有序序列查找-斐波那契查找(Fibonacci Search)
有序序列查找-斐波那契查找(Fibonacci Search)
- 前言
如果数组为有序表或有序数列,查找函数可以采用斐波那契查找实现。斐波那契查找与折半查找(二分查找)的最大区别是,斐波那契查找函数对有序表进行分对称分割,而折半查找则是对有序表进行对对称分割;另外斐波那契查找的位置确定仅涉及到加减运损,而折半查找则涉及到除法运算;研究表明斐波那契搜索在后续步骤中检查相对接近的元素,因此,当输入数组很大,无法放入 CPU 缓存甚至 RAM 时,斐波那契搜索会派上用场。
斐波那契查找本质上是对有序表进行分而治之,先对原来数组进行分裂处理,进而找到待查找元素所属的子区间,后面反复进行处理,直至找到查询的对象或查询失败。
- 算法分析
算法的关键是找到合适的分割点,这些分割点隶属于某个斐波那契数,所以问题转化为,每次分治前,需要寻找到合适的斐波那契数字。为了查询方便,我们可以引入Fib数组,这个数组中储存的最大斐波那契数字恰好大于数组中元素的个数,也就是Fib[u]>n,其中u为的最小的下标值,定义u为查询问题中Fib数组的上界(upper bound)。
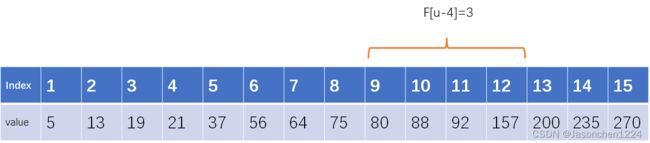
先看一个具体的例子,给定有序数列,数列中包含15个元素,并且元素为有序递增排列。
在此条件下,我们就要寻找斐波那契数字,斐波那契的值需要大于15的最小值,显而易见21为我们需要搜索的具体值,上界下标的值(upper bound)u等于7。
假定要寻找目标数字等于88,第一个分割点位置为low+F[u-1],那么其左边元素个数不超过F[u-2],右半部分元素数量不超过F[u-3],由于右半部分的分割点的值可能大于最高点位置,所以mid在这里就需要取low+F[u-1]-1和high之间的最小值,确保mid值不越界。
- 搜索过程
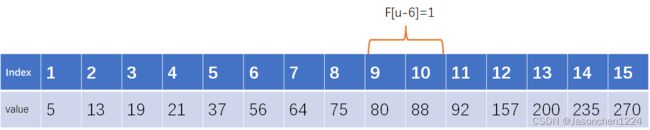
假定搜索目标为88,那么第一次分割,选择左半部分,继续搜索,
第二次分割后,88属于右半部分,
第三次分割后,88属于左半部分,
此时mid=10,所以查询结束。
- 代码实现
代码的数据结构参考清华大学严蔚敏的《数据结构(C语言版)》的基本数据类型,利用这些数据类型构建查询表(Search Table),构造数据类型过程中利用到文件指针的相关知识,在此不再赘述。
代码分为三个关键函数,第一部分是寻找斐波那契的下标的上界值和构建斐波那契数组:
第一部分为头文件定义
/**
* @file Fib_search.h
* @author your name ([email protected])
* @brief
* @version 0.1
* @date 2023-04-08
*
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
*
*/
#ifndef FIB_SEARCH_H
#define FIB_SEARCH_H
#include 第二部分关键函数的实现
/**
* @file Fib_search.c
* @author your name ([email protected])
* @brief
* @version 0.1
* @date 2023-04-08
*
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
*
*/
#ifndef FIB_SEARCH_C
#define FIB_SEARCH_C
#include "Fib_search.h"
void CreateTable(FILE *fp, SSTable *st)
{
int n;
char str[MAX_LEN];
int i;
n=0;
// 当读取 (n-1) 个字符时,或者读取到换行符时,或者到达文件末尾时,它会停止,具体视情况而定。
while(fgets(str,MAX_LEN,fp)!=NULL)
{
n++;
}
fseek(fp,0,SEEK_SET);
st->len=n;
st->elem=(SElemType *)malloc(sizeof(SElemType)*(n+1));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
st->elem[i].value=(Record)malloc(sizeof(char)*MAX_LEN);
memset(st->elem[i].value,0,sizeof(char)*MAX_LEN);
fscanf(fp,"%d %s",&(st->elem[i].key),st->elem[i].value);
}
return;
}
int find_upper_bound(SSTable st, int **fib)
{
int n;
int u;
int i;
int max_num=10;
int dp[max_num];
dp[0]=1;
dp[1]=1;
n=st.len;
for(i=2;i<max_num;i++)
{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
if(dp[i]>n)
{
break;
}
}
*fib=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*(i+1));
memcpy(*fib,dp,sizeof(int)*(i+1));
return i;
}
int fib_search_iteration(SSTable st, KeyType key, int u, int *fib)
{
int low;
int high;
int mid;
int index;
low=1;
high=st.len;
index=u-1;
while(low<=high && index>=0)
{
mid=min(low+fib[index]-1,high);
// 1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34
if(EQ(key,st.elem[mid].key))
{
return mid;
}
else if (LT(key, st.elem[mid].key))
{
high=mid-1;
index=index-1;
}
else
{
low=mid+1;
index=index-2;
}
}
if (low==high && EQ(key, st.elem[low].key) && index <0)
{
return low;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
int min(int a, int b)
{
return (a<b?a:b);
}
#endif
第三部分为测试函数
/**
* @file Fib_search_main.c
* @author your name ([email protected])
* @brief
* @version 0.1
* @date 2023-04-08
*
* @copyright Copyright (c) 2023
*
*/
#ifndef FIB_SEARCH_MAIN_C
#define FIB_SEARCH_MAIN_C
#include "Fib_search.c"
int main(void)
{
FILE *fp;
KeyType key_1=88;
KeyType key_2 = 85;
SSTable st;
int u;
int index_1;
int index_2;
int *fib;
fp=fopen("data.txt","r");
CreateTable(fp,&st);
// 1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34
u=find_upper_bound(st,&fib);
index_1=fib_search_iteration(st,key_1,u,fib);
//index_2=fib_search_recursion(1,st.len,st,key_1,u,fib);
printf("The index is %d and %d\n",index_1,index_2);
getchar();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
data.txt文件
5 fox
13 the
19 jump
21 out
37 box
56 it
64 looks
75 very
80 sad
88 do
92 feel
157 good
200 bad
235 june
270 nice
- 小结
通过本问题的分析,对斐波那契搜索方法有了更进一步的认识,同时理解斐波那契搜索为非对称搜索,在过程中可能产生越界,处理越界称为本搜索问题的关键。
参考资料:
- Fibonacci Search - GeeksforGeeks