Java高级学习篇之网络编程
一.基本概述
(一)基本介绍
JAVA 是Internet上的语言,它从语言级上提供了对于网络应用程序的支持,使得可以很容易开发常见的应用程序,同时, Java中也提供了网络类库 ,可以很方便的进行网络连接。
(二)计算机网络
计算机网络是分布在 不同地点 的具有 自治功能 (具有完整的自处理设备)的 计算机集合 (>=2)。
网络编程(目的):
直接或间接的通过网络协议与其他计算机实现数据的交换,进行通讯。
核心问题
(1)如何准确地定位网络上的一台主机或多台主机及主机上的具体应用??
(2)如何进行高效的数据传输??
网络要素
(1)IP地址
用来标识计算机网络中的一台主机
本地环回地址( hostAdderss ): 127.0.0.1
主机名( hostName ):localhost
IP分类
① IPV4 :四个字节,能够表示大约42个亿的不同主机(点分十进制)
② IPV6 :十六个字节,写成八个无符号整数,每个整数使用四个十六进制位表示,
之间使用“:”分开
(2)端口号
每台计算机中都具有很多进程,为了便于两台计算机中的进程进行通信,便引入了端口号,表示计算机中正在运行的进程
说明
①不同的进程具有不同的端口号
②端口号是使用一个十六位的二进制整数表示(范围0~65535)
端口号和IP地址组合可以得出一个网络套接字: Socket
(3)主机表示方式
方式一:IP地址(hostAddress)
方式二:域名(hostName)
由于IP地址比较难以记忆和管理,所以引入了“ 域名 ”,网络连接时输入主机域名,域名服务器(DNS)会将该域名解析为
IP地址,这样才能够和主机建立连接。
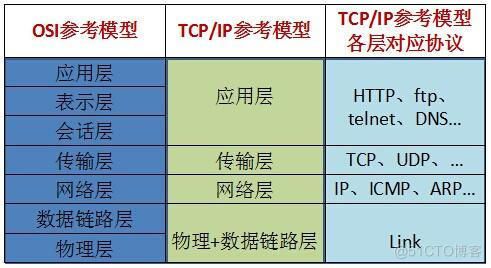
(4)网络通信协议
传输层两个重要的协议是:
TCP( Transmisssion Control Protocol ):传输控制协议。
UDP( User Datagram Protocol ):用户数据块协议。
介绍如下:
套接字( Socket ):表示唯一标识的IP地址和端口号组合。
①网络中的两台主机进行通信时,通信的两端都需要有Socket,网络通信实质上就是Socket通信。
②Socket允许程序吧网络连接当做一个流,数据在两个Socket间通过IO传输。
③发起通信服务的一方为客户端,等待通信请求的一方为服务端。
分类:
流套接字 :使用TCP提供可依赖的字节流服务。
数据报套接字 :使用UDP提供“尽力而为”的数据报服务。
具体详细内容可参考: 计算机网络总体概述
二.实战应用
(一)实例化
@Test
public void test(){
InetAddress inet1= null;
InetAddress inet2= null;
InetAddress inet3= null;
try {
//实例化(方式一)
inet1 = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
inet2 = InetAddress.getByName("www.baidu.com");
//实例化(方式二)
inet3 = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(inet1);
System.out.println(inet2);
System.out.println(inet2.getHostName());
System.out.println(inet2.getHostAddress());
System.out.println(inet3);
}
}说明:
①方式一:getByName( HostAddress)
②方式二:getLocalHost()
基于TCP协议实现的信息交换
例题一:客户端发送内容给数据端,服务端将内容打印到控制台。
@Test
public void client(){
Socket socket= null;
OutputStream os= null;
try {
InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
socket = new Socket(inet,8899);
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("北京你好!".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(os!=null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void server(){//服务端
ServerSocket serverSocket= null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is= null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos= null;
try {
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8899);
socket = serverSocket.accept();
is = socket.getInputStream();
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[]buffer=new byte[5];
int len;
while((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(baos!=null) {
try {
baos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is!=null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(serverSocket!=null) {
try {
serverSocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}说明:
首先,通过Server()开通服务,进入监听状态
而后,开启client,开始向Server端发送消息
例题二:客户端发送文件给服务器,服务端将文件保存到本地
@Test
public void client(){
OutputStream os = null;
FileInputStream fis= null;
try {
//创建一个Socket
Socket socket=new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),9090);
//获取一个输出流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
//获取一个输入流
fis = new FileInputStream(new File("美男子.png"));
//写入数据
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read(buffer))!=-1){
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭流
if(fis!=null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(os!=null) {
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void server(){
ServerSocket ss= null;
Socket socket= null;
InputStream is= null;
FileOutputStream fos= null;
try {
//创建一个ServerSocket
ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
//获取一个客户端的一个Socket
socket = ss.accept();
//创建一个输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
//创建一个本地文件用来存储传递的内容
fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("beauty.png"));
//将server传送来的数据保存到文件中
byte[]buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=is.read(buffer))!=-1){
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fos!=null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(is!=null) {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(socket!=null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(ss!=null) {
try {
ss.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}