就像生活中的排队买东西一样)在删除队列时,需要判断队列是否为空(如下代码:header.next == null)。当对头(header)和队尾(tail)指向同一个节点时,则队列为空 ,所以空队列也需要一个节点
2. 图示
package datastructure.queue;
public class LinkedQueue {
class Node{
/**
* The data
*/
int data;
/**
* The reference to the next node
*/
Node next;
/**
* The constructor
* @param paraValue The data
*/
public Node(int paraValue){
data = paraValue;
next = null;
}
}
/**
* The header of the queue
*/
Node header;
/**
* The tail of the queue
*/
Node tail;
/**
* Construct an empty sequential list.
*/
public LinkedQueue(){
header = new Node(-1);
tail = header;
}
/**
* Enqueue
* @param paraValue The value of the new node.
*/
public void enqueue(int paraValue){
Node tempNode = new Node(paraValue);
tail.next = tempNode;
tail = tempNode;
}
/**
* Dequeue
* @return The value at the header.
*/
public int dequeue(){
if (header == tail){
System.out.println("No element in the queue");
return -1;
}
int resultValue = header.next.data;
header.next = header.next.next;
// The queue becomes empty.
if (header.next == null){
tail = header;
}
return resultValue;
}
/**
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* @return
*/
@Override
public String toString(){
String resultString = "";
if (header.next == null){
return "empty";
}
Node tempNode = header.next;
while (tempNode != null){
resultString += tempNode.data + ", ";
tempNode = tempNode.next;
}
return resultString;
}
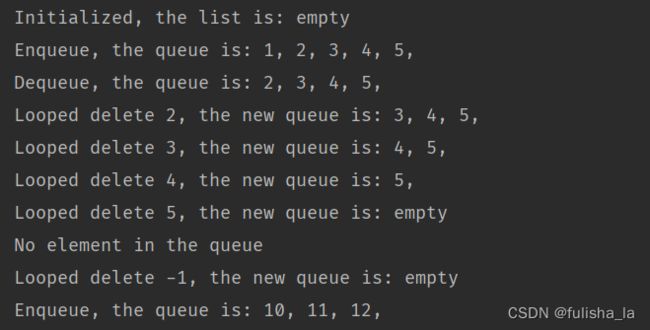
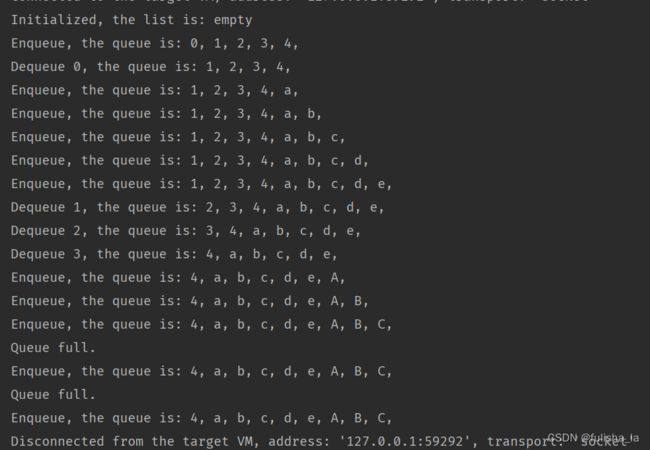
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedQueue tempQueue = new LinkedQueue();
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 1);
}
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
int tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Looped delete " + tempValue + ", the new queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 10);
}
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
}
day18 循环队列
1. 循环队列特点
-
用图去理解代码,循环队列我觉得一定要结合图去理解是容易的。入队时判断队是否已满再入队(顺序:先入值再修改指针);出队时判断队是否为空再出队(顺序:先出值再修改指针)
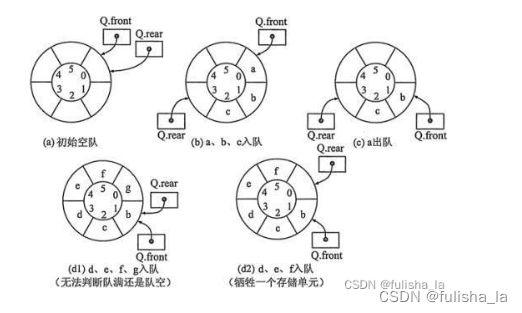
-
队空 对满的判定条件
(1)队满:(rear + 1) % MAX_SIZE = front;
(2)队空:front = rear
这里的队满判断是牺牲了一个空间,还有其他方式也是可以判断队满的。
2. 取模
我们可以从链队列可以看出,出队头指针加1,入队尾指针加1,头/尾指针不做任何处理,则会一直无限制向上加,会导致空间浪费。通过取模运行,就可以避免上述的问题,循环队列最大长度假设只有MAX_SIZE=10,取模则可以使头/尾指针做循环,进而空间最大化的使用。
3.代码
package datastructure.queue;
public class CircleIntQueue {
/**
* The total space. One space can never be used.
*/
public static final int TOTAL_SPACE = 10;
int[] data;
/**
* The index for calculating the head. The actual head is head % TOTAL_SPACE.
*/
int head;
/**
* The index for calculating the tail.
*/
int tail;
public CircleIntQueue(){
data = new int[TOTAL_SPACE];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}
/**
* enqueue
* @param paraValue The value of the new node.
*/
public void enqueue(int paraValue){
if ((tail+1)%TOTAL_SPACE == head){
System.out.println("Queue full.");
return;
}
data[tail%TOTAL_SPACE] = paraValue;
tail++;
}
public int dequeue(){
if (head == tail){
System.out.println("No element in the queue");
return -1;
}
int resultValue = data[head%TOTAL_SPACE];
head++;
return resultValue;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
String resultString = "";
if (head == tail){
return "empty";
}
for (int i = head; i < tail; i++){
resultString += data[i%TOTAL_SPACE] + ", ";
}
return resultString;
}
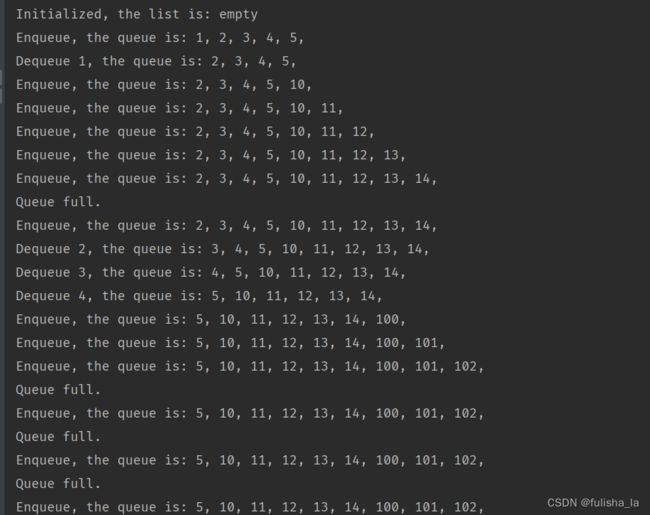
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleIntQueue tempQueue = new CircleIntQueue();
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 1);
}
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
int tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 10);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i + 100);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
}
}
字符类型:
package datastructure.queue;
public class CircleCharQueue {
public static final int TOTAL_SPACE = 10;
char[] data;
int head;
int tail;
/**
* The constructor
*/
public CircleCharQueue() {
data = new char[TOTAL_SPACE];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}
/**
* Enqueue.
* @param paraValue The value of the new node.
*/
public void enqueue(char paraValue) {
if ((tail + 1) % TOTAL_SPACE == head) {
System.out.println("Queue full.");
return;
}
data[tail % TOTAL_SPACE] = paraValue;
tail++;
}
/**
* Dequeue
* @return The value at the head.
*/
public char dequeue() {
if (head == tail) {
System.out.println("No element in the queue");
return '\0';
}
char resultValue = data[head % TOTAL_SPACE];
head++;
return resultValue;
}
/**
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
* @return
*/
@Override
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
if (head == tail) {
return "empty";
}
for (int i = head; i < tail; i++) {
resultString += data[i % TOTAL_SPACE] + ", ";
}
return resultString;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
CircleCharQueue tempQueue = new CircleCharQueue();
System.out.println("Initialized, the list is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (char i = '0'; i < '5'; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i);
}
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
char tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
for (char i = 'a'; i < 'f'; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
tempValue = tempQueue.dequeue();
System.out.println("Dequeue " + tempValue + ", the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
for (char i = 'A'; i < 'F'; i++) {
tempQueue.enqueue(i);
System.out.println("Enqueue, the queue is: " + tempQueue.toString());
}
}
}
day19 字符串匹配
1. 思路
字符串匹配,将子串和主串进行匹配。若子串和主串不匹配,则主串从下一个字符开始与子串重新开始匹配,直到多次匹配结束都无匹配则返回不匹配有则返回地址。这样两个串的“指针”都要回溯。若用KMP,则只需要回溯子串指针。
2. 代码
package main.java.datastructure;
import sun.applet.Main;
import java.time.Year;
public class MyString {
/**
* The maximal length.
*/
public static final int MAX_LENGTH = 10;
/**
* The actual length.
*/
int length;
/**
* The data.
*/
char[] data;
/**
* Construct an empty char array.
*/
public MyString(){
length = 0;
data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
}
/**
*Construct using a system defined string.
* @param paraString The given string. Its length should not exceed MAX_LENGTH - 1.
*/
public MyString(String paraString){
data = new char[MAX_LENGTH];
length = paraString.length();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
data[i] = paraString.charAt(i);
}
}
public String toString(){
String resultString = "";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++){
resultString += data[i];
}
return resultString;
}
/**
* Locate the position of a substring.
* @param paraString The given substring.
* @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
*/
public int locate(MyString paraString){
boolean tempMatch = false;
for (int i = 0; i < length - paraString.length + 1; i++){
tempMatch = true;
for (int j = 0; j < paraString.length; j++){
if (data[i+j] != paraString.data[j]){
tempMatch = false;
break;
}
}
if (tempMatch){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
/**
* Get a substring
* @param paraStartPosition The start position in the original string.
* @param paraLength The length of the new string.
* @return The first position. -1 for no matching.
*/
public MyString substring(int paraStartPosition, int paraLength){
if (paraStartPosition + paraLength > length){
System.out.println("The bound is exceeded.");
return null;
}
MyString resultMyString = new MyString();
resultMyString.length = paraLength;
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++){
resultMyString.data[i] = data[paraStartPosition + i];
}
return resultMyString;
}
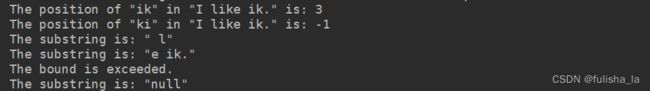
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyString tempFirstString = new MyString("I like ik.");
MyString tempSecondString = new MyString("ik");
int tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempSecondString);
System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempSecondString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
+ "\" is: " + tempPosition);
MyString tempThirdString = new MyString("ki");
tempPosition = tempFirstString.locate(tempThirdString);
System.out.println("The position of \"" + tempThirdString + "\" in \"" + tempFirstString
+ "\" is: " + tempPosition);
tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(1, 2);
System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 5);
System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
tempThirdString = tempFirstString.substring(5, 6);
System.out.println("The substring is: \"" + tempThirdString + "\"");
}
}
day20 小结
1.面向对象与面向过程相比, 有哪些优势?
面向过程我们主要放在操作步骤上,如之前写的“矩阵相加”,而这个类主要就是完成一个功能及如何完成矩阵相加,MatrixAddition
面向对象:例如之前写了一个链表类,我们把链表类抽象为一个类对象,在这个对象有自己的变量和方法,实现了查找,插入,删除等功能,当我想用其中任何一个方法,我可以通过对象去调用,当我想用另一个方法时,发现没有,我可以去对象中加,以后也可以复用方法。
所以面向对象更容易扩展修改,更容易模块化,减少代码的冗余。
2.比较顺序表和链表的异同;分析顺序表和链表的优缺点
(1)顺序表在定义时需要预先分配空间,顺序表在插入和删除时,需要遍历顺序表且需要移动元素;链表在定义时不需要预先分配空间,可以动态分配而链表在插入时只需要改变他的指针指向
(2)查找数据,对于顺序表(通过数组来标识),只要给出查找位置,直接可以定位到数据,查找方便 但增删很慢。对于链表,必须要从头节点开始查找,查找慢;但增删快。
3.分析调拭程序常见的问题及解决方案
(1) 空指针异常 在写代码过程中,对可能出现为空的要对代码多加一层为空的判断保护代码。例如数组已为null,还要去取数据;对象为null还要去取对象某个值。
(2)数组越界异常 在初始化数组,对长度的定义要合适并且要在有数组进行增删是要多一层判断数组成都操作
4. 分析链队列与循环队列的优缺点.
相比于链队列,循环队列对空间利用率更大,删除后的元素空间还可以再利用,但循环队列大小是提前定义好了,不像链队列能动态增加。
5. 是否合理
第 18 天建立的两个队列, 其区别仅在于基础数据不同, 一个是 int, 一个是 char. 按这种思路, 对于不同的基础数据类型, 都需要重写一个类, 这样合理吗? 你想怎么样
这样不合理,不满足面向对象思想。可以使用泛型。但我使用Object类型来实现,因为Object类是所以类的超类,并试用int和char类型都可以满足,但正因为Object类任何类型都能接收,可能会在运行中出现bug。
public static final int TOTAL_SPACE = 10;
Object[] data;
//The index for calculating the head
int head;
//The index for calculating the tail
int tail;
public CircleQueue () {
data = new Object[TOTAL_SPACE];
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}