HBase 教程(超详细)
文章目录
- 1. HBase 简介
-
- 1.1 HBase 定义
- 1.2 HBase 背景
- 1.3 HBase 数据模型
-
- 1.3.1 HBase 逻辑结构
- 1.3.2 HBase 物理存储结构
- 1.3.3 数据模型
- 1.4 HBase 基本架构
- 2. HBase 快速入门
-
- 2.1 HBase 官网地址
- 2.2 HBase 安装流程
- 2.3 HBase Shell 操作
-
- 2.3.1 基本操作
- 2.3.2 表的操作
- 2.3.3 命名空间的基本操作
- 3. HBase 进阶
-
- 3.1 架构原理
- 3.2 读流程
- 3.3 MemStore Flush
- 3.4 读流程
- 3.5 StoreFile Compaction
- 3.6 Region Split
- 4. HBase API 操作
-
- 4.1 环境准备
- 4.2 HBase API
-
- 4.2.1 Hbase 的连接与断开
- 6.2.2 判断表是否存在
- 4.2.3 创建表
- 4.2.4 删除表
- 4.2.5 创建命名空间
- 4.2.6 向表中插入数据
- 4.2.7 删除多行数据
- 4.2.8 全表扫描
- 4.2.9 获取指定 rowKey 的数据
- 4.2.10 获取指定“列族:列”的数据
- 4.3 MapReduce
-
- 4.3.1 官方 HBase-MapReduce
- 4.3.2 自定义 HBase-MapReduce1
- 4.3.3 自定义 HBase-MapReduce2
- 4.4 与 Hive 集成
-
- 4.4.1 HBase 与 Hive 对比
- 4.4.2 HBase 与 Hive 集成使用
- 5. HBase 优化
-
- 5.1 高可用
- 5.2 预分区
- 5.3 RowKey 设计
- 5.4 内存优化
- 5.5 基础优化
1. HBase 简介
1.1 HBase 定义
HBase 是一种分布式、可扩展、支持海量数据存储的 NoSQL 数据库。
1.2 HBase 背景
HBase 的原型是 Google 的 BigTable 论文,受到了该论文思想的启发,目前作为 Hadoop的子项目来开发维护,用于支持结构化的数据存储。
- 2006 年 Google 发表 BigTable 白皮书
- 2006 年开始开发 HBase
- 2008 年北京成功开奥运会,程序员默默地将 HBase 弄成了 Hadoop 的子项目
- 2010 年 HBase 成为 Apache 顶级项目
- 现在很多公司二次开发出了很多发行版本
HBase 是一个高可靠性、高性能、面向列、可伸缩的分布式存储系统,利用 HBASE 技术可在廉价 PC Server 上搭建起大规模结构化存储集群。HBase 的目标是存储并处理大型的数据,更具体来说是仅需使用普通的硬件配置,就能够处理由成千上万的行和列所组成的大型数据。
HBase 是 Google Bigtable 的开源实现,但是也有很多不同之处。比如:
- Google Bigtable 利用 GFS 作为其文件存储系统,HBase 利用 Hadoop HDFS 作为其文件存储系统;
- Google 运行 MapReduce 来处理 Bigtable 中的海量数据,HBase 同样利用 Hadoop MapReduce 来处理 HBase 中的海量数据;
- Google Bigtable 利用 Chubby 作为协同服务,HBase 利用 Zookeeper 作为对应。
1.3 HBase 数据模型
逻辑上,HBase 的数据模型同关系型数据库很类似,数据存储在一张表中,有行有列。但从 HBase 的底层物理存储结构(K-V)来看,HBase 更像是一个 multi-dimensional map。
1.3.1 HBase 逻辑结构
1.3.2 HBase 物理存储结构
1.3.3 数据模型
-
NameSpace
命名空间,类似于关系型数据库的 DatabBase 概念,每个命名空间下有多个表。HBase 有两个自带的命名空间,分别是 hbase 和 default,hbase 中存放的是 HBase 内置的表,default 表是用户默认使用的命名空间。
-
Region
类似于关系型数据库的表概念。不同的是,HBase 定义表时只需要声明列族即可,不需要声明具体的列。这意味着,往 HBase 写入数据时,字段可以动态、按需指定。因此,和关系型数据库相比,HBase 能够轻松应对字段变更的场景。
-
Row
HBase 表中的每行数据都由一个 RowKey 和多个 Column(列)组成,数据是按照 RowKey 的字典顺序存储的,并且查询数据时只能根据 RowKey 进行检索,所以 RowKey 的设计十分重要。
-
Column
HBase 中的每个列都由 Column Family(列族)和 Column Qualifier(列限定符)进行限
定,例如 info:name,info:age。建表时,只需指明列族,而列限定符无需预先定义。 -
Time Stamp
用于标识数据的不同版本(version),每条数据写入时,如果不指定时间戳,系统会
自动为其加上该字段,其值为写入 HBase 的时间。 -
Cell
由 {rowkey, column Family:column Qualifier, time Stamp} 唯一确定的单元。cell 中的数
据是没有类型的,全部是字节码形式存贮。
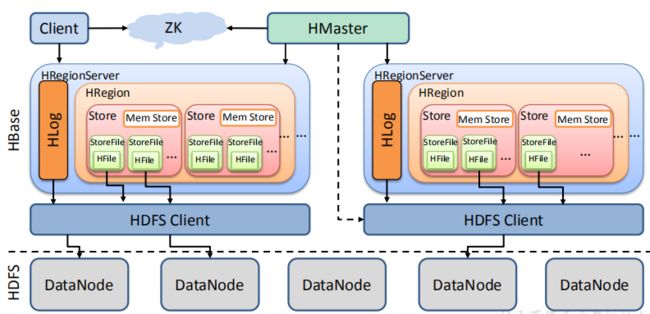
1.4 HBase 基本架构
-
RegionServer
Region Server 为 Region 的管理者,其实现类为 HRegionServer,主要作用如下:
① 对于数据的操作:get, put, delete;
② 对于 Region 的操作:splitRegion、compactRegion。 -
Master
Master 是所有 RegionServer 的管理者,其实现类为 HMaster,主要作用如下:
① 对于表的操作:create, delete, alter
② 对于 RegionServer的操作:分配 regions 到每个 RegionServer,监控每个 RegionServer 的状态,负载均衡和故障转移。 -
Zookeeper
HBase 通过 Zookeeper 来做 Master 的高可用、RegionServer 的监控、元数据的入口以及
集群配置的维护等工作。 -
HDFS
HDFS 为 HBase 提供最终的底层数据存储服务,同时为 HBase 提供高可用的支持。
2. HBase 快速入门
2.1 HBase 官网地址
HBase 官网
2.2 HBase 安装流程
- 启动 Hadoop 集群
- 启动 Zookeeper
- 将 HBase 的安装包上传到服务器上(hbase-2.2.2-bin.tar.gz)
- 解压 HBase 到指定目录
tar -zxvf hbase-2.2.2-bin.tar.gz -C /hadoop/
-
修改 HBase 的配置文件(/hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/conf/ 目录下)
① hbase-env.sh 修改内容:
# The java implementation to use. Java 1.8+ required.
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/java/jdk1.8.0_151
# Tell HBase whether it should manage it's own instance of ZooKeeper or not.
export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=false
② hbase-site.xml 修改内容:
<configuration>
<property>
<name>hbase.rootdirname>
<value>hdfs://master:9000/hbasevalue>
property>
<property>
<name>hbase.cluster.distributedname>
<value>truevalue>
property>
<property>
<name>hbase.master.portname>
<value>16000value>
property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.quorumname>
<value>master:2181,slave1:2181,slave2:2181value>
property>
<property>
<name>hbase.zookeeper.property.dataDirname>
<value>/hadoop/zookeeper-3.5.6/zkDatavalue>
property>
configuration>
③ regionservers:
master
slave1
slave2
⑤ 软连接 hadoop 配置文件到 hbase:
ln -s /hadoop/hadoop-2.7.7/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml /hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/conf/core-site.xml
ln -s /hadoop/hadoop-2.7.7/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml /hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/conf/hdfs-site.xml
- 将 HBase 同步到其他机器上
xsync /hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/
- 配置环境变量
vim /etc/profile
添加以下内容:
#HBASE
export HBASE_HOME=/hadoop/hbase-2.2.2
export PATH=$PATH:$HBASE_HOME/bin
使配置文件生效
source /etc/profile
同步其他机器配置文件并分别使配置文件生效
xsync /etc/profile
-
HBase 服务的启动
① 方式一
hbase-daemon.sh start master
hbase-daemon.sh start regionserver
② 方式二
start-hbase.sh
对应的停止服务
stop-hbase.sh
- 查看 HBase 页面
2.3 HBase Shell 操作
2.3.1 基本操作
- 进入 HBase 客户端命令行
hbase shell
- 查看帮助命令
help
- 查看当前数据库中有哪些表
list
2.3.2 表的操作
- 创建表
create 'student','info'
- 插入数据到表
put 'student','1001','info:sex','male'
put 'student','1001','info:age','18'
put 'student','1002','info:name','Janna'
put 'student','1002','info:sex','female'
put 'student','1002','info:age','20'
- 扫描查看表数据
scan 'student'
scan 'student',{STARTROW => '1001', STOPROW => '1001'}
scan 'student',{STARTROW => '1001'}
- 查看表结构
describe 'student'
- 更新指定字段的数据
put 'student','1001','info:name','Nick'
put 'student','1001','info:age','100'
- 查看 “指定行” 或 “指定列族:列” 的数据
get 'student','1001'
get 'student','1001','info:name'
- 统计表数据行数
count 'student'
-
变更表信息
将 info 列族中的数据存放 3 个版本
alter 'student',{NAME=>'info',VERSIONS=>3}
get 'student','1001',{COLUMN=>'info:name',VERSIONS=>3}
-
删除数据
① 删除某 rowkey 的全部数据
deleteall 'student','1001'
② 删除某 rowkey 的某一列数据
delete 'student','1002','info:sex'
- 清空表数据
truncate 'student'
提示:清空表的操作顺序为先 disable,然后再 truncate。
- 删除表
① 首先需要先让该表为 disable 状态
disable 'student'
② 然后才能 drop 这个表
drop 'student'
2.3.3 命名空间的基本操作
- 查看命名空间
list_namespace
- 创建命名空间
create_namespace 'bigdata'
- 在新的命名空间中创建表
create 'bigdata:student','info'
-
删除命名空间
只能删除空的命名空间,如果不为空,需要先删除该命名空间下的所有表
drop_namespace 'bigdata'
3. HBase 进阶
3.1 架构原理
-
StoreFile
保存实际数据的物理文件,StoreFile 以 HFile 的形式存储在 HDFS 上。每个 Store 会有一个或多个 StoreFile(HFile),数据在每个 StoreFile 中都是有序的。
-
MemStore
写缓存,由于 HFile 中的数据要求是有序的,所以数据是先存储在 MemStore 中,排好序后,等到达刷写时机才会刷写到 HFile,每次刷写都会形成一个新的 HFile。
-
WAL
由于数据要经 MemStore 排序后才能刷写到 HFile,但把数据保存在内存中会有很高的概率导致数据丢失,为了解决这个问题,数据会先写在一个叫做 Write-Ahead logfile 的文件中,然后再写入 MemStore 中。所以在系统出现故障的时候,数据可以通过这个日志文件重建。
3.2 读流程
- Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个 Region Server。
- 访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbase:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
- 与目标 Region Server 进行通讯;
- 将数据顺序写入(追加)到 WAL;
- 将数据写入对应的 MemStore,数据会在 MemStore 进行排序;
- 向客户端发送 ack;
- 等达到 MemStore 的刷写时机后,将数据刷写到 HFile。
3.3 MemStore Flush
-
当某个 memstroe 的大小达到了 hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size(默认值 128M), 其所在 region 的所有 memstore 都会刷写,并且会阻止继续往该 memstore 写数据。
-
当 region server 中 memstore 的总大小达到 *hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值 0.4), *hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size.lower.limit(默认值 0.95),region 会按照其所有 memstore 的大小顺序(由大到小)依次进行刷写。直到 region server 中所有 memstore 的总大小减小到上述值以下。
当 region server 中 memstore 的总大小达到 java_heapsize*hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size(默认值 0.4)时,会阻止继续往所有的 memstore 写数据。
-
到达自动刷写的时间,也会触发 memstore flush。自动刷新的时间间隔由该属性进行配置 hbase.regionserver.optionalcacheflushinterval(默认 1 小时)
-
当 WAL 文件的数量超过 hbase.regionserver.max.logs,region 会按照时间顺序依次进
行刷写,直到 WAL 文件数量减小到 hbase.regionserver.max.log 以下(该属性名已经废弃,
现无需手动设置,最大值为 32)。
3.4 读流程
- Client 先访问 zookeeper,获取 hbase:meta 表位于哪个 Region Server。
- 访问对应的 Region Server,获取 hbase:meta 表,根据读请求的 namespace:table/rowkey,查询出目标数据位于哪个 Region Server 中的哪个 Region 中。并将该 table 的 region 信息以及 meta 表的位置信息缓存在客户端的 meta cache,方便下次访问。
- 与目标 Region Server 进行通讯;
- 分别在 Block Cache(读缓存),MemStore 和 Store File(HFile)中查询目标数据,并将查到的所有数据进行合并。此处所有数据是指同一条数据的不同版本(time stamp)或者不同的类型(Put/Delete)。
- 将从文件中查询到的数据块(Block,HFile 数据存储单元,默认大小为 64KB)缓存到 Block Cache。
- 将合并后的最终结果返回给客户端。
3.5 StoreFile Compaction
由于 memstore 每次刷写都会生成一个新的HFile,且同一个字段的不同版本(timestamp)和不同类型(Put/Delete)有可能会分布在不同的 HFile 中,因此查询时需要遍历所有的 HFile。为了减少 HFile 的个数,以及清理掉过期和删除的数据,会进行 StoreFile Compaction。
Compaction 分为两种,分别是 Minor Compaction 和 Major Compaction。Minor Compaction 会将临近的若干个较小的 HFile 合并成一个较大的 HFile,但不会清理过期和删除的数据。
Major Compaction 会将一个 Store 下的所有的 HFile 合并成一个大 HFile,并且会清理掉过期和删除的数据。

3.6 Region Split
默认情况下,每个 Table 起初只有一个 Region,随着数据的不断写入,Region 会自动进
行拆分。刚拆分时,两个子 Region 都位于当前的 Region Server,但处于负载均衡的考虑,HMaster 有可能会将某个 Region 转移给其他的 Region Server。
- 当 1 个 region 中的某个 Store 下所有 StoreFile 的总大小超过 hbase.hregion.max.filesize, 该 Region 就会进行拆分(0.94 版本之前)。
- 当 1 个 region 中 的 某 个 Store 下所有 StoreFile 的 总 大 小 超 过 Min(R^2 *
“hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size”,hbase.hregion.max.filesize"),该 Region 就会进行拆分,其
中 R 为当前 Region Server 中属于该 Table 的个数(0.94 版本之后)。

4. HBase API 操作
4.1 环境准备
新建项目后在 pom.xml 中添加依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-serverartifactId>
<version>2.2.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbasegroupId>
<artifactId>hbase-clientartifactId>
<version>2.2.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId>
<version>2.8.2version>
dependency>
dependencies>
在 resources 目录下创建 log4j.properties(在控制台打印日志)
log4j.rootLogger=INFO, stdout
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m%n
log4j.appender.logfile=org.apache.log4j.FileAppender
log4j.appender.logfile.File=target/spring.log
log4j.appender.logfile.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.logfile.layout.ConversionPattern=%d %p [%c] - %m%n
4.2 HBase API
4.2.1 Hbase 的连接与断开
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import java.io.IOException;
public class TestHBase {
static Admin admin = null;
static Connection connection = null;
static {
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "192.168.217.130");
// 获取连接对象
try {
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
admin = connection.getAdmin();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void close(Connection conn, Admin admin) throws IOException {
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
if (admin != null) {
admin.close();
}
}
}
6.2.2 判断表是否存在
public static boolean tableExist(String tableName) throws IOException {
boolean tableExists = admin.tableExists(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
return tableExists;
}
4.2.3 创建表
public static void createTable(String tableName, String... columnFamily) throws IOException {
// 判断是否存在列族信息
if (columnFamily.length <= 0) {
System.out.println("请设置列族信息!");
return;
}
//判断表是否存在
if (tableExist(tableName)) {
System.out.println("表" + tableName + "已存在");
} else {
//创建表描述器
TableDescriptorBuilder tableDescriptorBuilder = TableDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//创建多个列族
for (String cf : columnFamily) {
// 创建列族描述器
ColumnFamilyDescriptor columnFamilyDescriptor = ColumnFamilyDescriptorBuilder.newBuilder(Bytes.toBytes("data")).build();
tableDescriptorBuilder.setColumnFamily(columnFamilyDescriptor);
}
//根据对表的配置,创建表
admin.createTable(tableDescriptorBuilder.build());
System.out.println("表" + tableName + "创建成功!");
}
}
4.2.4 删除表
public static void deleteTable(String tableName) throws IOException {
if (tableExist(tableName)) {
// 使表不可用
admin.disableTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
// 执行删除操作
admin.deleteTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
System.out.println("表" + tableName + "删除成功!");
} else {
System.out.println("表" + tableName + "不存在!");
}
}
4.2.5 创建命名空间
public static void createNameSpace(String nameSpace) {
NamespaceDescriptor namespaceDescriptor = NamespaceDescriptor.create(nameSpace).build();
try {
admin.createNamespace(namespaceDescriptor);
} catch (NamespaceExistException e) {
System.out.println(nameSpace + "命名空间已经存在!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4.2.6 向表中插入数据
public static void addRowData(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String column, String value) throws IOException {
// 获取Table对象
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//向表中插入数据
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
//向Put对象中组装数据
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(column), Bytes.toBytes(value));
table.put(put);
table.close();
System.out.println("插入数据成功");
}
4.2.7 删除多行数据
public static void deleteData(String tableName, String... rowKey) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
List<Delete> deleteList = new ArrayList<Delete>();
for (String row : rowKey) {
Delete delete = new Delete(Bytes.toBytes(row));
deleteList.add(delete);
}
table.delete(deleteList);
table.close();
}
4.2.8 全表扫描
public static void scanTable(String tableName) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
//得到用于扫描region的对象
Scan scan = new Scan();
//使用table得到resultcanner实现类的对象
ResultScanner results = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : results) {
Cell[] cells = result.rawCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
//得到rowkey
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
",列族" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
",列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
",值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
table.close();
}
4.2.9 获取指定 rowKey 的数据
public static void getData(String tableName, String rowKey) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
//get.setMaxVersions();显示所有版本
//get.setTimeStamp();显示指定时间戳的版本
Result result = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
",列族" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
",列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
",值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
table.close();
}
4.2.10 获取指定“列族:列”的数据
public static void getData(String tableName, String rowKey, String columnFamily, String column) throws IOException {
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(tableName));
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
get.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(column));
Result result = table.get(get);
for (Cell cell : result.rawCells()) {
System.out.println("行键:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneRow(cell)) +
",列族" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell)) +
",列:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)) +
",值:" + Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneValue(cell)));
}
}
4.3 MapReduce
通过 HBase 的相关JavaAPI,我们可以实现伴随 HBase 操作的 MapReduce 过程,比如使用 MapReduce 将数据从本地文件系统导入到 HBase 的表中,比如我们从 HBase 中读取一些原始数据后使用 MapReduce 做数据分析。
4.3.1 官方 HBase-MapReduce
- 查看 HBase 的 MapReduce 任务的执行
hbase mapredcp
-
环境变量的导入
① 执行环境变量的导入(临时生效,在命令行执行下述操作)
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`
说明:前提已经配置了 HBASE_HOME 和 HADOOP_HOME 环境变量
② 永久生效:修改 hadoop-env.sh 中配置
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$HADOOP_CLASSPATH:/hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/lib/*
- 运行官方的 MapReduce 任务
(一)统计 Student 表中有多少行数据
yarn jar /hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/lib/hbase-mapreduce-2.2.2.jar rowcounter student
(二)使用 MapReduce 将本地数据导入到 HBase
① 在本地创建一个 tsv 格式的文件:fruit.tsv
1001 Apple Red
1002 Pear Yellow
1003 Pineapple Yellow
② 创建 HBase 表
create 'fruit','info'
③ 在 HDFS 中创建 input_fruit 文件夹并上传 fruit.tsv 文件
hadoop fs -mkdir /input_fruit/
hadoop fs -put data/fruit.tsv /input_fruit/
④ 执行 MapReduce 到 HBase 的 fruit 表中
yarn jar /hadoop/hbase-2.2.2/lib/hbase-mapreduce-2.2.2.jar importtsv \
-Dimporttsv.columns=HBASE_ROW_KEY,info:name,info:color fruit \
hdfs://master:9000/input_fruit
⑤ 使用 scan 命令查看导入后的结果
scan 'fruit'
4.3.2 自定义 HBase-MapReduce1
目标:实现将 HDFS 中的数据写入到 Hbase 表中。
任务:读取 HDFS 上的 fruit.tsv,将数据写到 HBase 中 fruit1 表。
- 编写 FruitMapper 类
package mr;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FruitMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable, Text> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, value);
}
}
- 编写 FruitReducer 类
package mr;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FruitReducer extends TableReducer<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
// 获取一行数据
String[] fields = value.toString().split("\t");
// 构建Put对象
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(fields[0]));
// 给Put对象赋值
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes(fields[1]));
put.addColumn(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("color"), Bytes.toBytes(fields[2]));
// 写出
context.write(NullWritable.get(), put);
}
}
}
- 编写 FruitDriver 类
package mr;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
public class FruitDriver implements Tool {
private Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.获取job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
// 2.设置驱动类路径
job.setJarByClass(FruitDriver.class);
// 3.设置Mapper类和输入输出类型
job.setMapperClass(FruitMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.setReducerClass(FruitReducer.class);
// 4.设置Reducer类型
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob(args[1], FruitReducer.class, job);
// 设置输入参数
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return result ? 0 : 1;
}
@Override
public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
}
@Override
public Configuration getConf() {
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
int run = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new FruitDriver(), args);
}
}
- 打包程序并上传到集群(hbase-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar)
- 创建 fruit1 表
create 'fruit1','info'
- 运行程序
yarn jar hbase-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar mr.FruitDriver /input_fruit/fruit.tsv fruit1
- 查看结果
scan 'fruit1'
4.3.3 自定义 HBase-MapReduce2
目标:将 fruit 表中的一部分数据,通过 MR 迁入到 fruit2 表中。
- 编写 Fruit2Mapper 类
package mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.Cell;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.CellUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Result;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Fruit2Mapper extends TableMapper<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put> {
@Override
protected void map(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Result value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Put put = new Put(key.get());
// 1.获取数据
for (Cell cell : value.rawCells()) {
// 2.判断当前cell是否为name列
if ("name".equals(Bytes.toString(CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell)))) {
// 3.给put对象赋值
put.add(cell);
}
}
// 4.写出
context.write(key, put);
}
}
- 编写 Fruit2Reducer 类
package mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Fruit2Reducer extends TableReducer<ImmutableBytesWritable, Put, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(ImmutableBytesWritable key, Iterable<Put> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Put put : values) {
context.write(NullWritable.get(),put);
}
}
}
- 编写 FruitDriver 类
package mr2;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Put;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Scan;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapReduceUtil;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
public class Fruit2Driver implements Tool {
private Configuration configuration = null;
@Override
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1.获取job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
// 2.设置驱动类路径
job.setJarByClass(Fruit2Driver.class);
// 3.设置Mapper类和输入输出类型
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob("fruit", new Scan(), Fruit2Mapper.class, ImmutableBytesWritable.class, Put.class, job);
// 4.设置Reducer类和输入输出类型
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob("fruit2", Fruit2Reducer.class, job);
// 5.提交任务
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return result ? 0 : 1;
}
@Override
public void setConf(Configuration conf) {
configuration = conf;
}
@Override
public Configuration getConf() {
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
ToolRunner.run(conf,new Fruit2Driver(),args);
}
}
- 将集群中 hbase-site.xml 拷贝到项目 resource 目录下
- 创建 fruit2 表
create 'fruit2','info'
- 运行程序
- 查看结果
scan 'fruit2'
4.4 与 Hive 集成
4.4.1 HBase 与 Hive 对比
-
Hive
① 数据仓库
Hive 的本质其实就相当于将 HDFS 中已经存储的文件在 Mysql 中做了一个双射关系,以方便使用 HQL 去管理查询。
② 用于数据分析、清洗
Hive 适用于离线的数据分析和清洗,延迟较高。
③ 基于 HDFS、MapReduce
Hive 存储的数据依旧在 DataNode 上,编写的 HQL 语句终将是转换为 MapReduce 代码执行。
-
HBase
① 数据库
是一种面向列族存储的非关系型数据库。
② 用于存储结构化和非结构化的数据
适用于单表非关系型数据的存储,不适合做关联查询,类似 JOIN 等操作。
③ 基于 HDFS
数据持久化存储的体现形式是 HFile,存放于 DataNode 中,被 ResionServer 以 region 的形式进行管理。④ 延迟较低,接入在线业务使用
面对大量的企业数据,HBase 可以直线单表大量数据的存储,同时提供了高效的数据访问速度。
4.4.2 HBase 与 Hive 集成使用
环境准备
因为后续会在操作 Hive 的同时对 HBase 也会产生影响,所以 Hive 需要持有操作 HBase 的 Jar,那么接下来拷贝 Hive 所依赖的 Jar 包(或者使用软连接的形式)。
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-common-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-common-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-server-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbaseserver-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-client-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-client-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-protocol-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-protocol-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-it-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-it-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/htrace-core-3.1.0-incubating.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop2-compat-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop2-compat-2.2.2.jar
ln -s $HBASE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop-compat-2.2.2.jar $HIVE_HOME/lib/hbase-hadoop-compat-2.2.2.jar
同时在 hive-site.xml 中修改 zookeeper 的属性,如下:
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.quorumname>
<value>master,slave1,slave2value>
property>
<property>
<name>hive.zookeeper.client.portname>
<value>2181value>
property>
案例一
目标: 建立 Hive 表,关联 HBase 表,插入数据到 Hive 表的同时能够影响 HBase 表。
- 在 Hive 中创建表同时关联 HBase
CREATE TABLE hive_hbase_emp_table(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" =
":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:co
mm,info:deptno")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");
- 通过 insert 命令将 emp 表中的数据导入到 Hive 关联 Hbase 的那张表中
insert into table hive_hbase_emp_table select * from emp;
-
查看 Hive 以及关联的 HBase 表中是否已经成功的同步插入了数据
Hive:
select * from hive_hbase_emp_table;
HBase:
scan ‘hbase_emp_table’
案例二
目标: 在 HBase 中已经存储了某一张表 hbase_emp_table,然后在 Hive 中创建一个外部表来关联 HBase 中的 hbase_emp_table 这张表,使之可以借助 Hive 来分析 HBase 这张表中的数据。
- 在 Hive 中创建外部表
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE relevance_hbase_emp(
empno int,
ename string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int)
STORED BY 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.hbase.HBaseStorageHandler'
WITH SERDEPROPERTIES ("hbase.columns.mapping" = ":key,info:ename,info:job,info:mgr,info:hiredate,info:sal,info:comm,info:deptno")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name" = "hbase_emp_table");
- 查看数据
select * from relevance_hbase_emp;
5. HBase 优化
5.1 高可用
在 HBase 中 HMaster 负责监控 HRegionServer 的生命周期,均衡 RegionServer 的负载,如果 HMaster 挂掉了,那么整个 HBase 集群将陷入不健康的状态,并且此时的工作状态并不会维持太久。所以 HBase 支持对 HMaster 的高可用配置。
- 关闭 HBase 集群
stop-hbase.sh
- 在 conf 目录下创建 backup-masters 文件,配置高可用 HMaster 节点
touch backup-masters
echo slave1 > backup-masters
- 同步配置
xsync backup-masters
- 启动 HBase
start-hbase.sh
5.2 预分区
每一个 region 维护着 StartRow 与 EndRow,如果加入的数据符合某个 Region 维护的 RowKey 范围,则该数据交给这个 Region 维护。那么依照这个原则,我们可以将数据所要投放的分区提前大致的规划好,以提高 HBase 性能。
- 手动设定预分区
create 'staff1','info','partition1',SPLITS => ['1000','2000','3000','4000']
- 生成 16 进制序列预分区
create 'staff2','info','partition2',{NUMREGIONS => 15, SPLITALGO => 'HexStringSplit'}
-
按照文件中设置的规则预分区
创建 splits.txt 文件内容如下:
aaaa
bbbb
cccc
dddd
然后执行:
create 'staff3','partition3',SPLITS_FILE => 'splits.txt'
5.3 RowKey 设计
一条数据的唯一标识就是 RowKey,那么这条数据存储于哪个分区,取决于 RowKey 处于哪个一个预分区的区间内,设计 RowKey 的主要目的 ,就是让数据均匀的分布于所有的 region 中,在一定程度上防止数据倾斜。(散列性、唯一性、长度原则)
- 生成随机数、hash、散列值
- 字符串反转
20170524000001 转成 10000042507102
20170524000002 转成 20000042507102
- 字符串拼接
20170524000001_a12e
20170524000001_93i7
5.4 内存优化
HBase 操作过程中需要大量的内存开销,毕竟 Table 是可以缓存在内存中的,一般会分配整个可用内存的 70%给 HBase 的 Java 堆。但是不建议分配非常大的堆内存,因为 GC 过程持续太久会导致 RegionServer 处于长期不可用状态,一般 16~48G 内存就可以了,如果因为框架占用内存过高导致系统内存不足,框架一样会被系统服务拖死。
5.5 基础优化
-
允许在 HDFS 的文件中追加内容
hdfs-site.xml、hbase-site.xml
属性: dfs.support.append
解释: 开启 HDFS 追加同步,可以优秀的配合 HBase 的数据同步和持久化。默认值为 true。 -
优化 DataNode 允许的最大文件打开数
hdfs-site.xml
属性: dfs.datanode.max.transfer.threads
解释: HBase 一般都会同一时间操作大量的文件,根据集群的数量和规模以及数据动作,设置为 4096 或者更高。默认值:4096 -
优化延迟高的数据操作的等待时间
hdfs-site.xml
属性: dfs.image.transfer.timeout
解释: 如果对于某一次数据操作来讲,延迟非常高,socket 需要等待更长的时间,建议把
该值设置为更大的值(默认 60000 毫秒),以确保 socket 不会被 timeout 掉。 -
优化数据的写入效率
mapred-site.xml
属性: mapreduce.map.output.compress、mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec
解释: 开启这两个数据可以大大提高文件的写入效率,减少写入时间。第一个属性值修改为 true,第二个属性值修改为:org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec 或者其他压缩方式。 -
设置 RPC 监听数量
hbase-site.xml
属性: Hbase.regionserver.handler.count
解释: 默认值为 30,用于指定 RPC 监听的数量,可以根据客户端的请求数进行调整,读写请求较多时,增加此值。 -
优化 HStore 文件大小
hbase-site.xml
属性: hbase.hregion.max.filesize
解释: 默认值 10737418240(10GB),如果需要运行 HBase 的 MR 任务,可以减小此值,因为一个 region 对应一个 map 任务,如果单个 region 过大,会导致 map 任务执行时间过长。该值的意思就是,如果 HFile 的大小达到这个数值,则这个 region 会被切分为两个 Hfile。 -
优化 HBase 客户端缓存
hbase-site.xml
属性: hbase.client.write.buffer
解释: 用于指定 Hbase 客户端缓存,增大该值可以减少 RPC 调用次数,但是会消耗更多内存,反之则反之。一般我们需要设定一定的缓存大小,以达到减少 RPC 次数的目的。 -
指定 scan.next 扫描 HBase 所获取的行数
hbase-site.xml
属性: hbase.client.scanner.caching
解释: 用于指定 scan.next 方法获取的默认行数,值越大,消耗内存越大。 -
flush、compact、split 机制
当 MemStore 达到阈值,将 Memstore 中的数据 Flush 进 Storefile;
compact 机制则是把 flush出来的小文件合并成大的 Storefile 文件;
split 则是当 Region 达到阈值,会把过大的 Region一分为二。涉及属性:
hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size:134217728
即:这个参数的作用是当单个 HRegion 内所有的 Memstore 大小总和超过指定值时,flush 该 HRegion 的所有 memstore。RegionServer 的 flush 是通过将请求添加一个队列,模拟生产消费模型来异步处理的。那这里就有一个问题,当队列来不及消费,产生大量积压请求时,可能会导致内存陡增,最坏的情况是触发 OOM。
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit:0.4
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.lowerLimit:0.38
即:当 MemStore 使用内存总量达到 hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.upperLimit 指定值时,将会有多个 MemStores flush 到文件中,MemStore flush 顺序是按照大小降序执行的,直到刷新到 MemStore 使用内存略小于 lowerLimit。